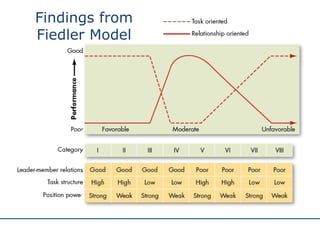
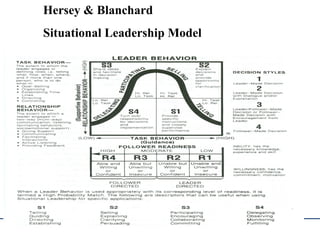
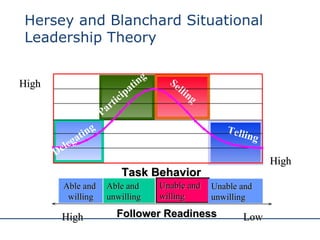
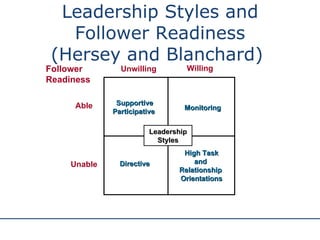
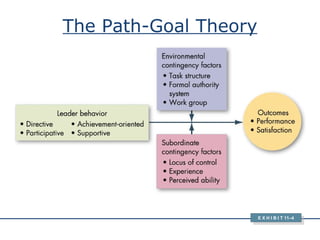
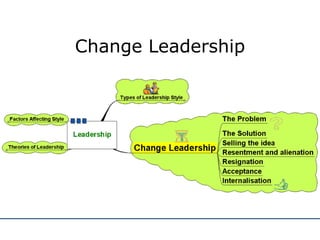
The document discusses various theories and styles of leadership. It describes trait theories which examine personality characteristics of leaders, and behavioral theories which propose that leadership can be taught. It also outlines contingency theories like Fiedler's model and situational leadership theory which emphasize that leadership style depends on situational factors. Additionally, it mentions transformational leadership requiring long-term planning and vision, and transactional leadership focusing on management through procedures and rules.