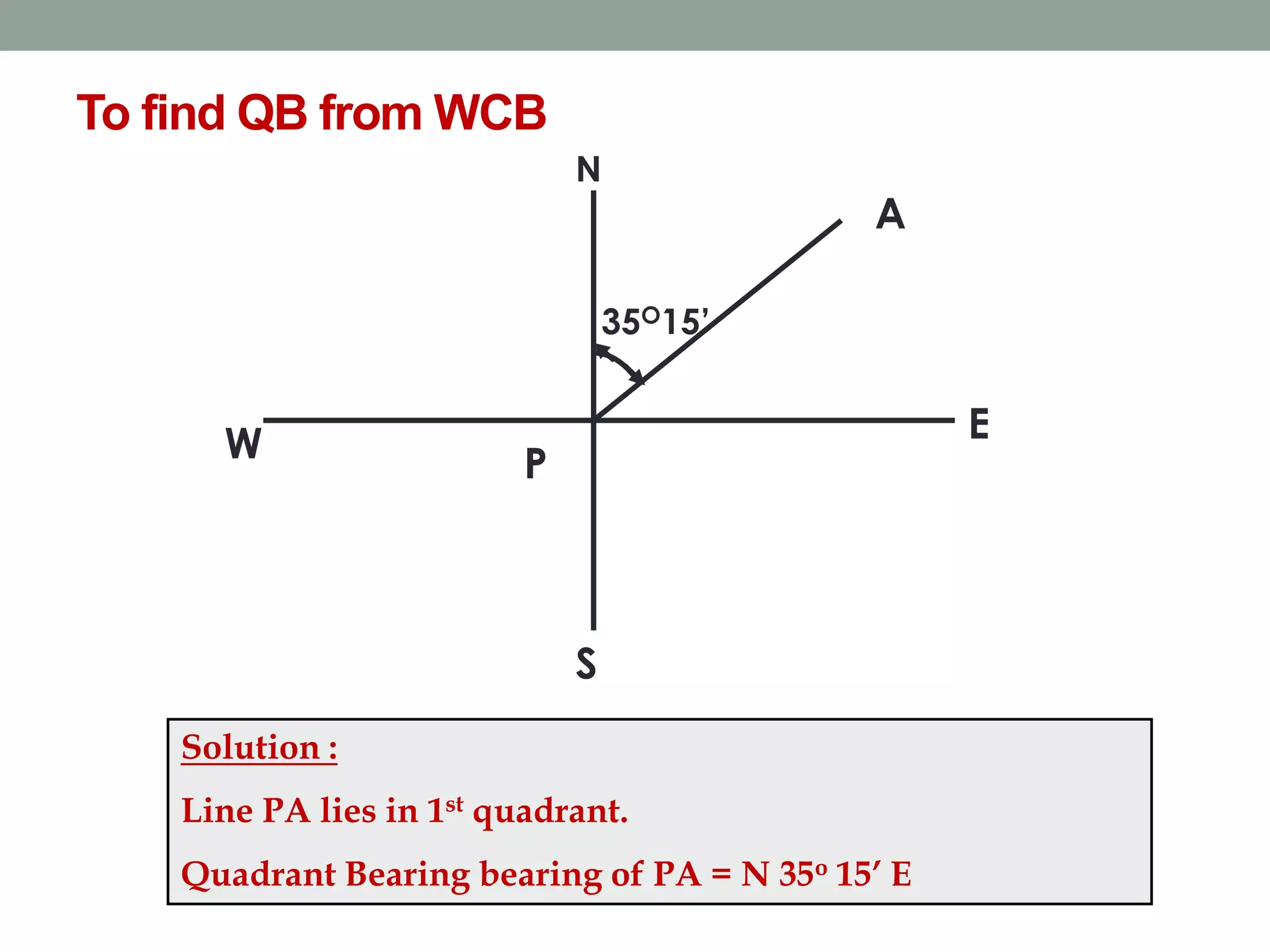
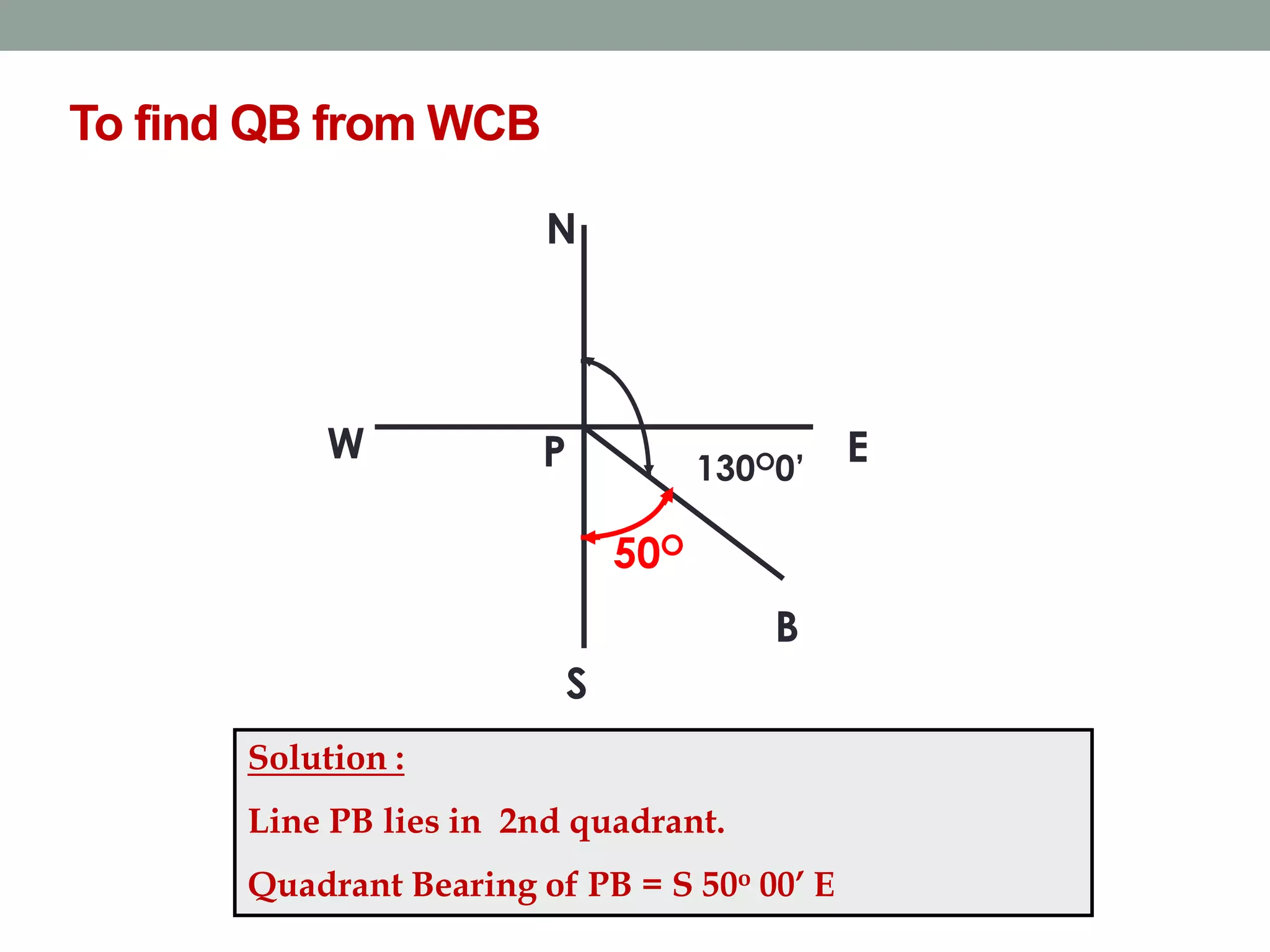
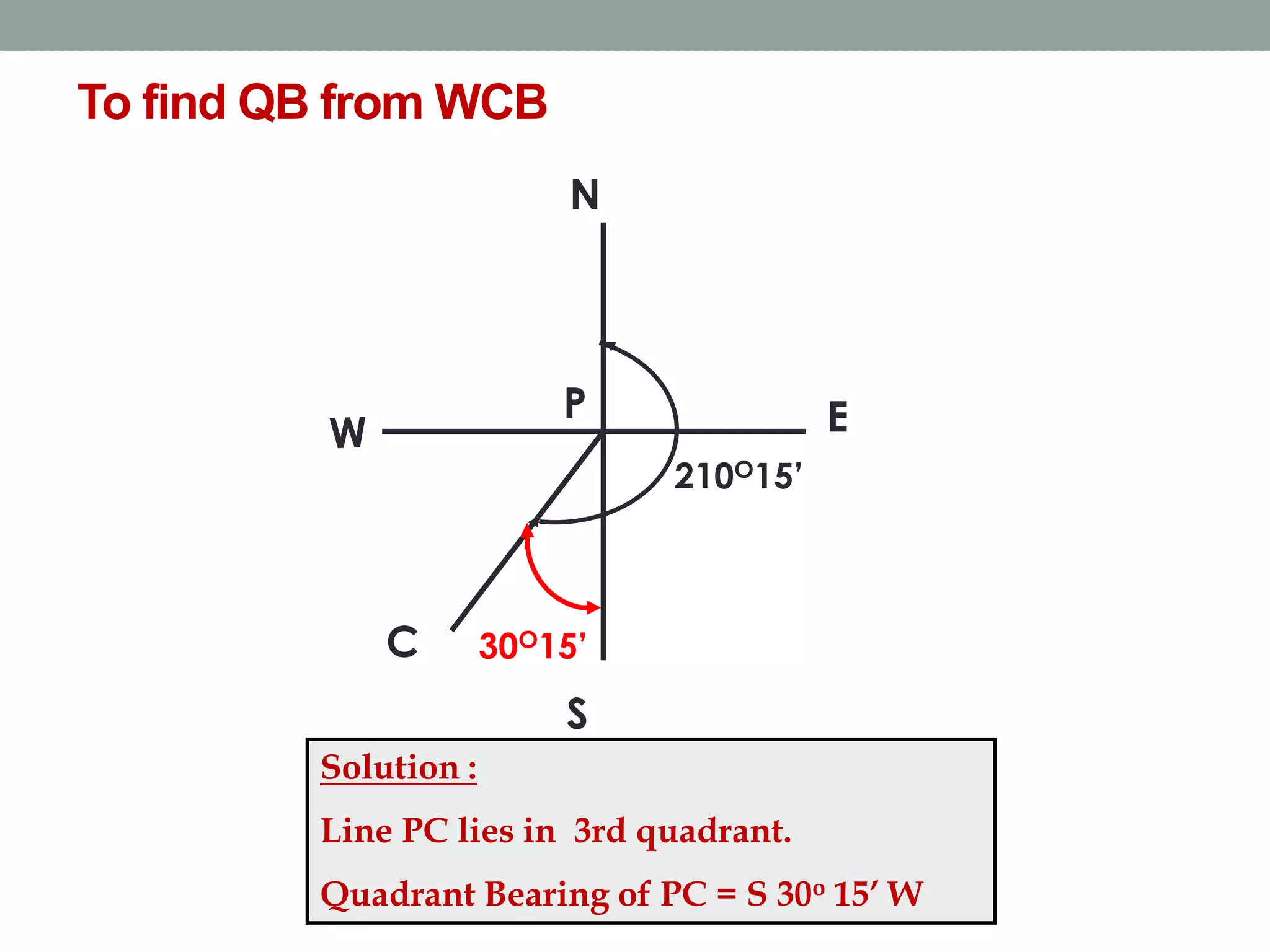
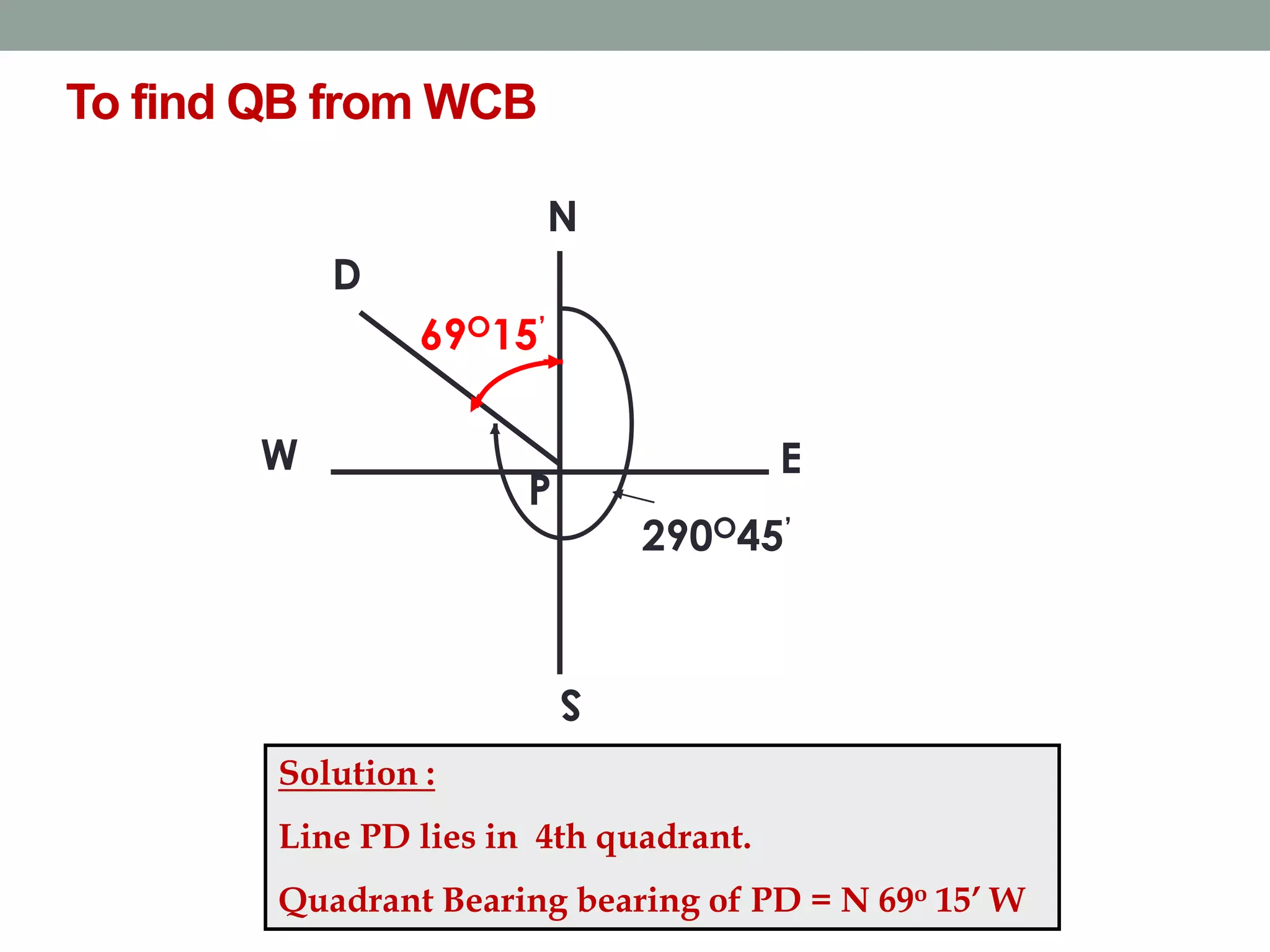
This document provides an overview of basic surveying principles and methods:
