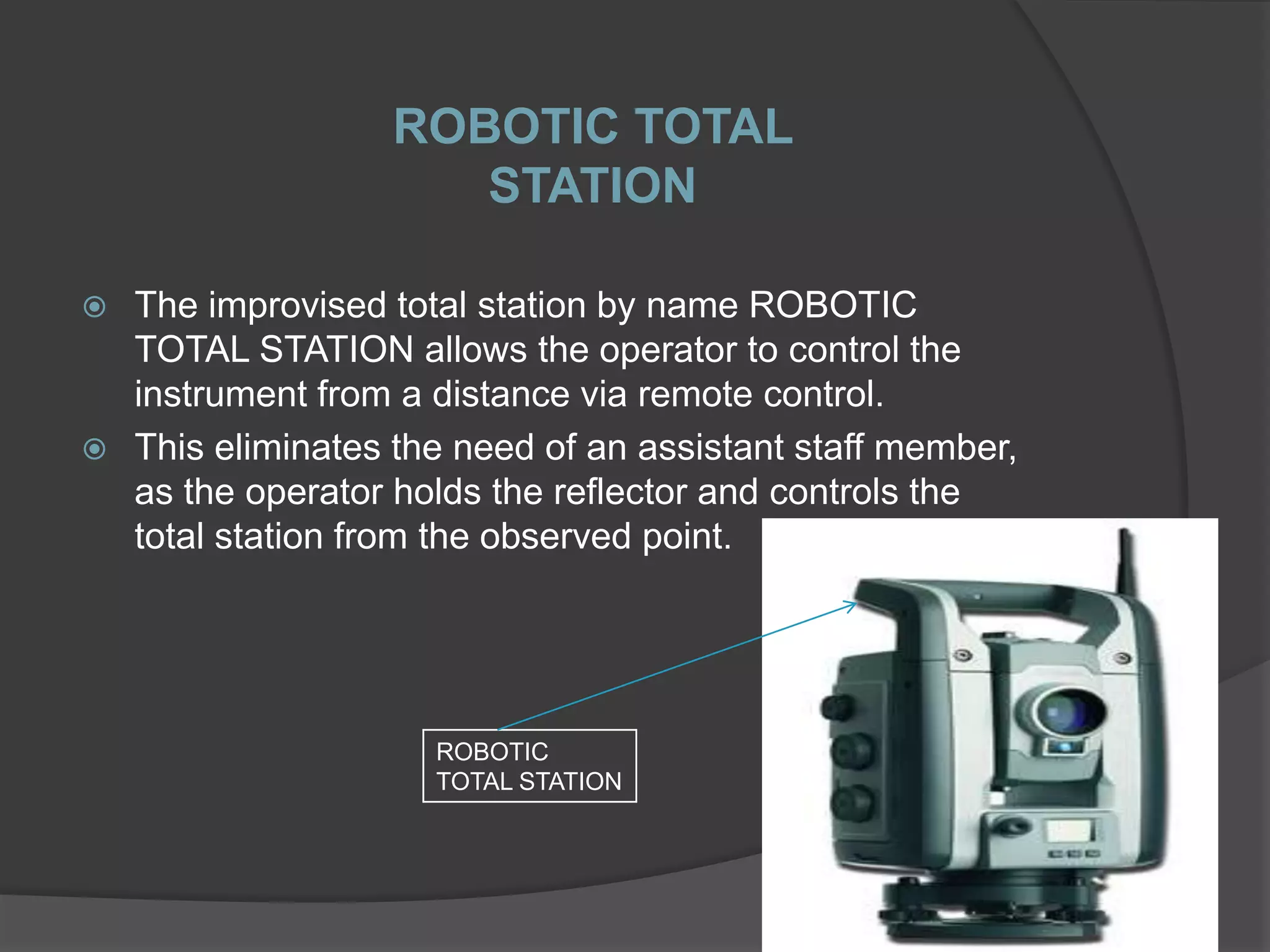
Total station is a modern surveying instrument that combines an electronic theodolite and electronic distance meter. It allows the user to determine coordinates of points by measuring horizontal and vertical angles and slope distances to a reflector target simultaneously. The total station records measurements directly into its internal microprocessor, allowing precise data collection and processing without manual calculations. It has made surveying work faster, more accurate and less tedious compared to traditional instruments.