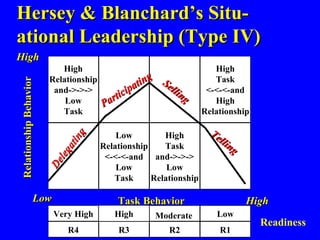
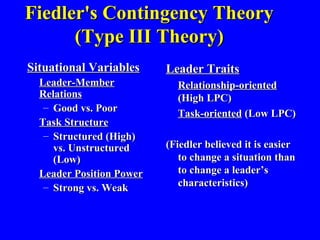
This document summarizes various leadership theories including: universal theories focused on traits and behaviors; contingency theories that consider traits and behaviors based on situational factors; and newer approaches like transformational, servant, and authentic leadership. It discusses leadership styles like initiating structure and consideration. Situational leadership models are presented, including Fiedler's contingency theory and Hersey and Blanchard's model relating leadership style to follower readiness. Substitutes and bases of social power are also covered.