1) Surveying works from establishing overall control points before measuring details. Control points are established through precise primary networks of triangles or traverses.
2) Secondary control networks further divide the primary network for less precise work. Survey of details then uses the established control points. This minimizes error accumulation.
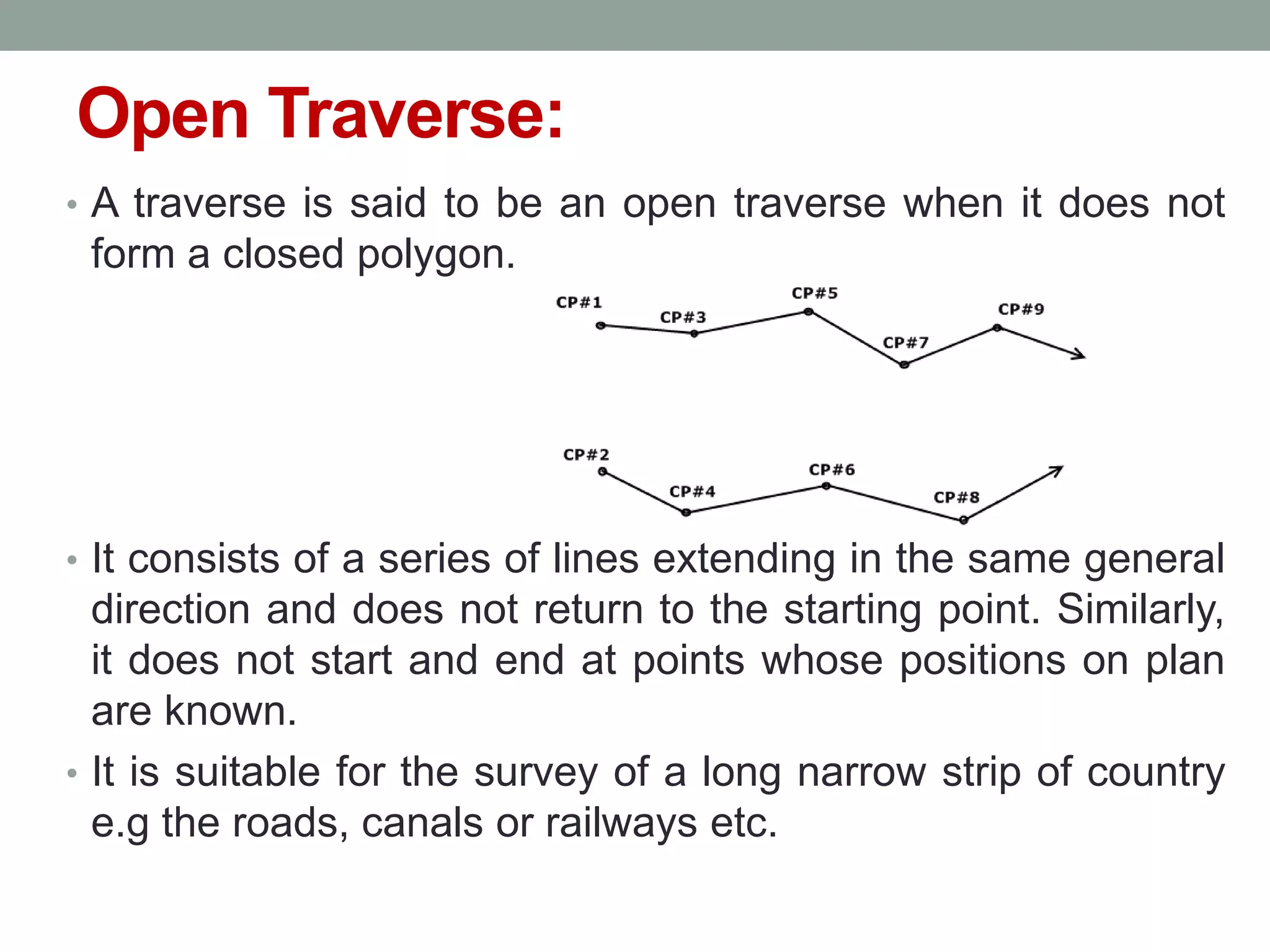
