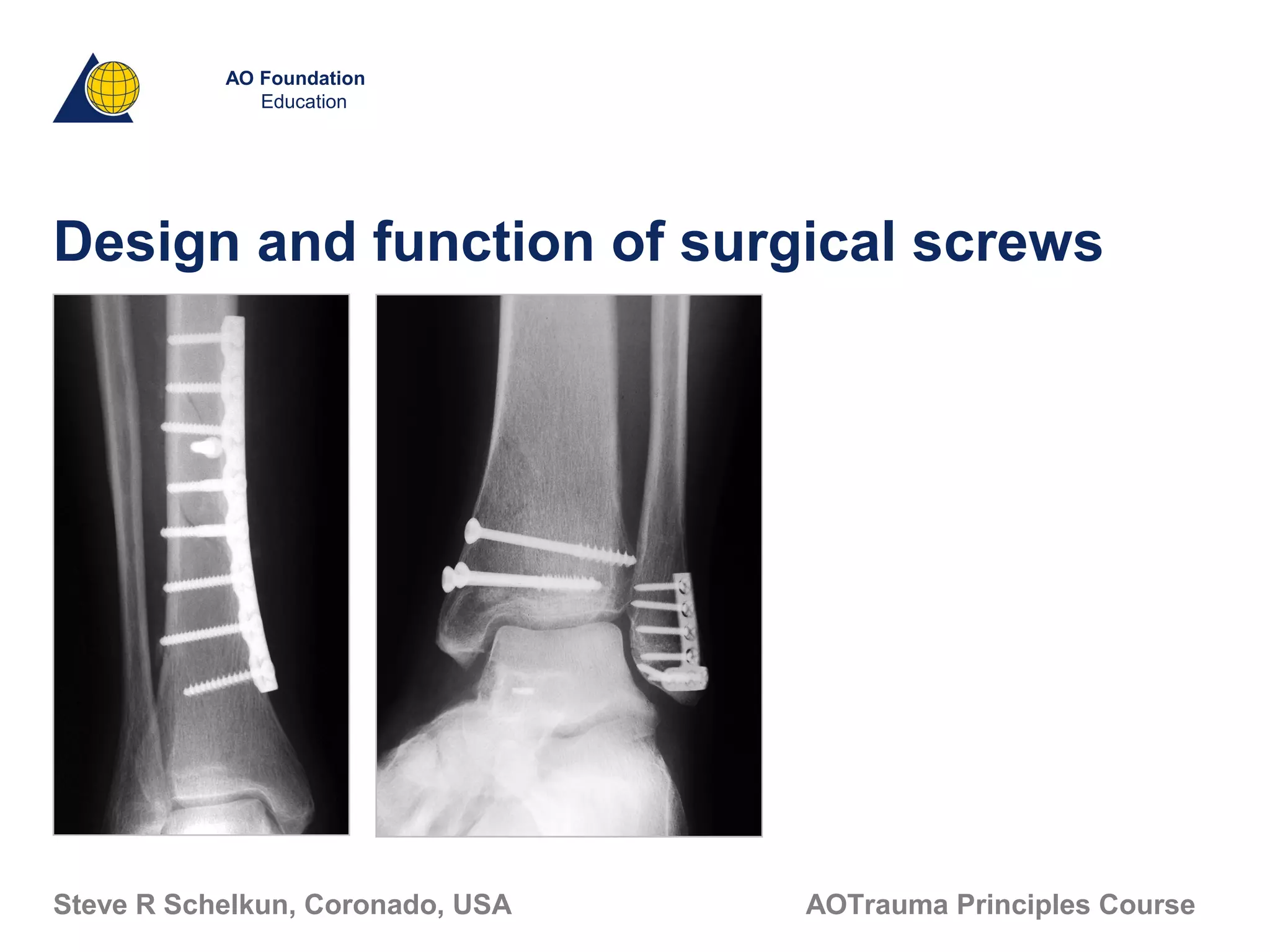
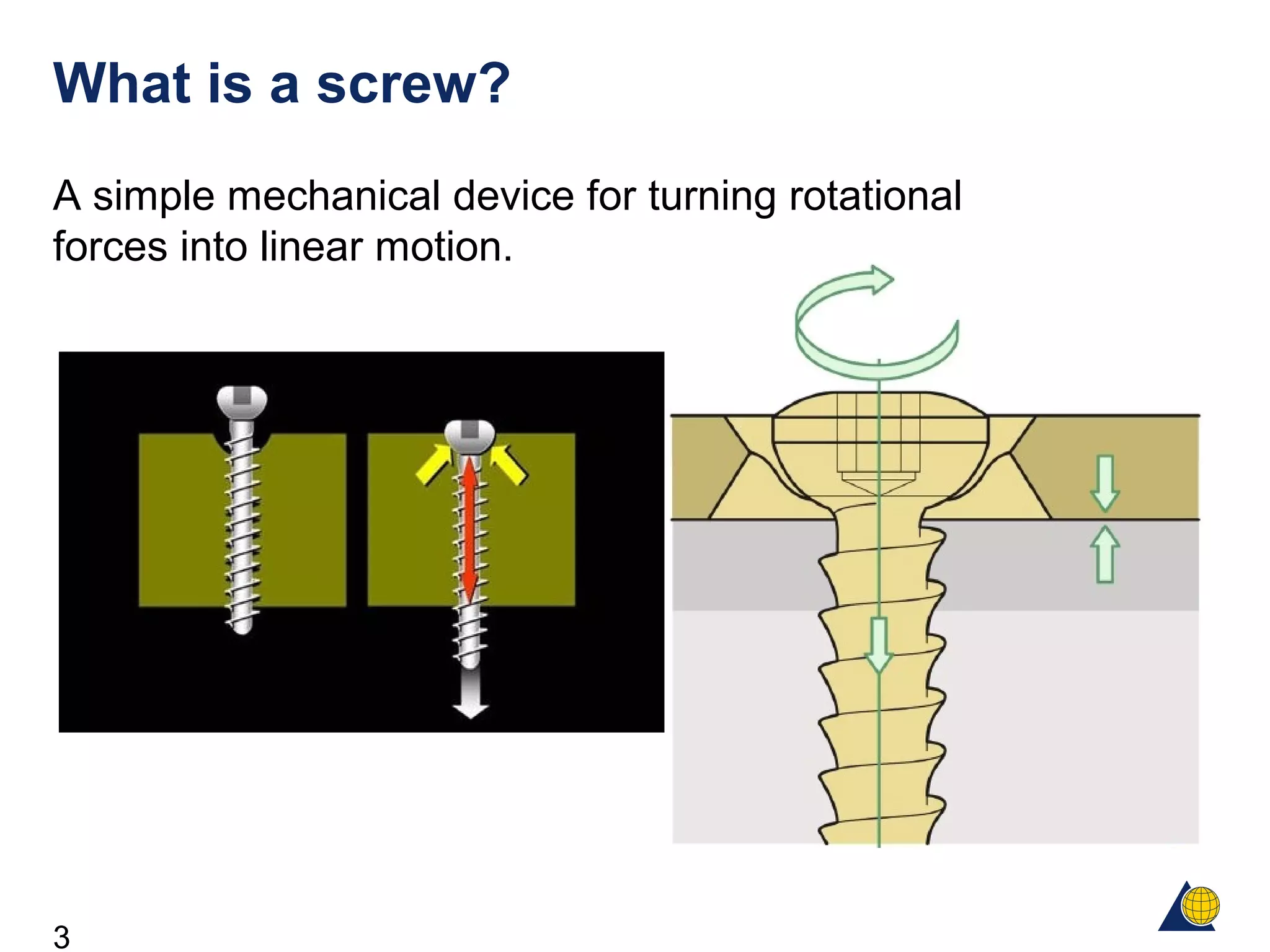
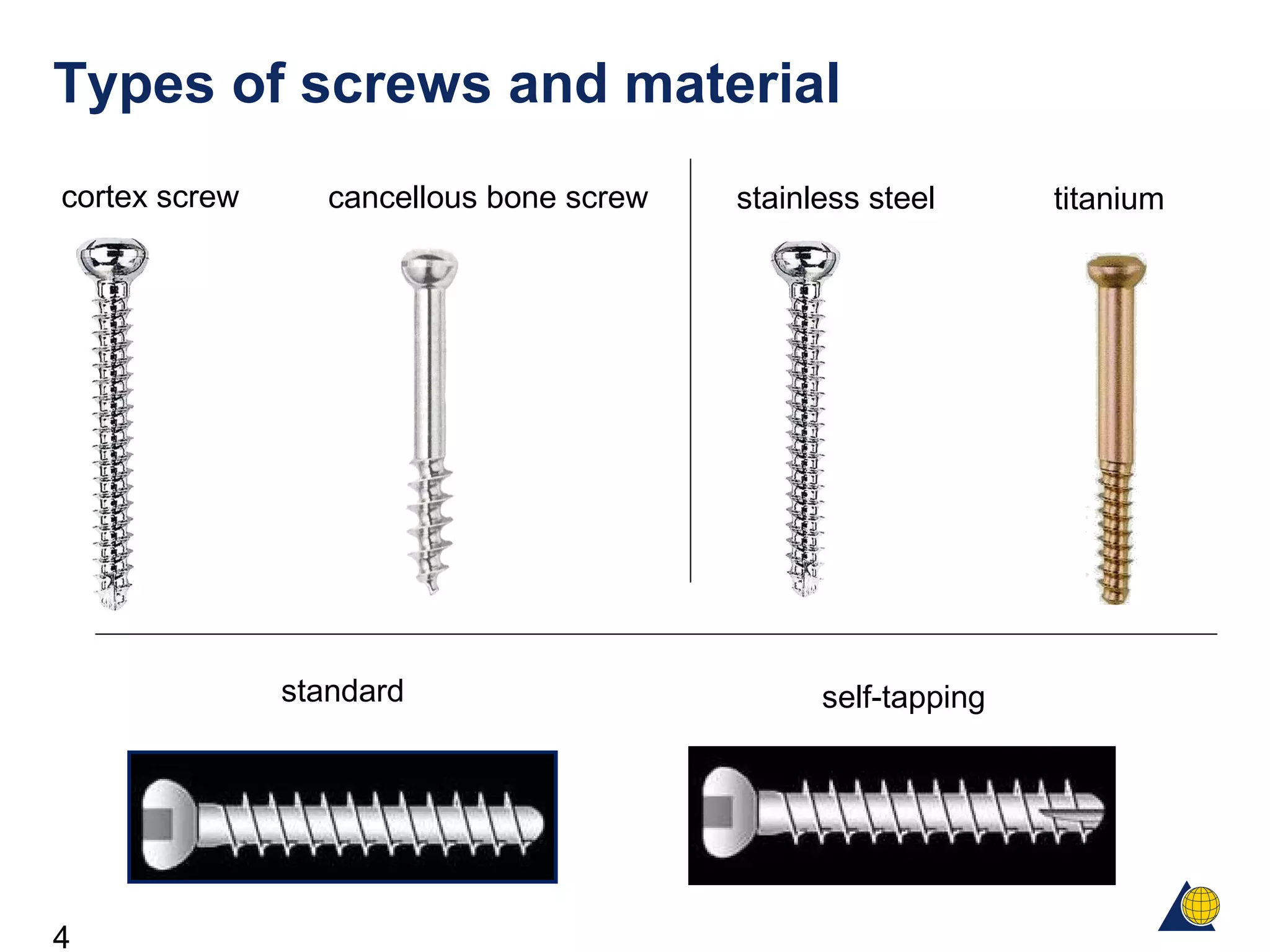
