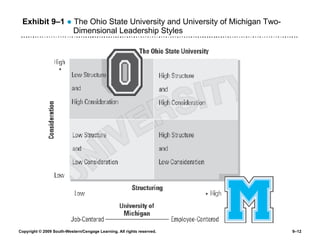
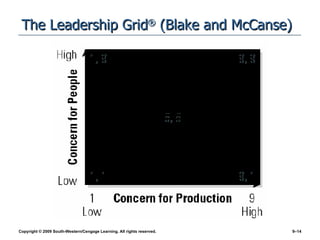
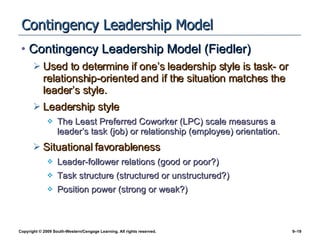
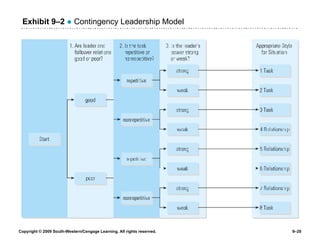
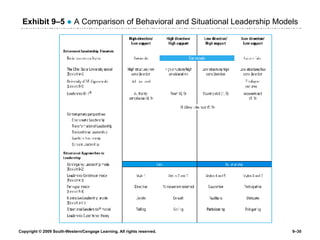
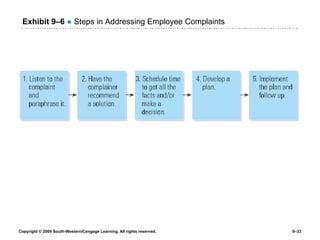
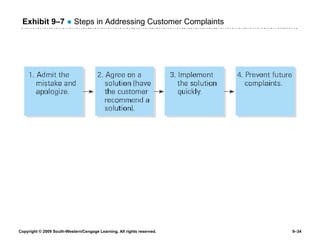
The document discusses different theories of leadership including trait theory, behavioral theories, situational theories and contemporary perspectives like transformational leadership. It summarizes several models of situational leadership including Fiedler's contingency model, the leadership continuum model, path-goal theory, and Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership model. It also discusses leadership substitutes theory and addresses ethical questions about leadership and gender.