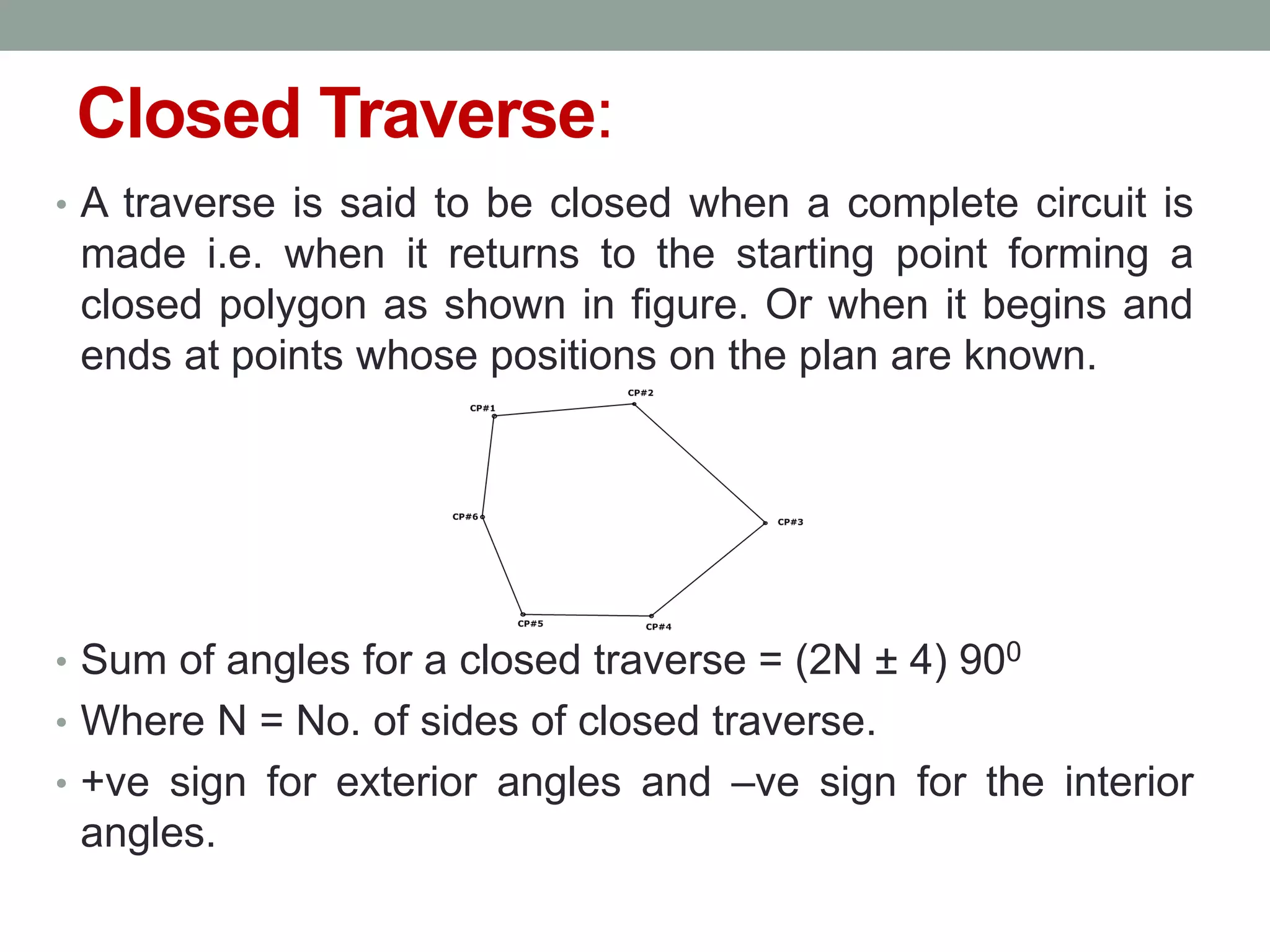
3) A traverse connects lines whose lengths and directions are measured to establish a framework. Traverses can be open or closed, with closed traverses returning to the starting point.