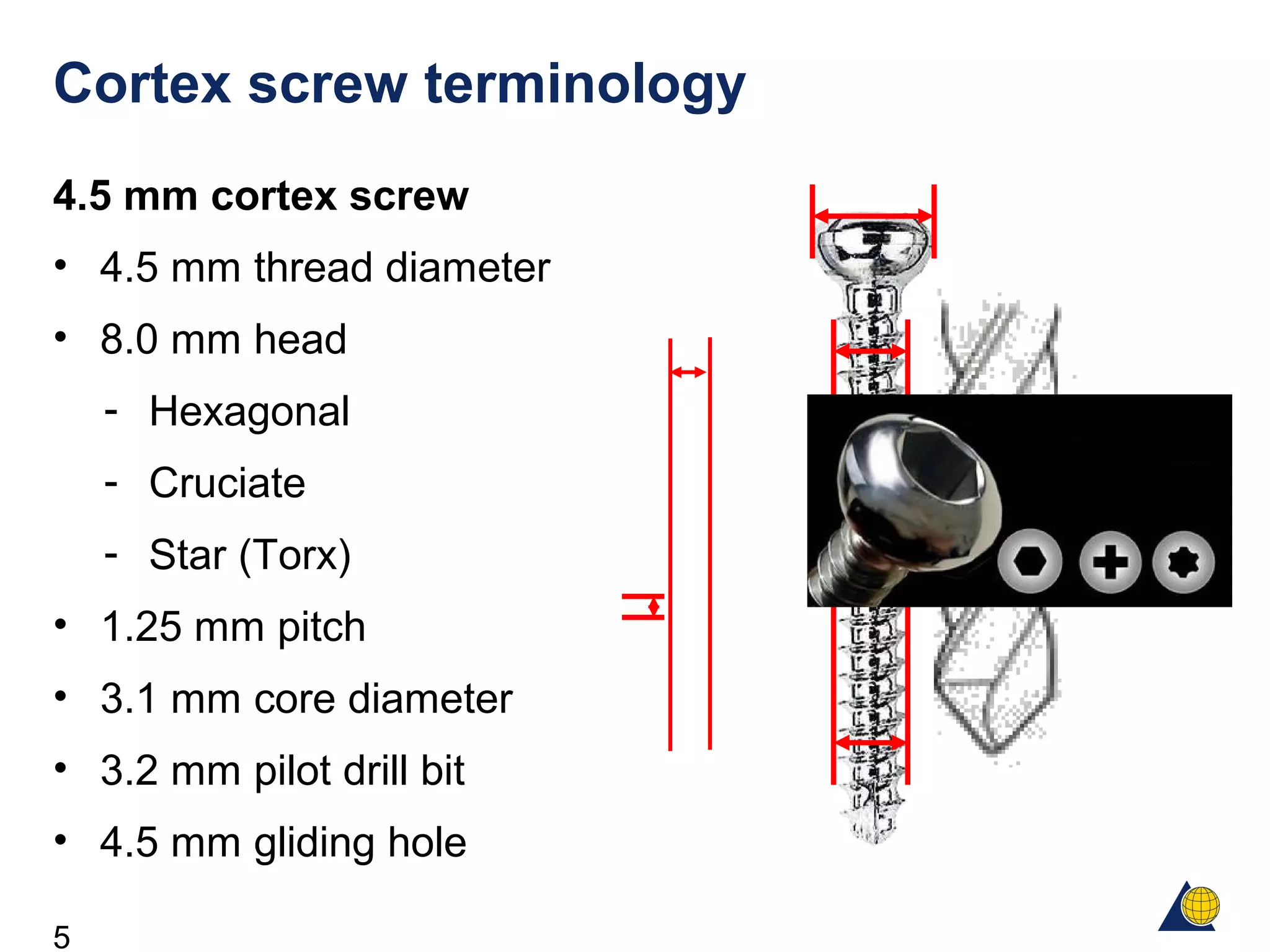
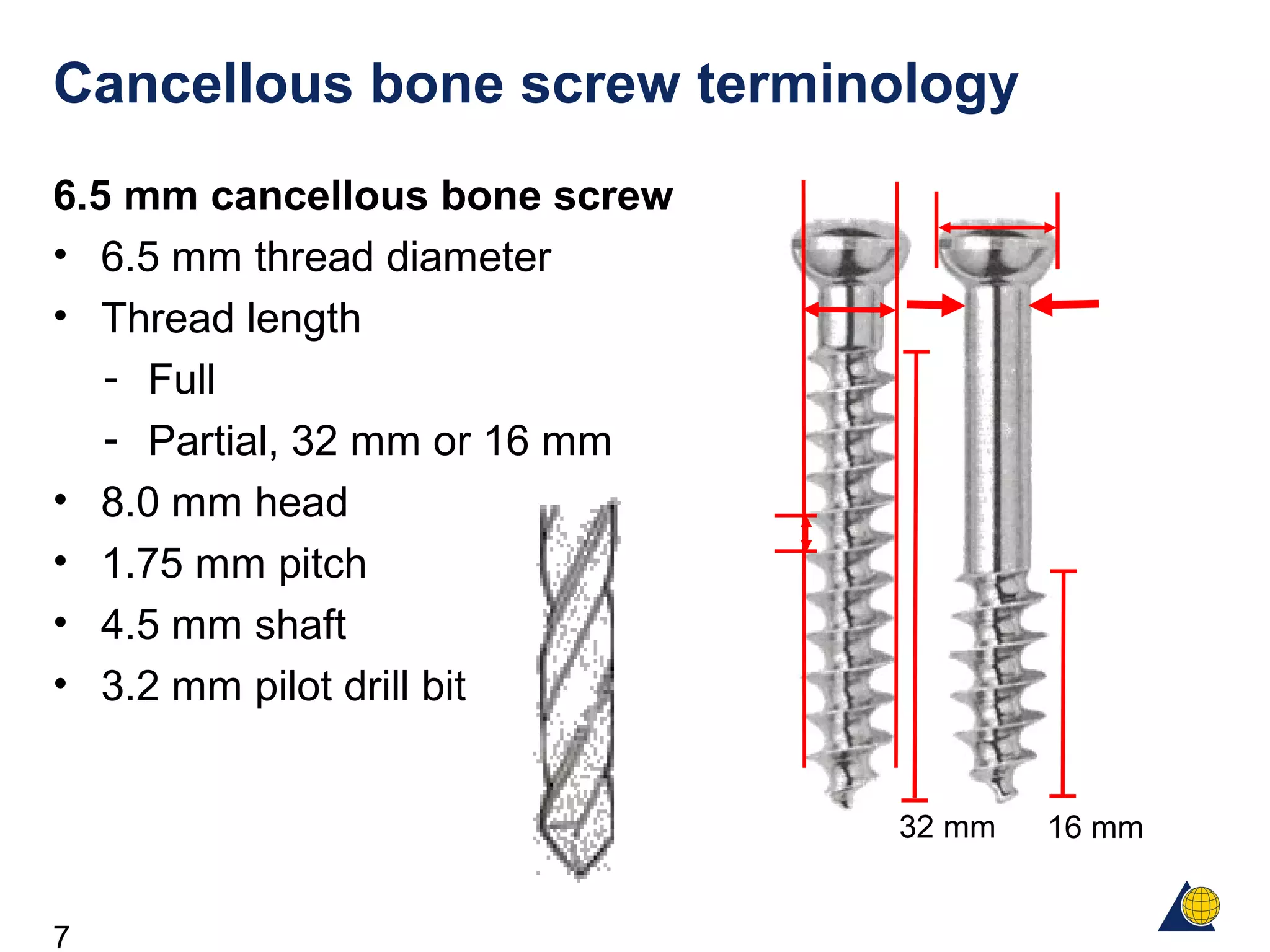
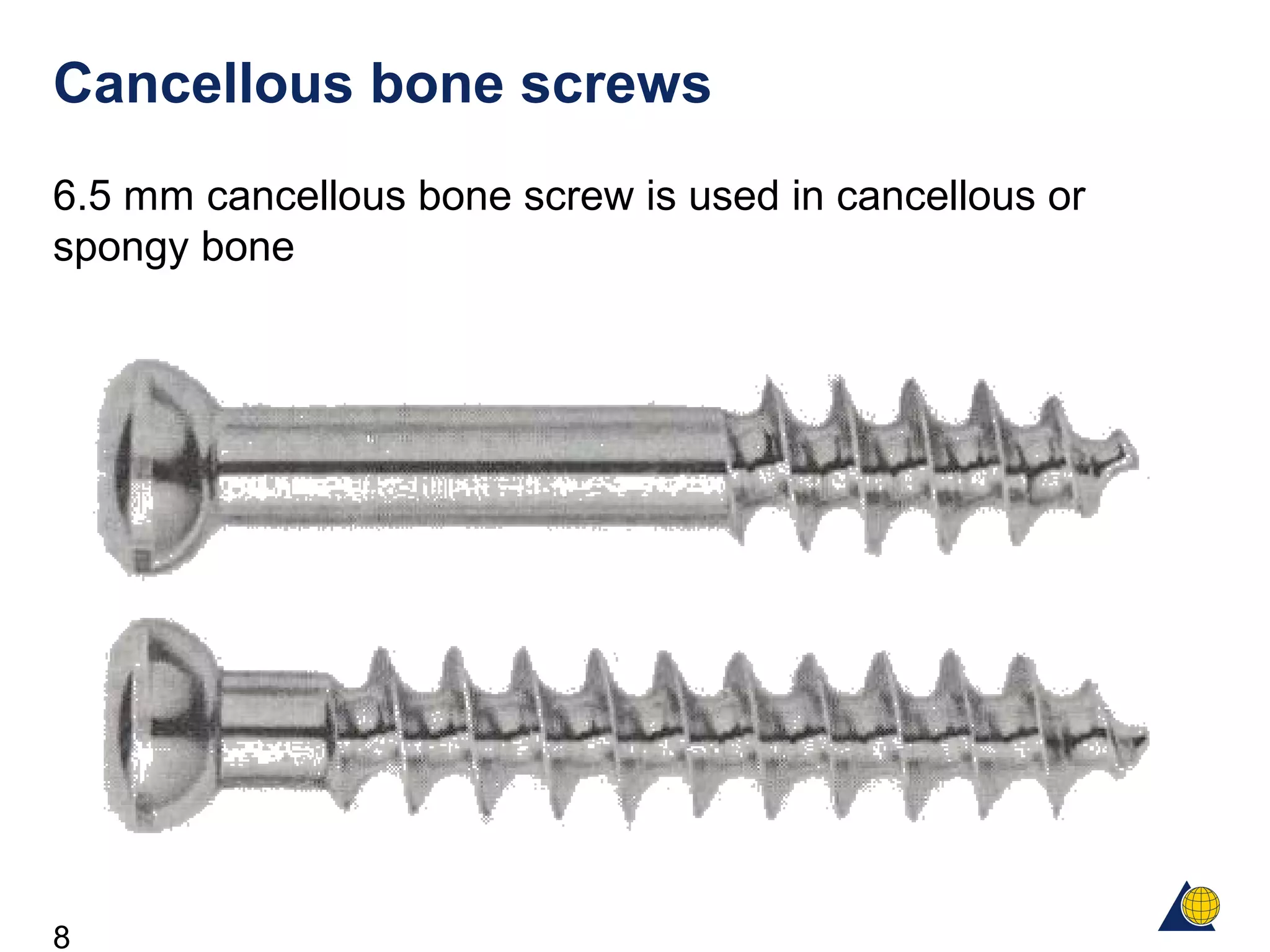
