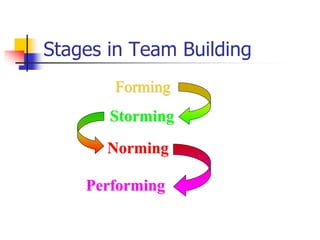
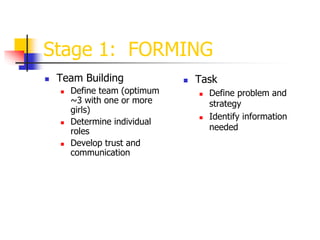
1. The document discusses the stages of team building, including forming, storming, norming, and performing.
2. It provides guidance on how to effectively build a team, including defining roles, developing trust, addressing conflicts, and giving constructive feedback.
3. High performing teams are characterized by commitment to shared goals, well-defined roles and responsibilities, effective communication systems, and good personal relationships between members.