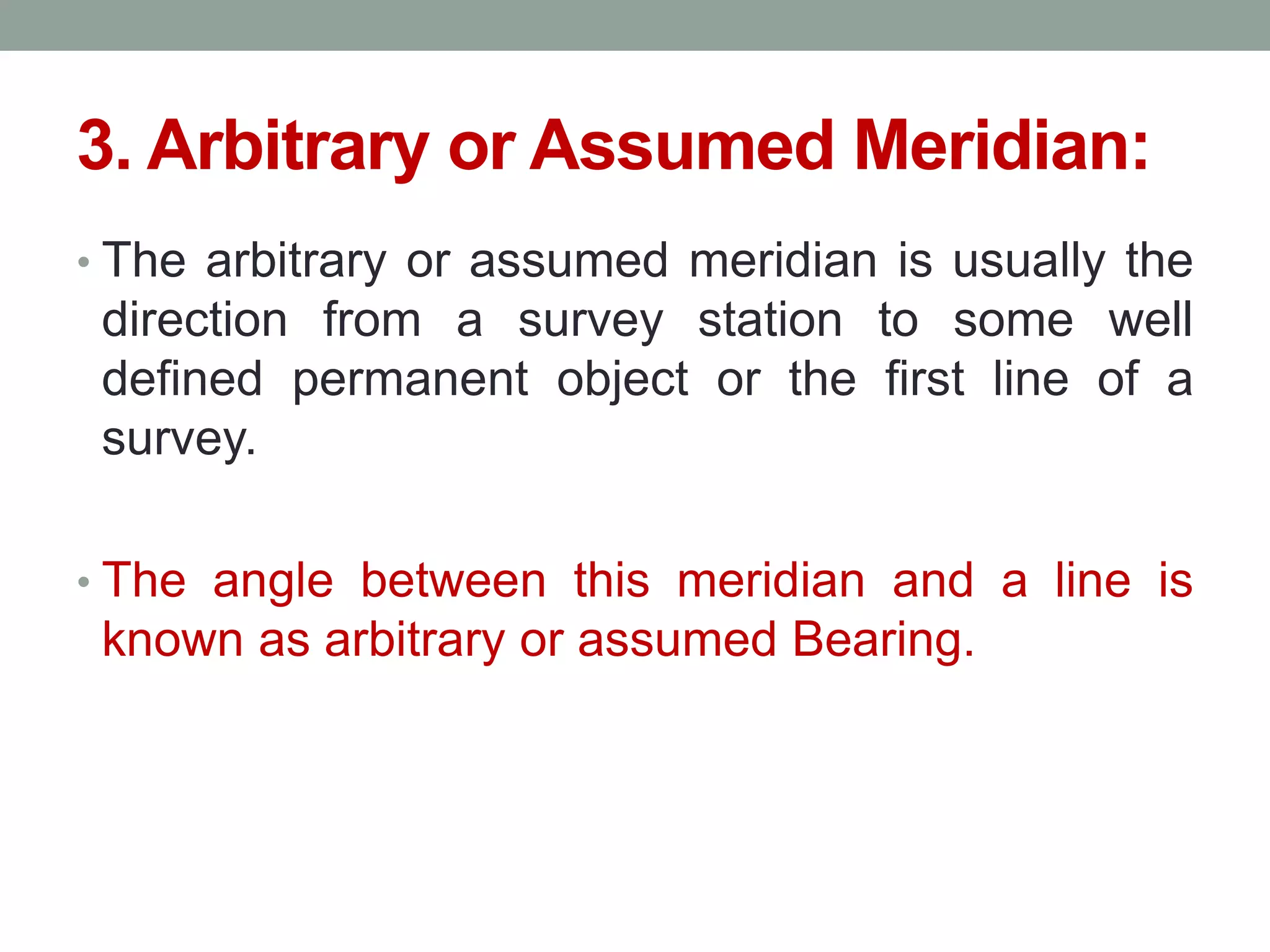
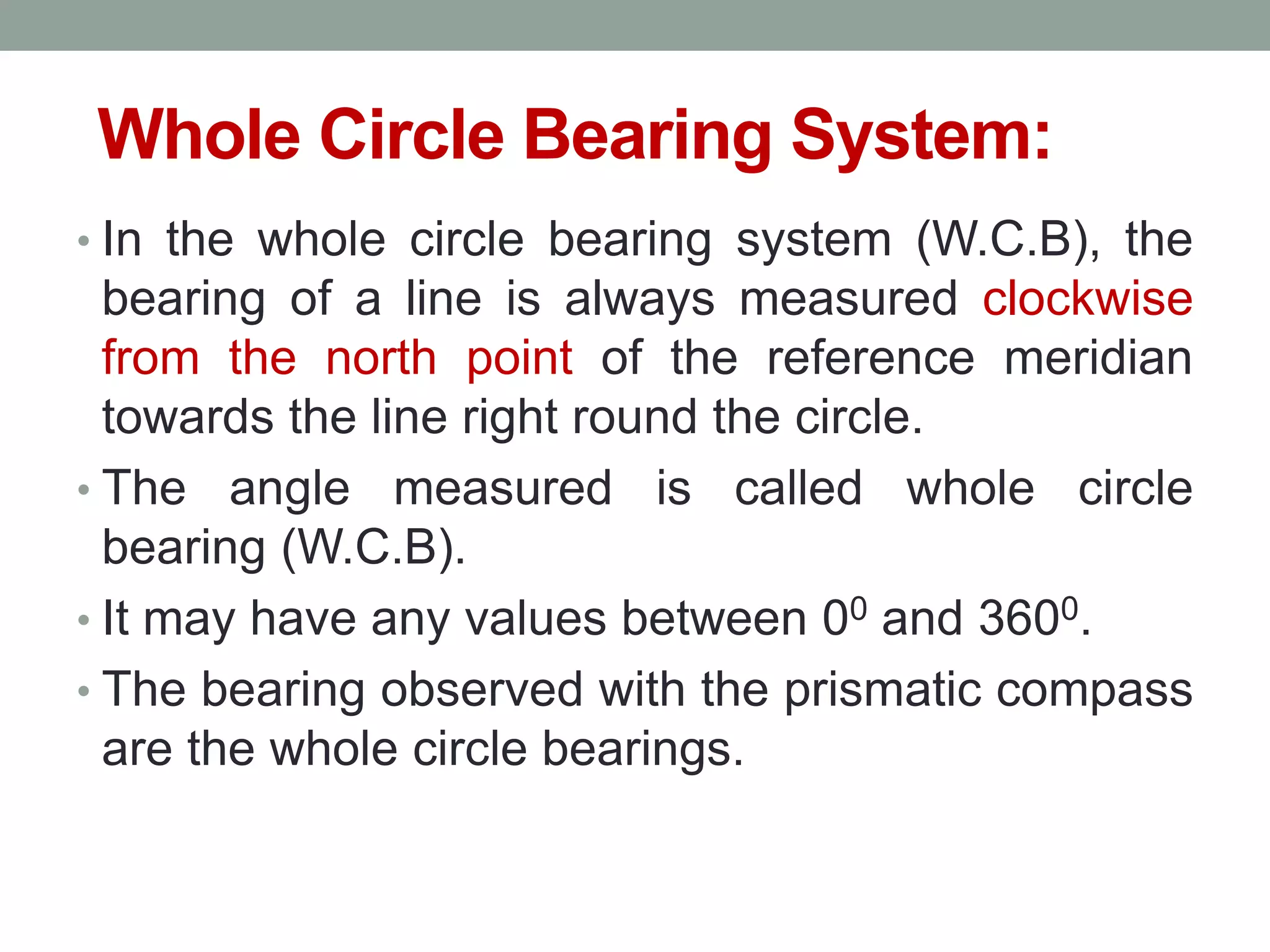
