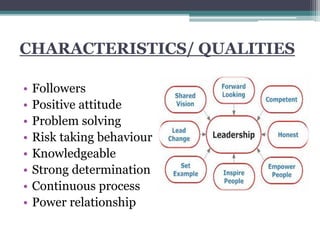
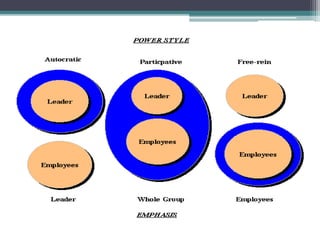
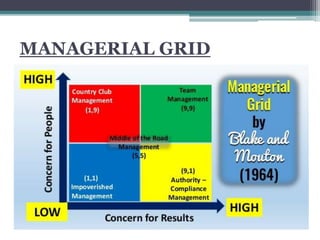
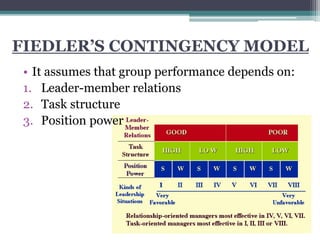
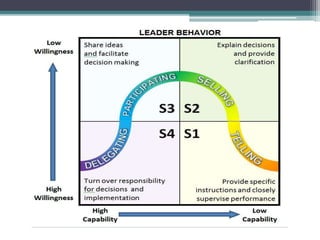
This document discusses various concepts and theories related to leadership. It defines leadership as the ability to influence others and motivate them towards common goals. Several leadership styles are described, including autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. Trait theory suggests leaders are born with certain qualities, while behavioural theory believes leadership can be learned. Contingency theory proposes that the most effective leadership style depends on internal and external situational factors. Fiedler's contingency model and the path-goal theory are contingency theories discussed in the document.