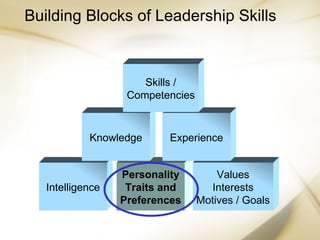
The document discusses leadership traits and the Five Factor Model of personality. It describes how early theories thought leaders were fundamentally different than followers, but studies found leaders and followers share many characteristics. Certain traits like intelligence, stress tolerance, and dominance can improve leadership success, but do not guarantee it. The Five Factor Model identifies five broad personality dimensions: Surgency (dominance, sociability), Agreeableness (empathy, friendliness), Dependability (organization, credibility), Adjustment (steadiness, self-acceptance), and Intellectance (openness to experience). The document also discusses "dark-side" personality traits like argumentativeness, narcissism, and impulsivity that can negatively impact leadership.