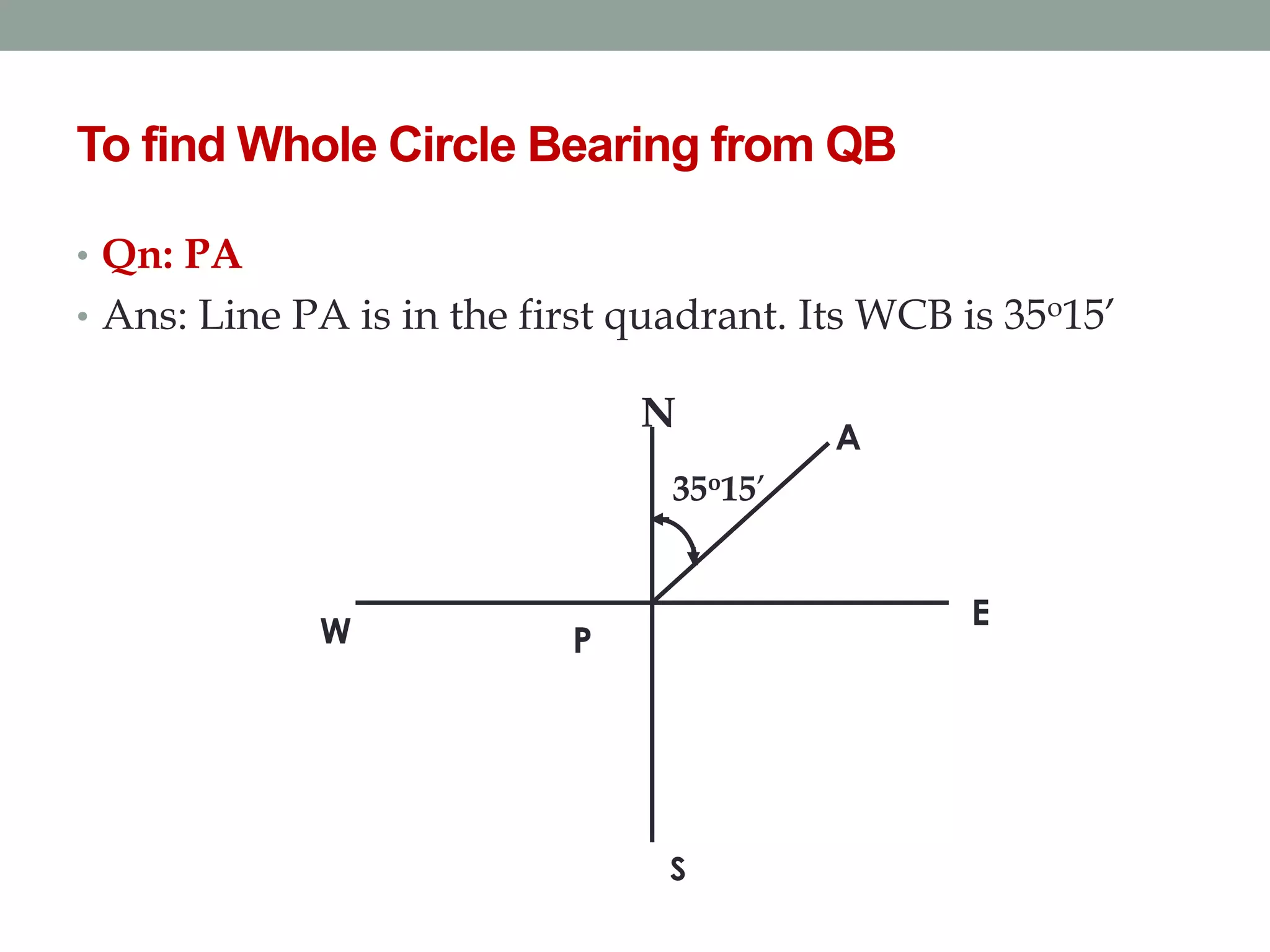
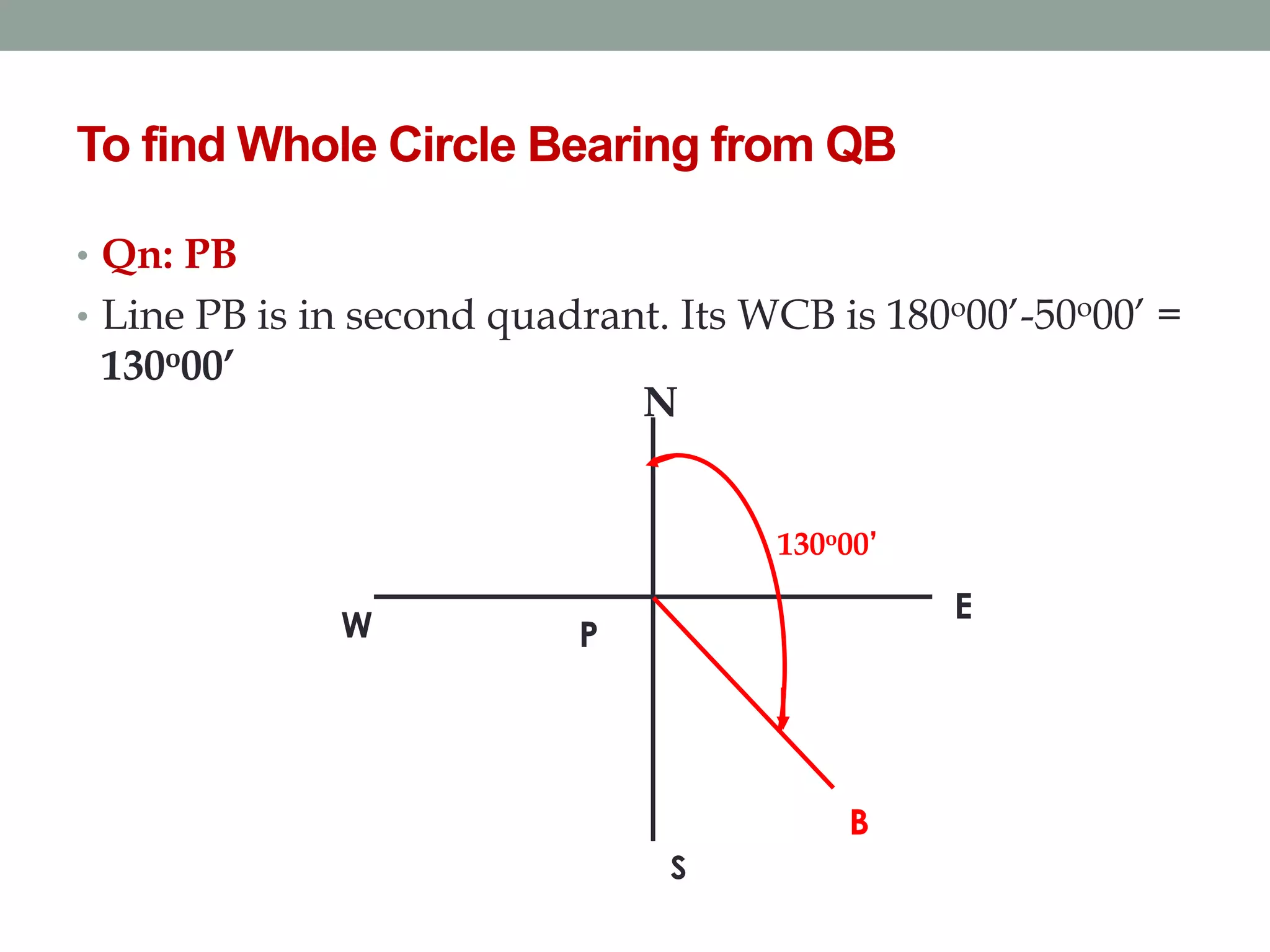
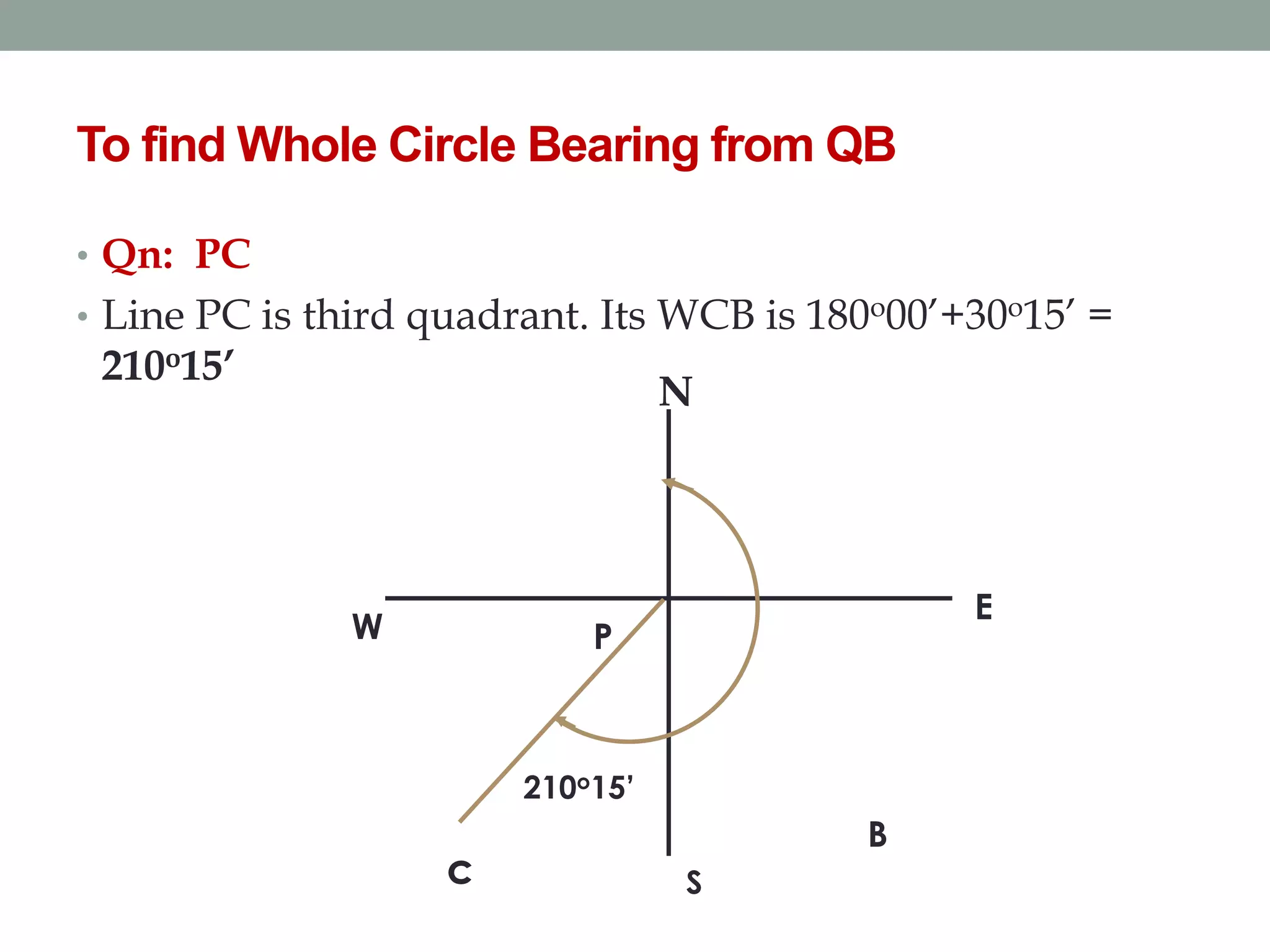
