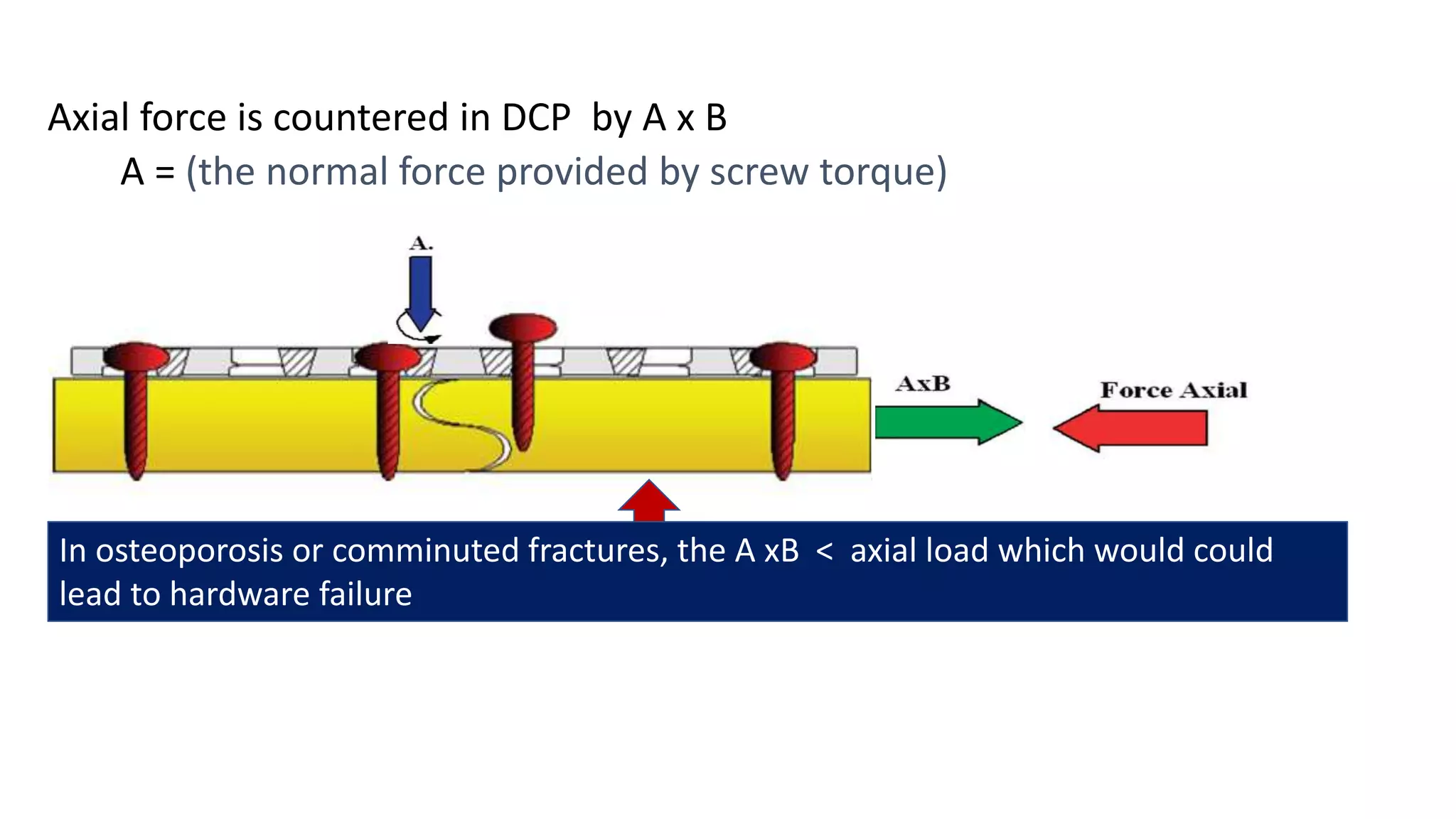
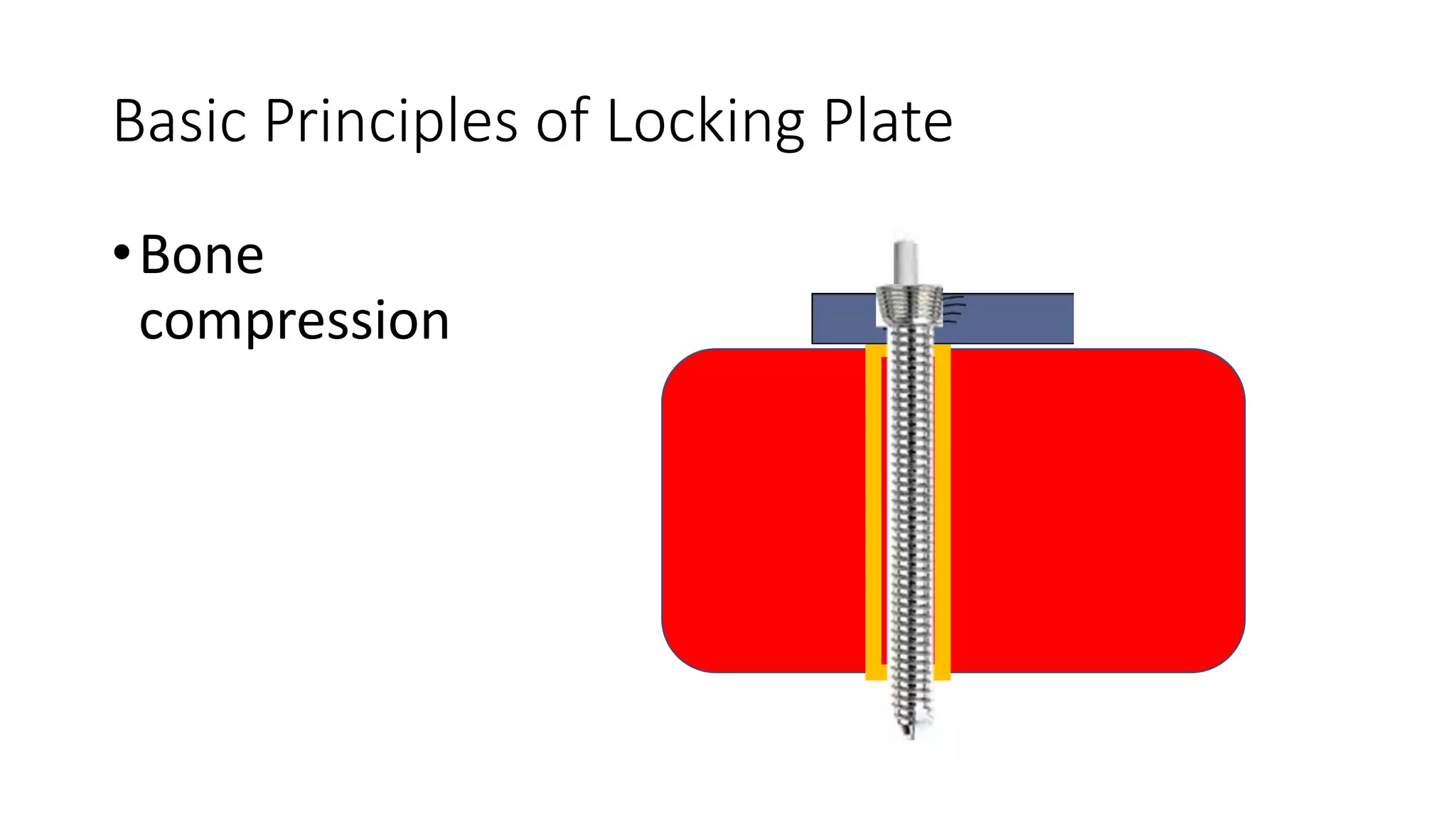
Locking plates work by converting axial loads into compressive stresses at the screw-bone interface. This increases fixation strength and prevents hardware failure, especially in osteoporotic bone. Locking plates provide stability for early motion while protecting blood supply, aiding fracture healing. Key advantages over conventional plates are increased axial and angular stability with less dependence on bone quality. Proper technique requires initial fracture reduction before plate fixation with a combination of locking and conventional screws. Over-rigid constructs with too many screws can impair healing and cause nonunion.