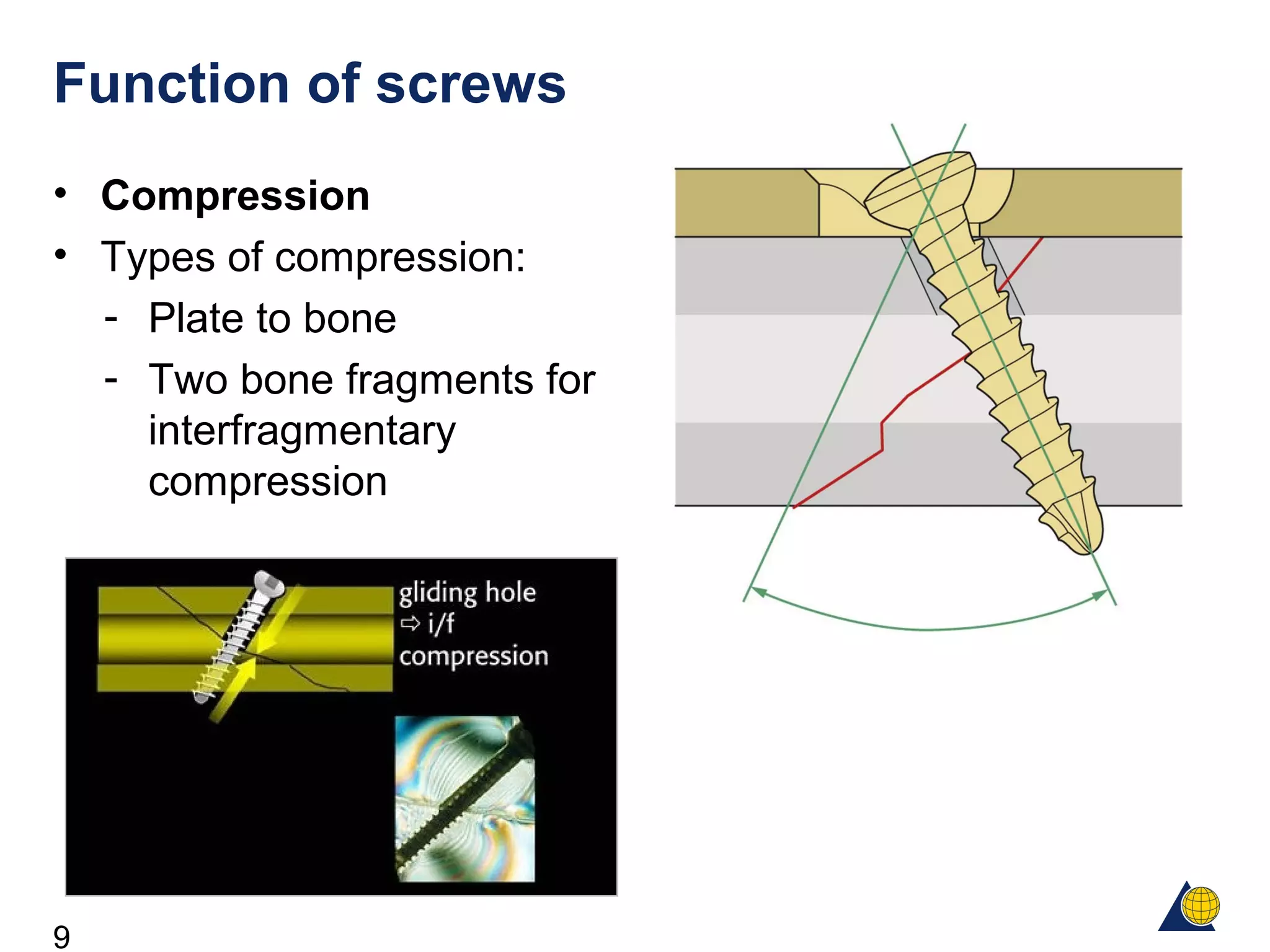
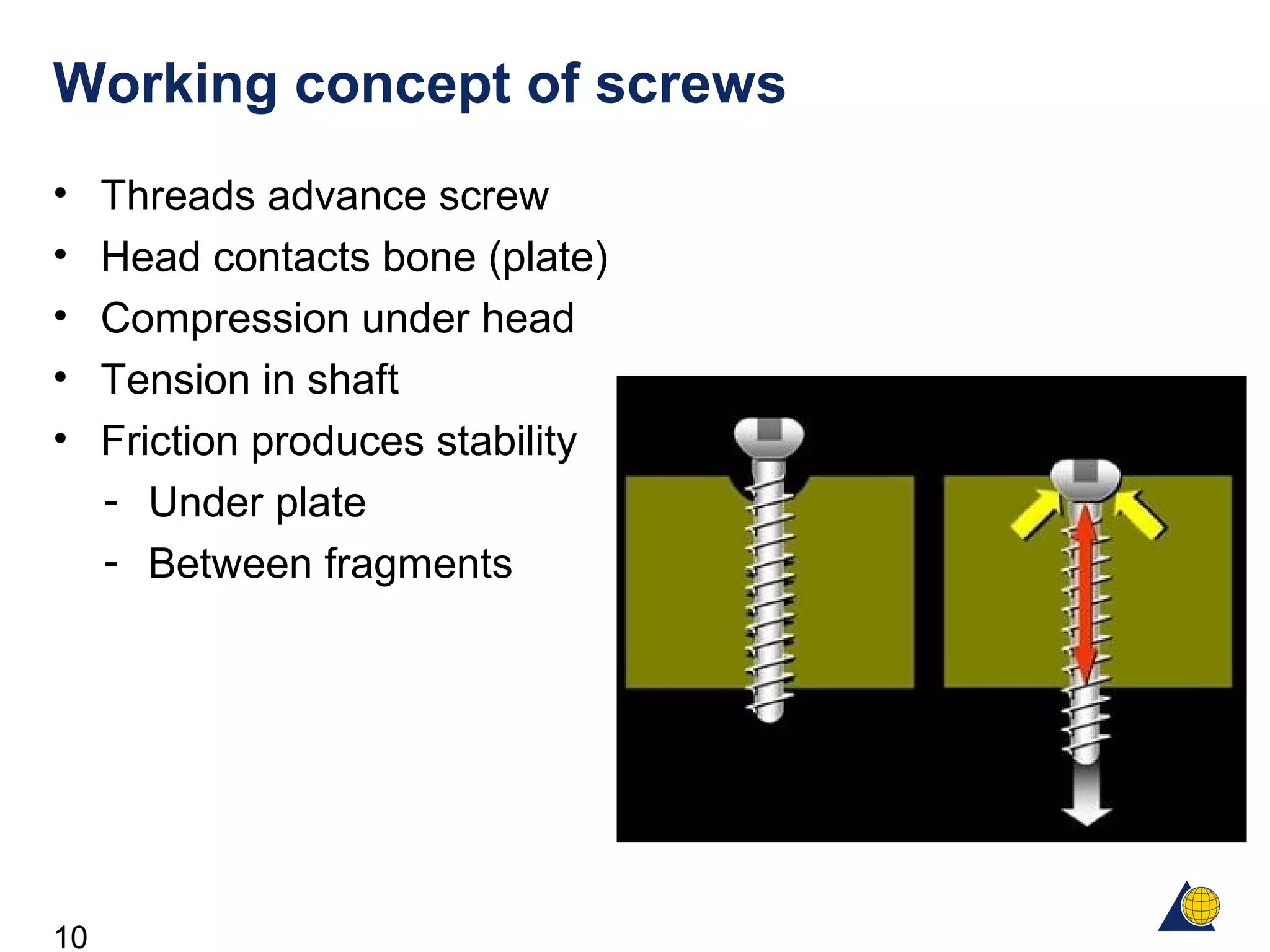
