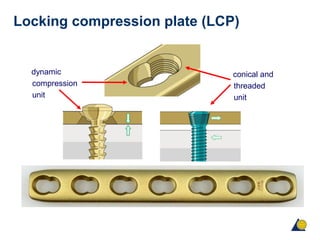
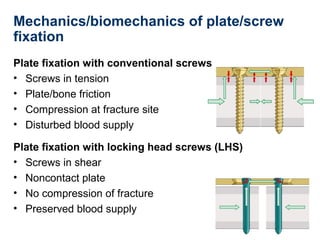
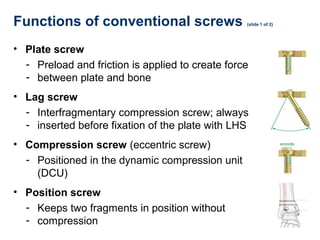
This document provides an overview of fracture fixation using locking compression plates (LCP). It discusses the different principles of fixation, including compression for absolute stability and splinting for relative stability. Compression plates use conventional screws and interfragmentary compression, while locked plates utilize locking head screws to provide angular stability without compression. Certain fractures are best treated with compression and direct bone healing, while others such as multifragmentary or osteoporotic fractures are better suited to splinting and indirect healing with locked plating. Both techniques can be combined in segmental fractures involving different zones.