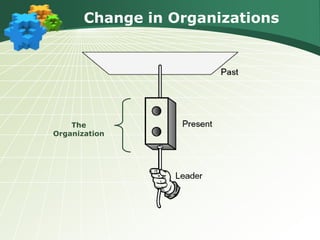
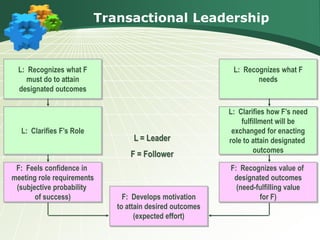
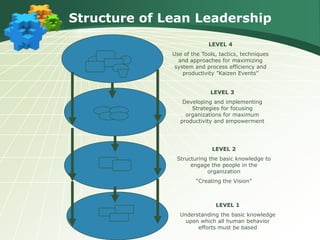
This document discusses various leadership styles and concepts, including:
- Charismatic leadership, which influences followers through supernatural gifts and attractive powers. It has two types: visionary and crisis-based.
- Transactional leadership, where the leader helps followers achieve goals through contingent rewards and management by exception.
- Transformational leadership, which inspires followers to achieve more through vision, changes to mission/operations, and human resource management.
- Lean leadership focuses on influence, example-setting, knowledge, engagement, and building systems to empower people without waste. The key skills for lean leaders are people skills, conceptual skills, and technical skills.