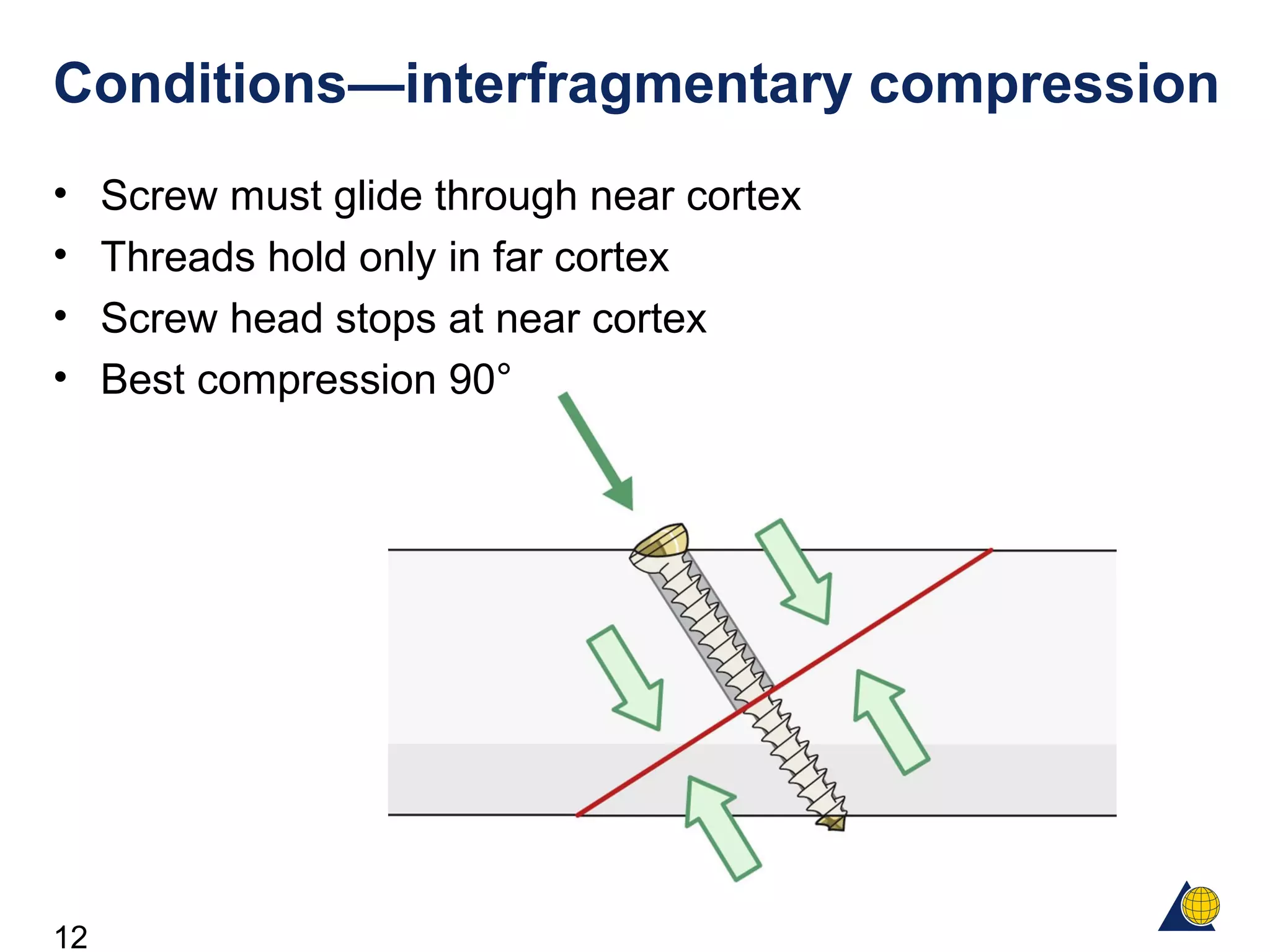
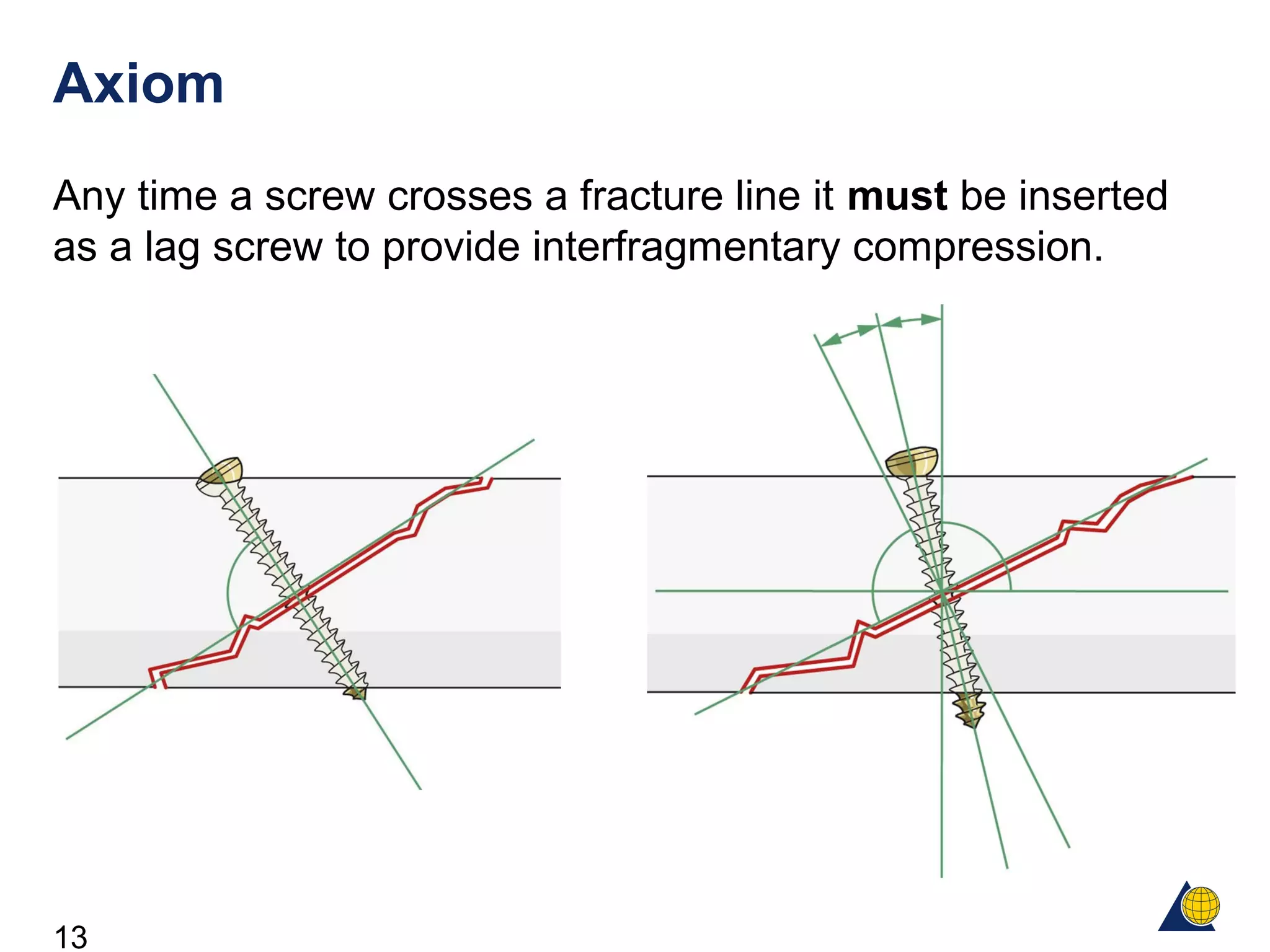
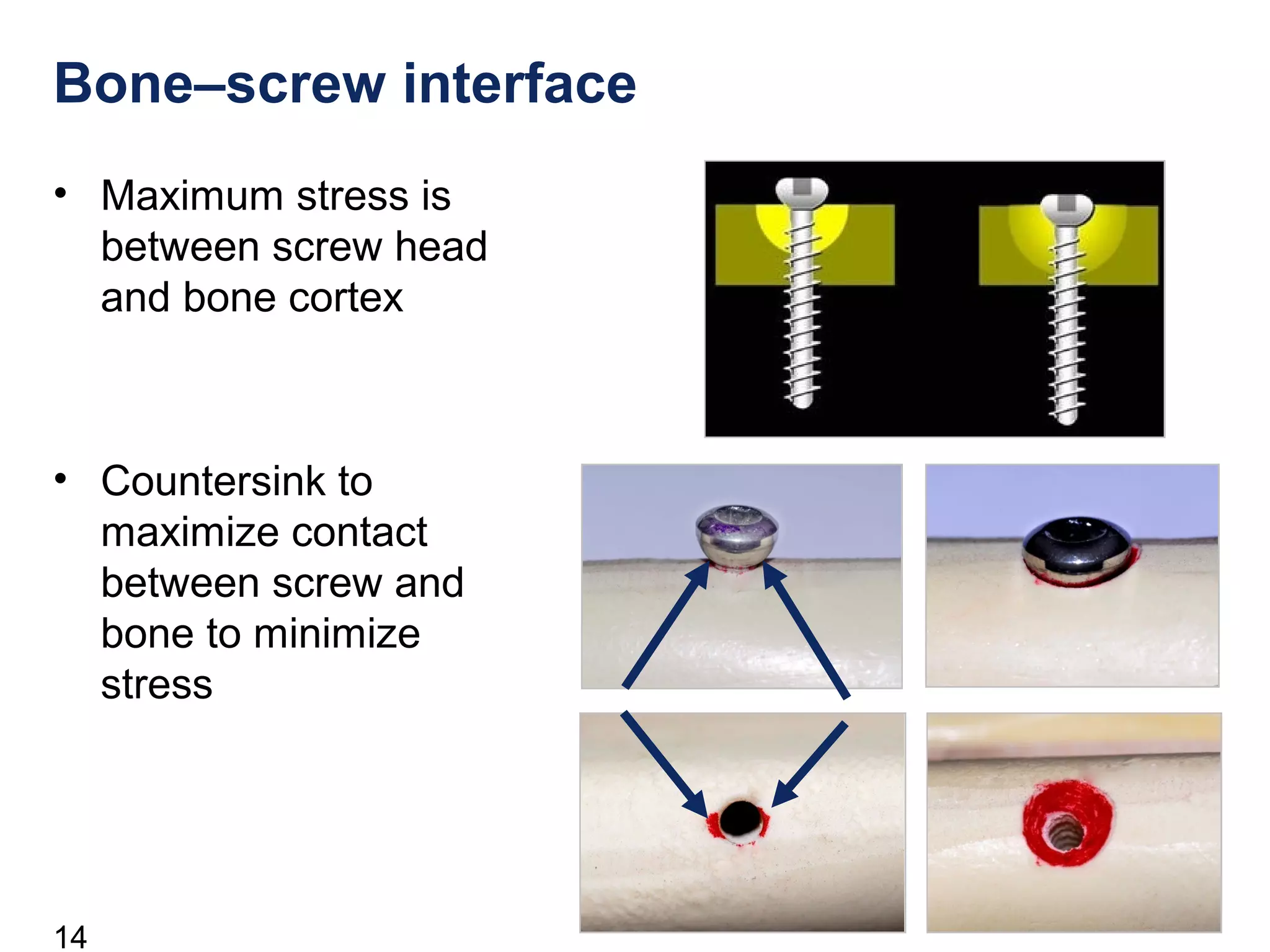