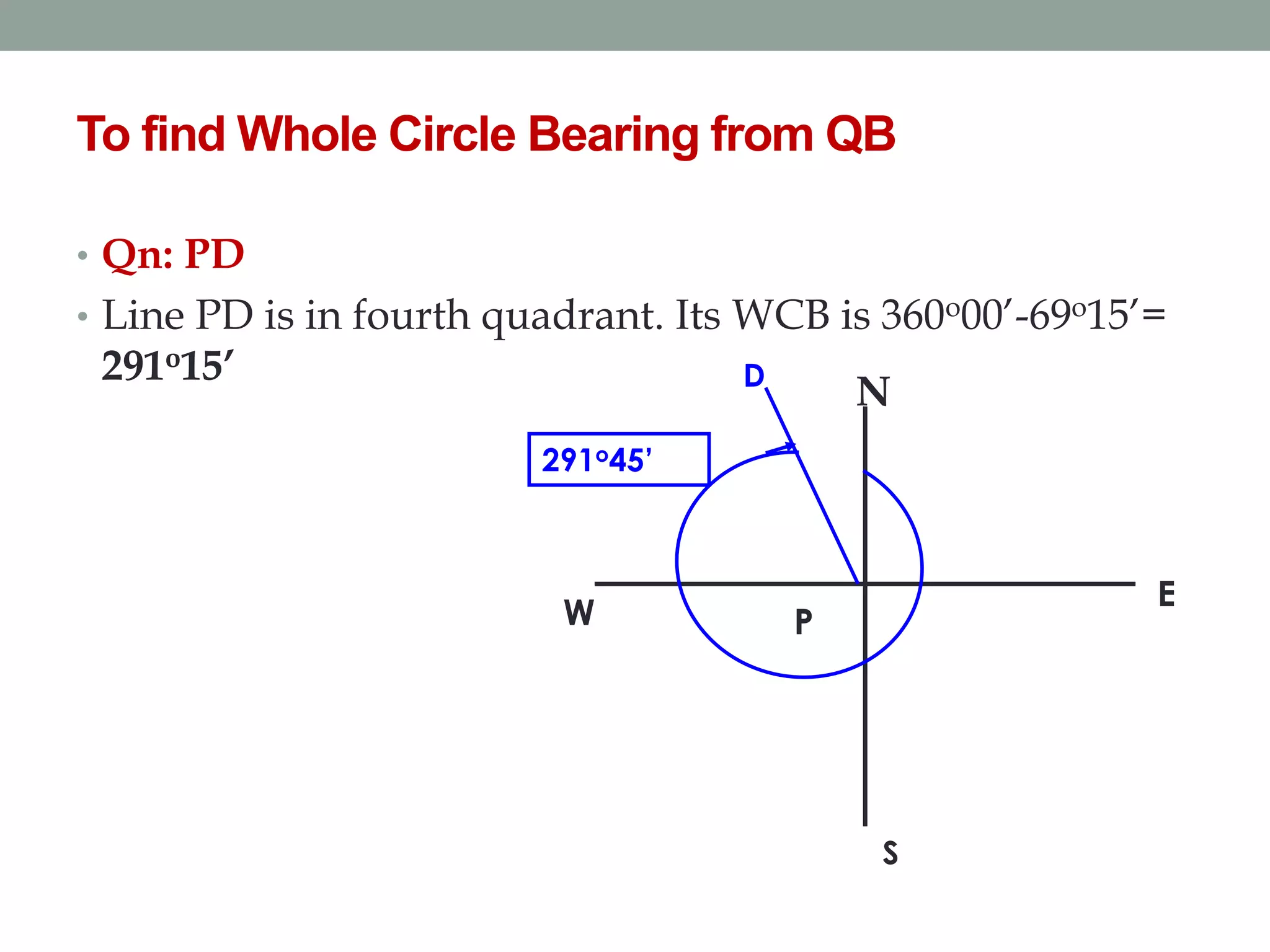
4) The direction of lines is defined by their bearing from a reference meridian using different systems like true, magnetic, or arbitrary meridians.