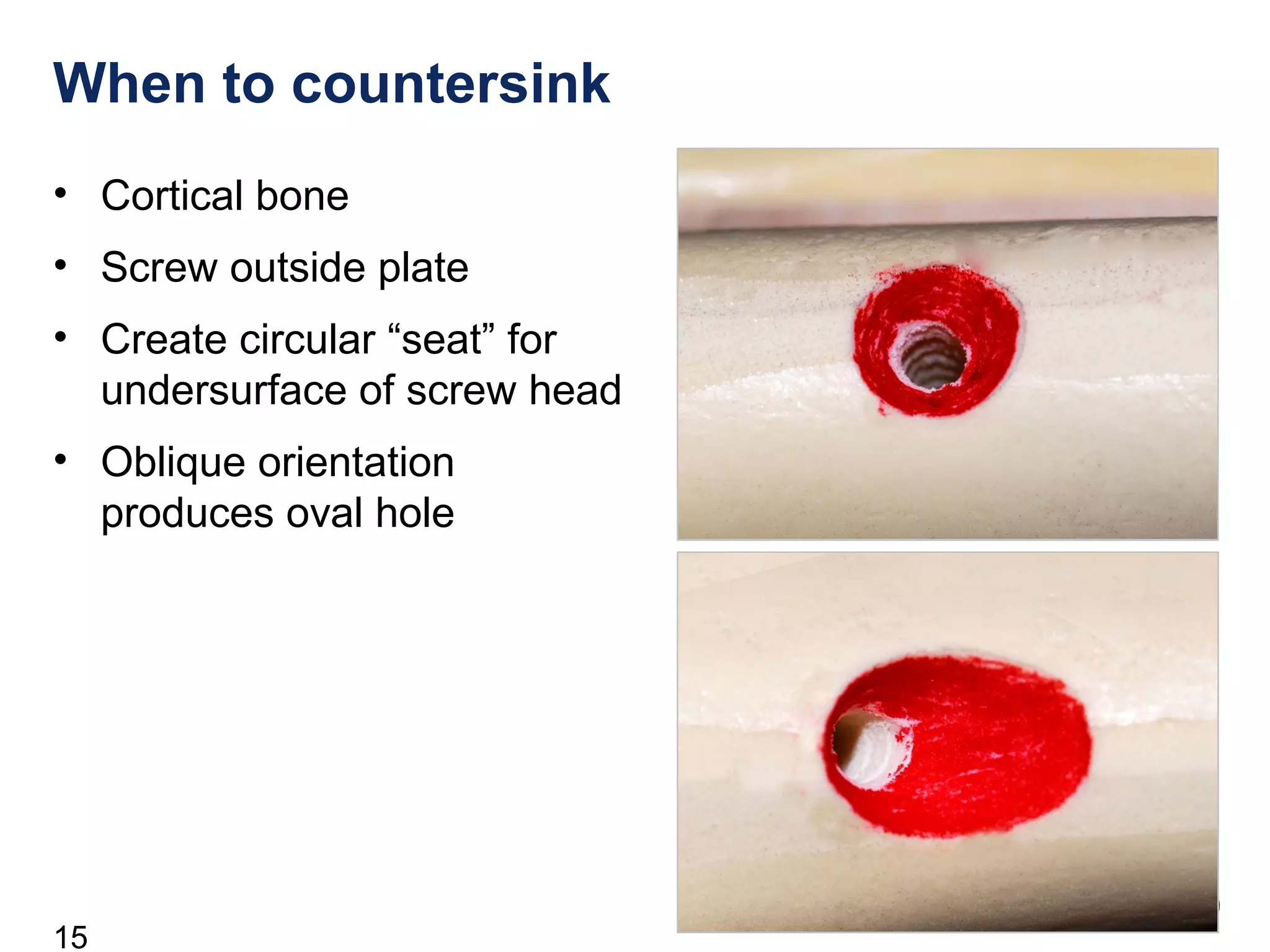
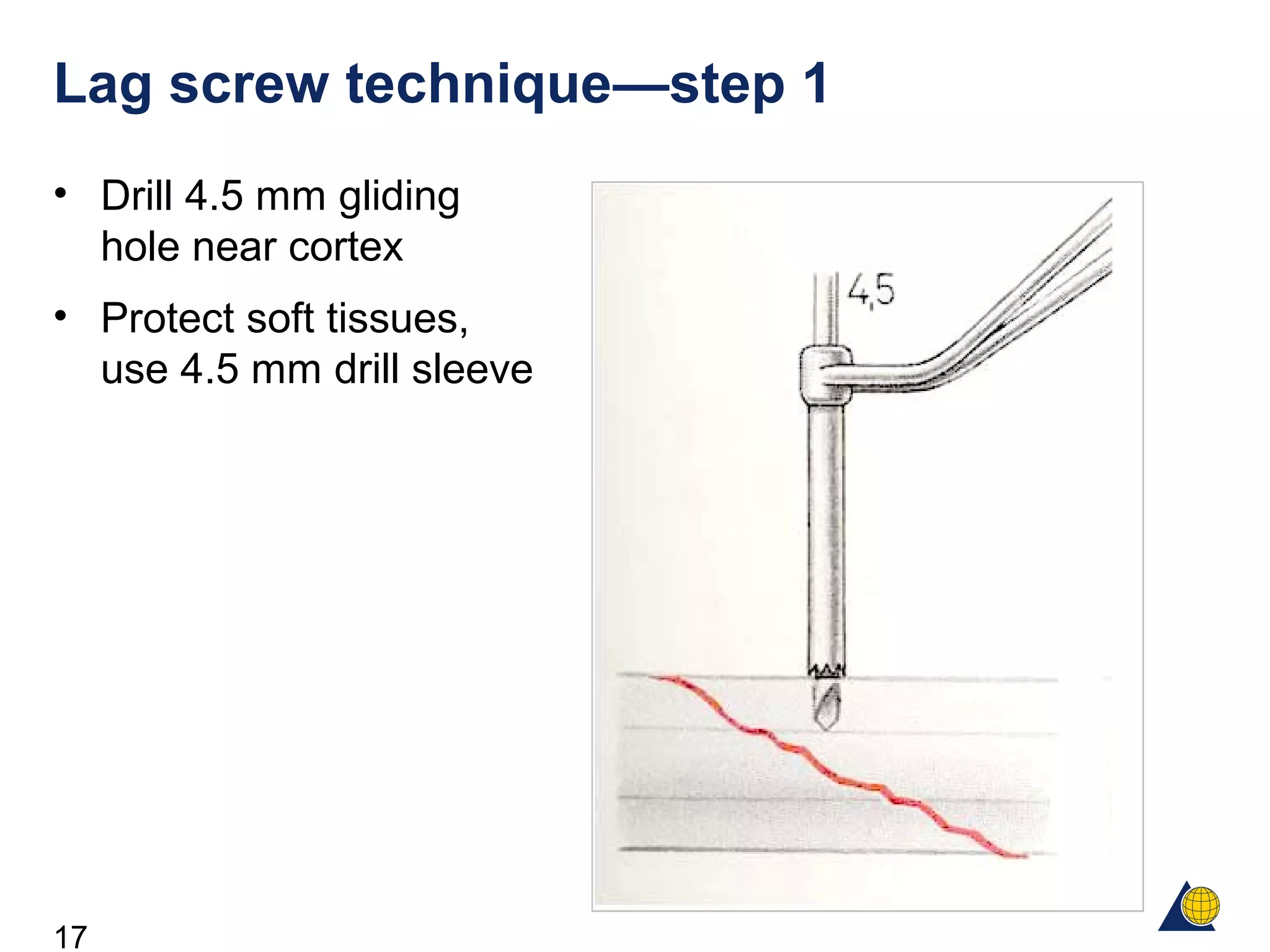
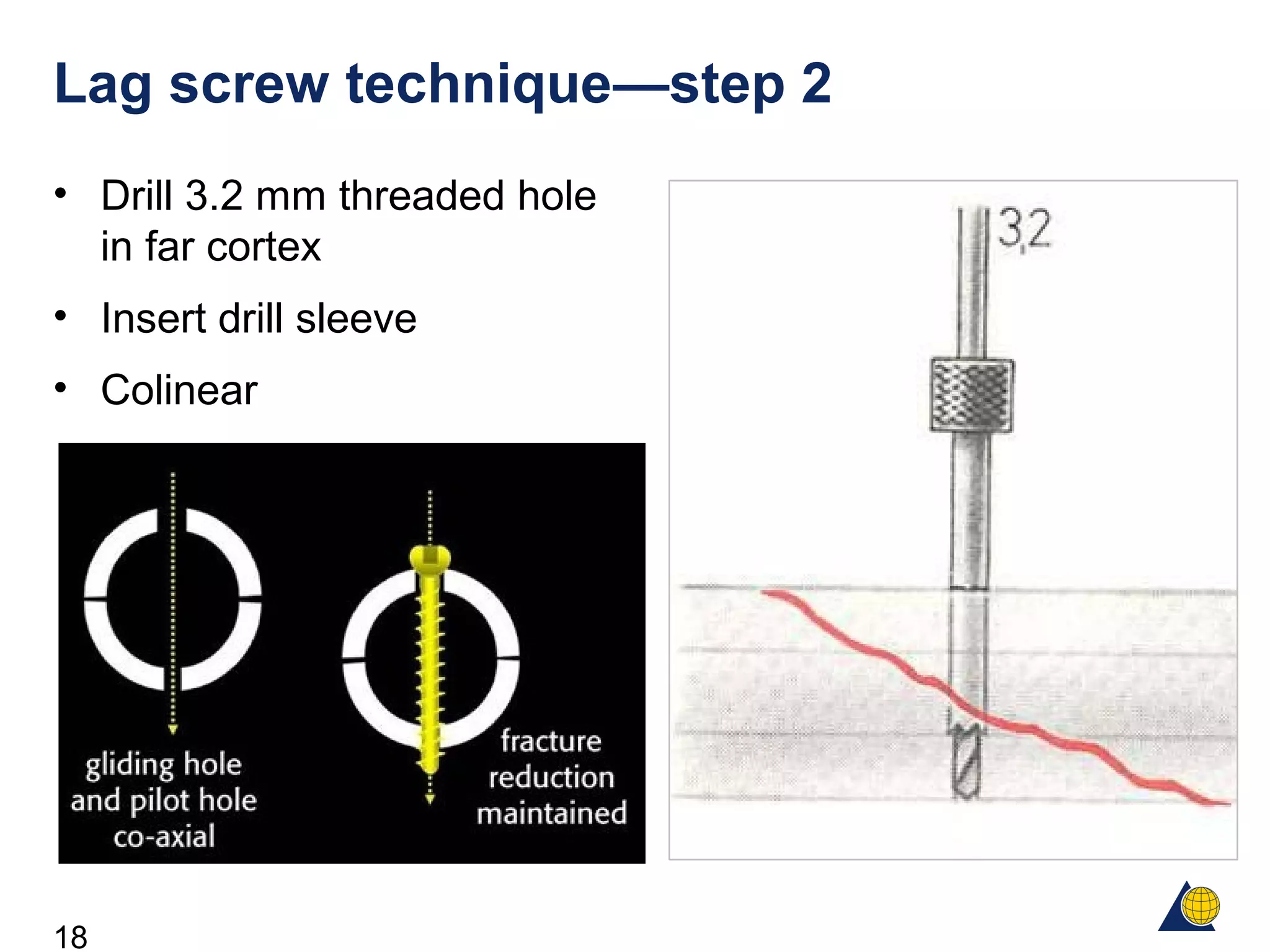
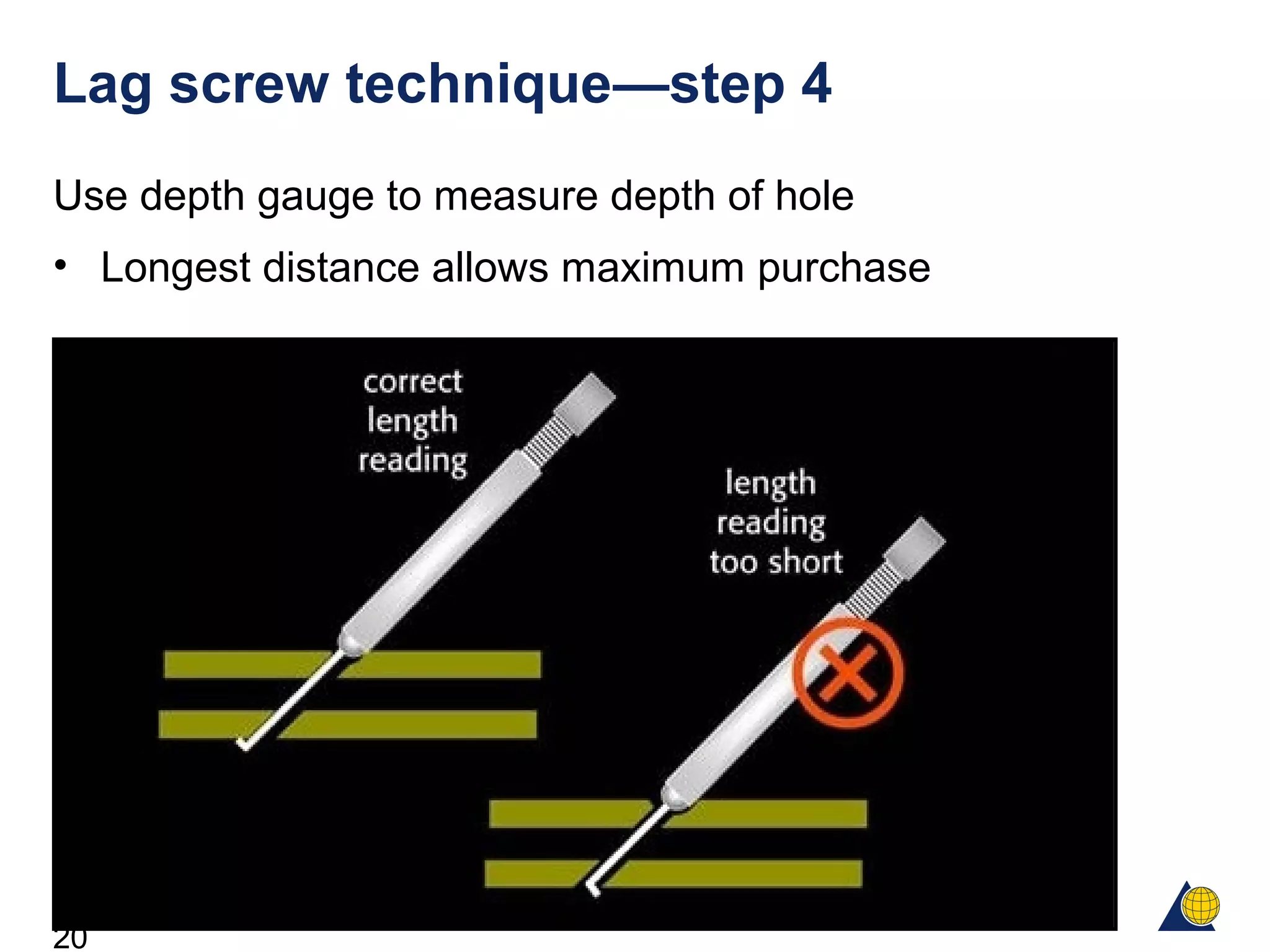
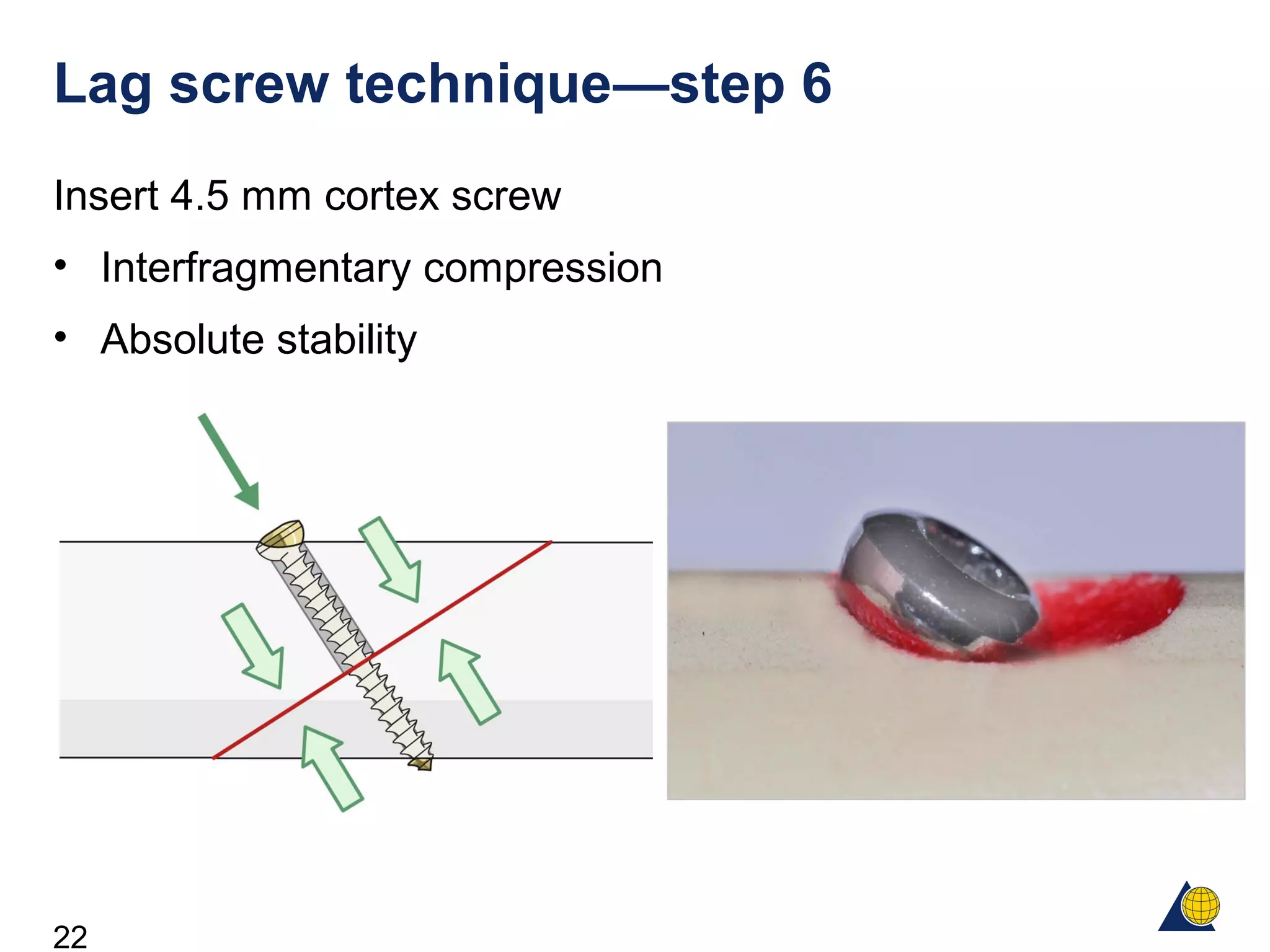
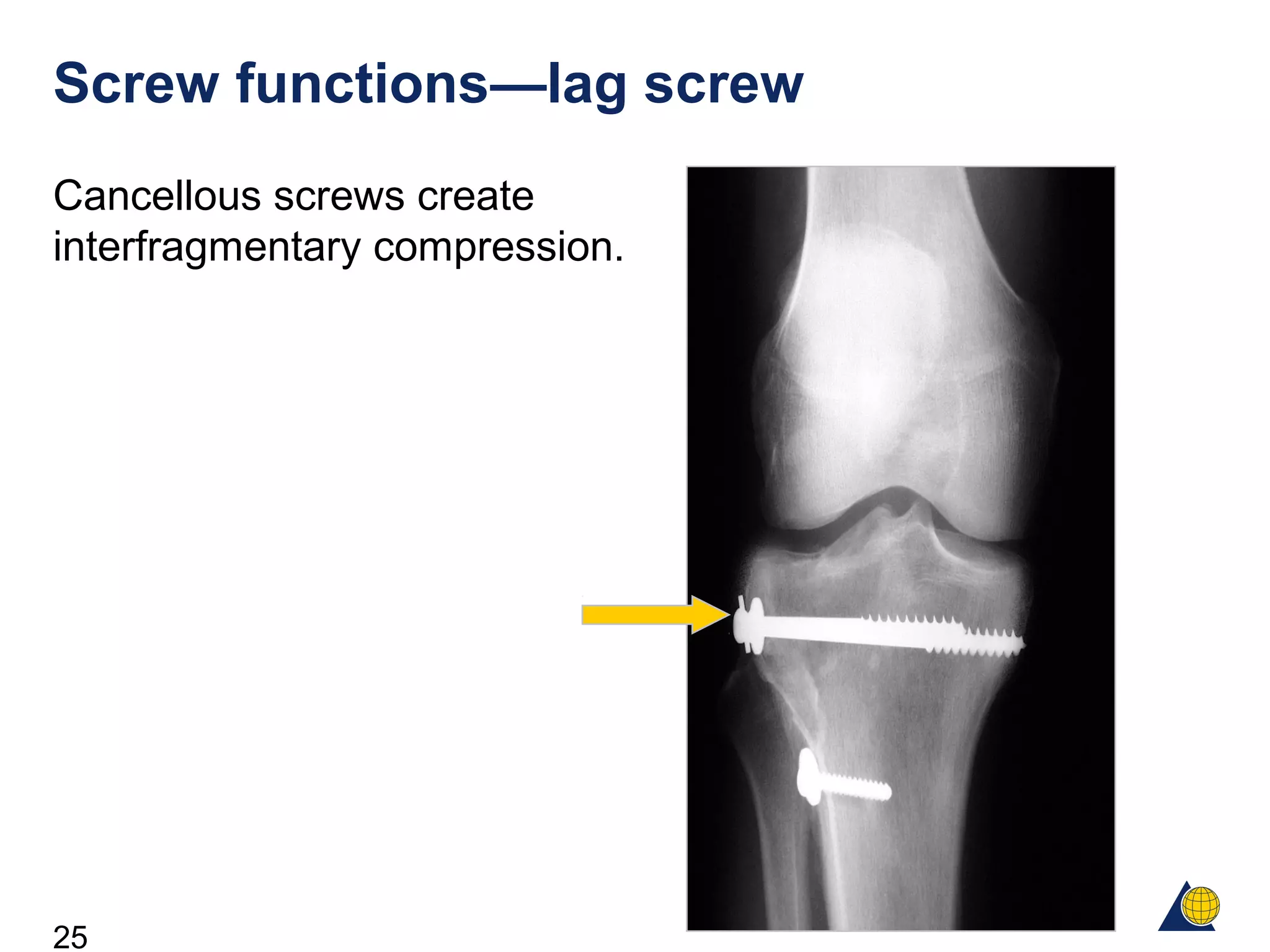
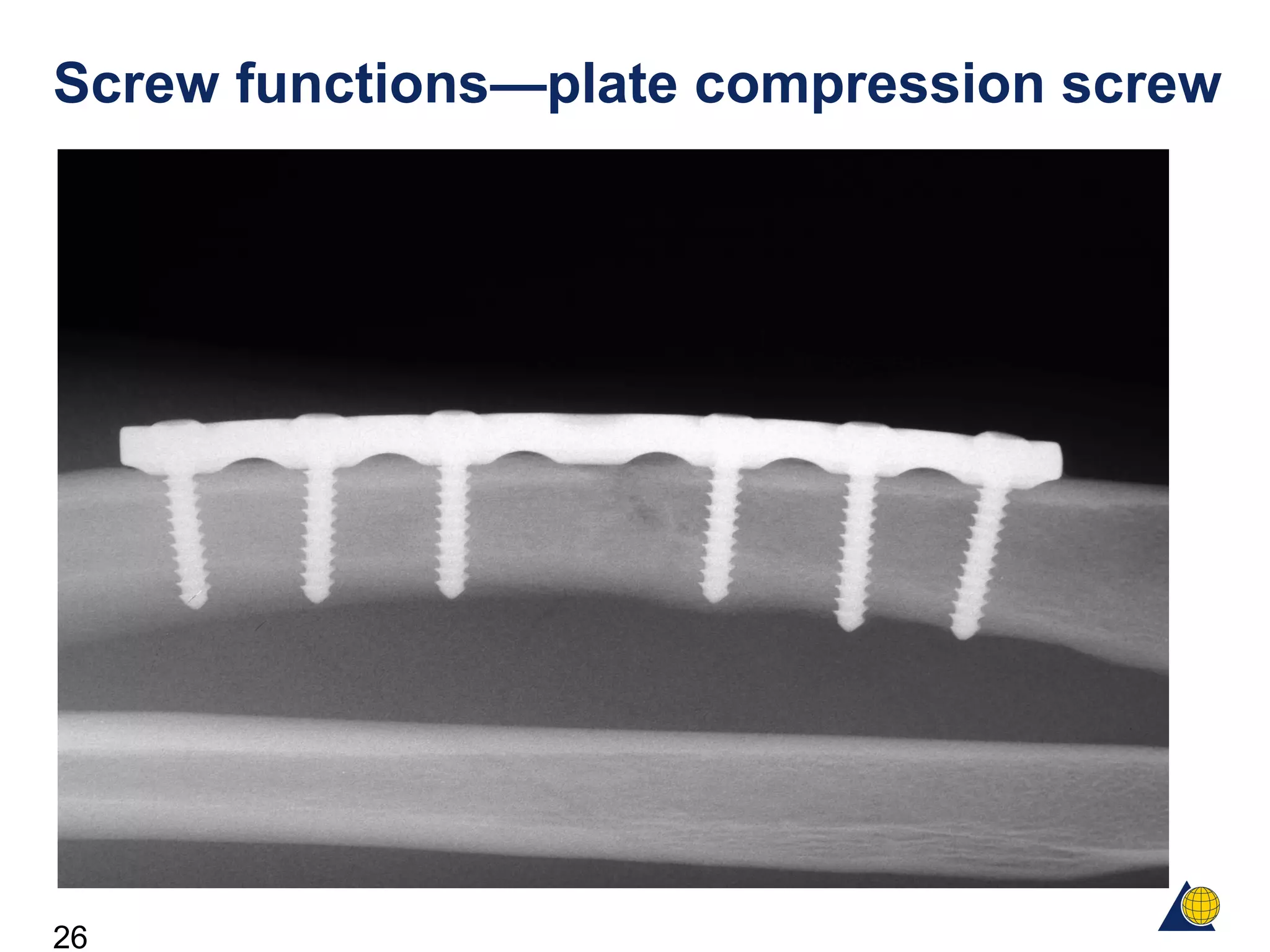
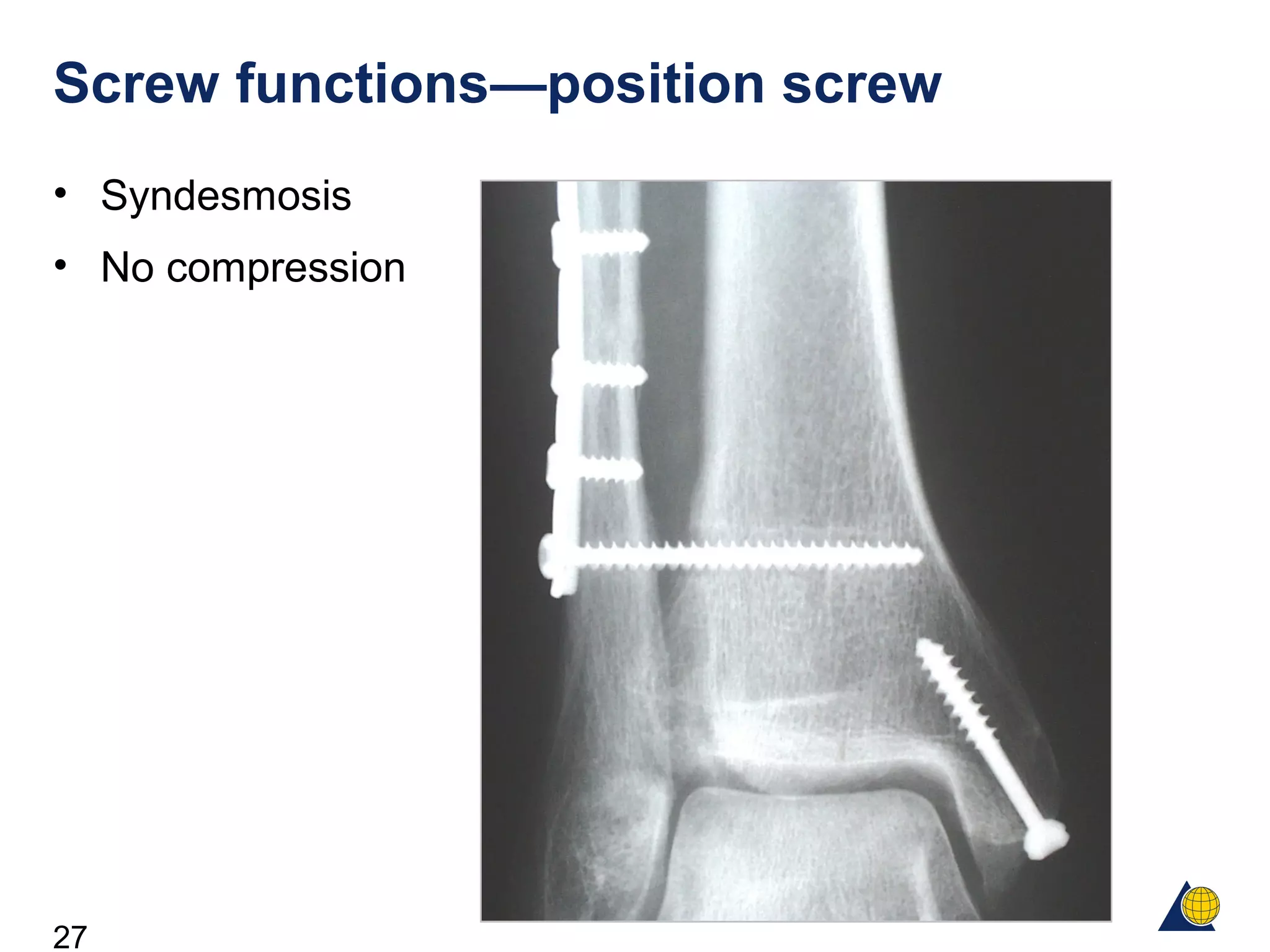
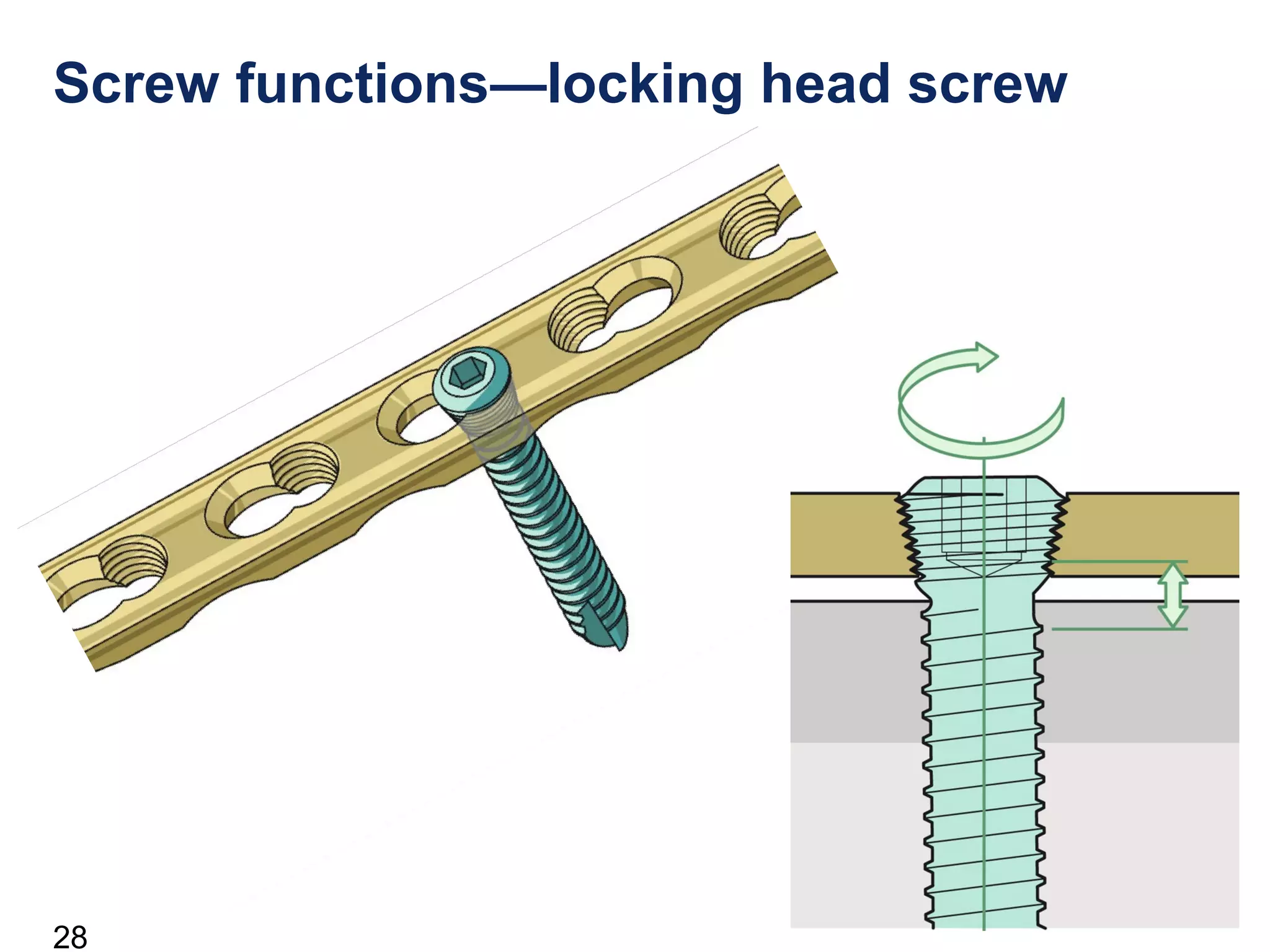
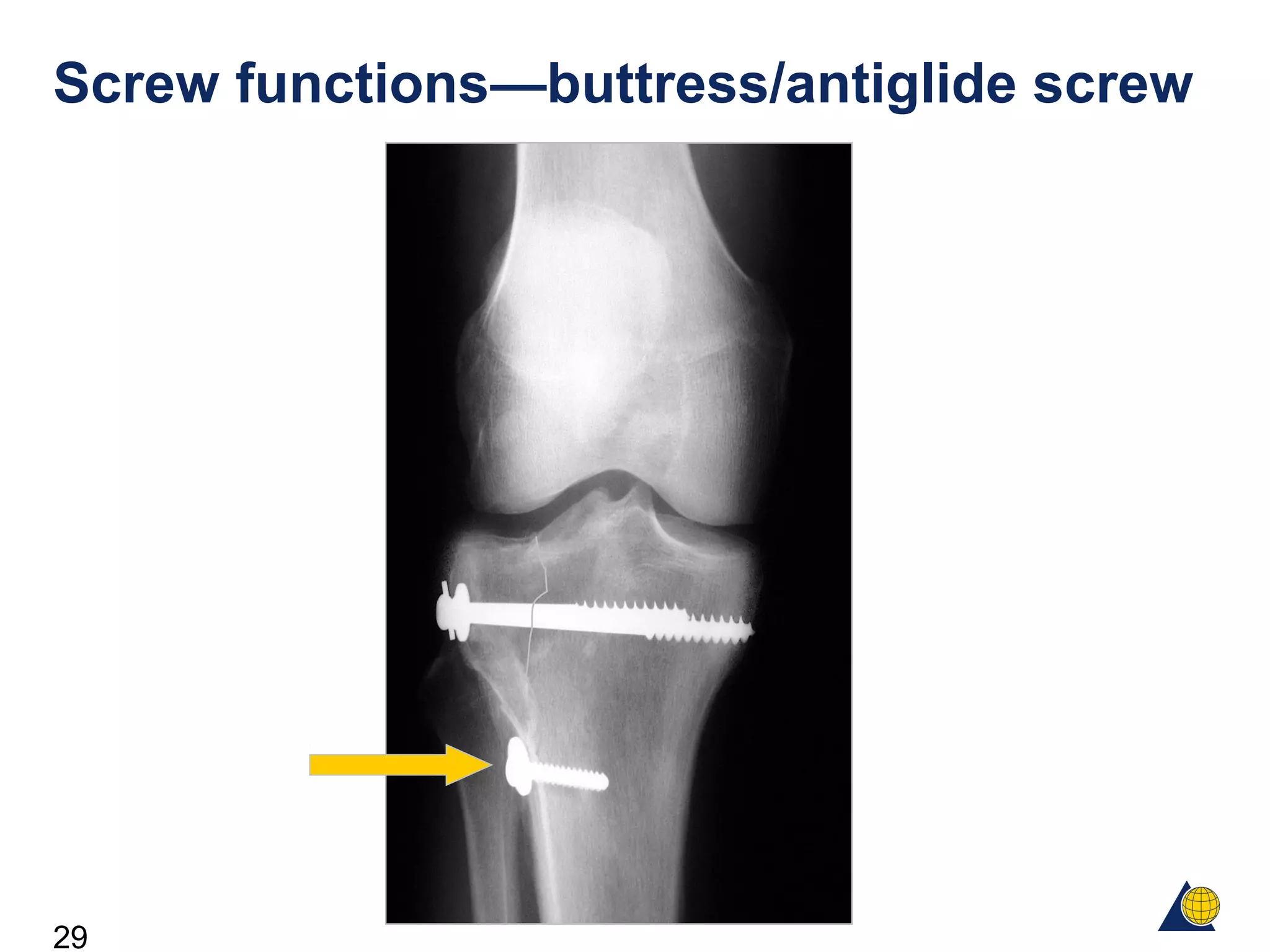
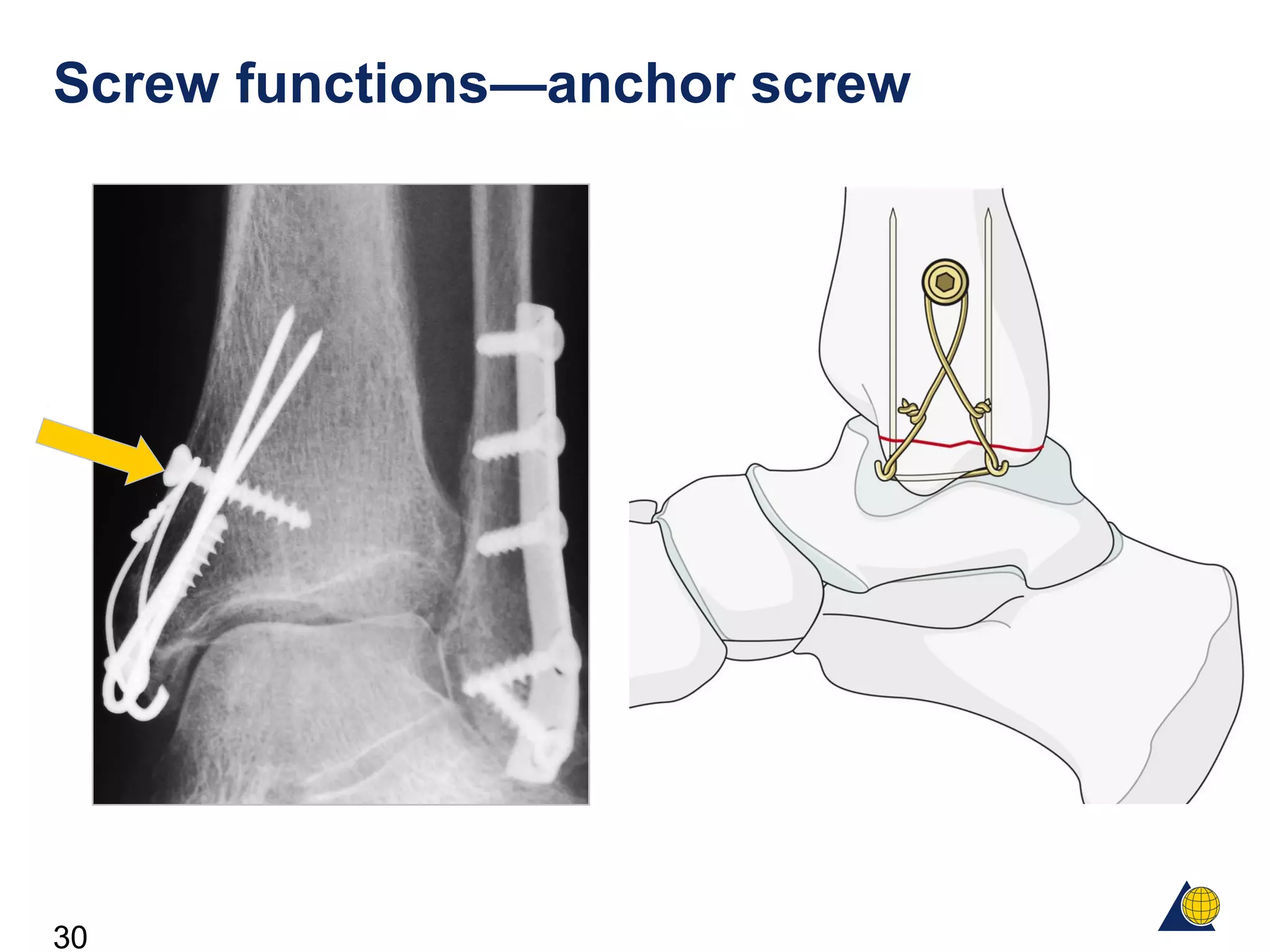
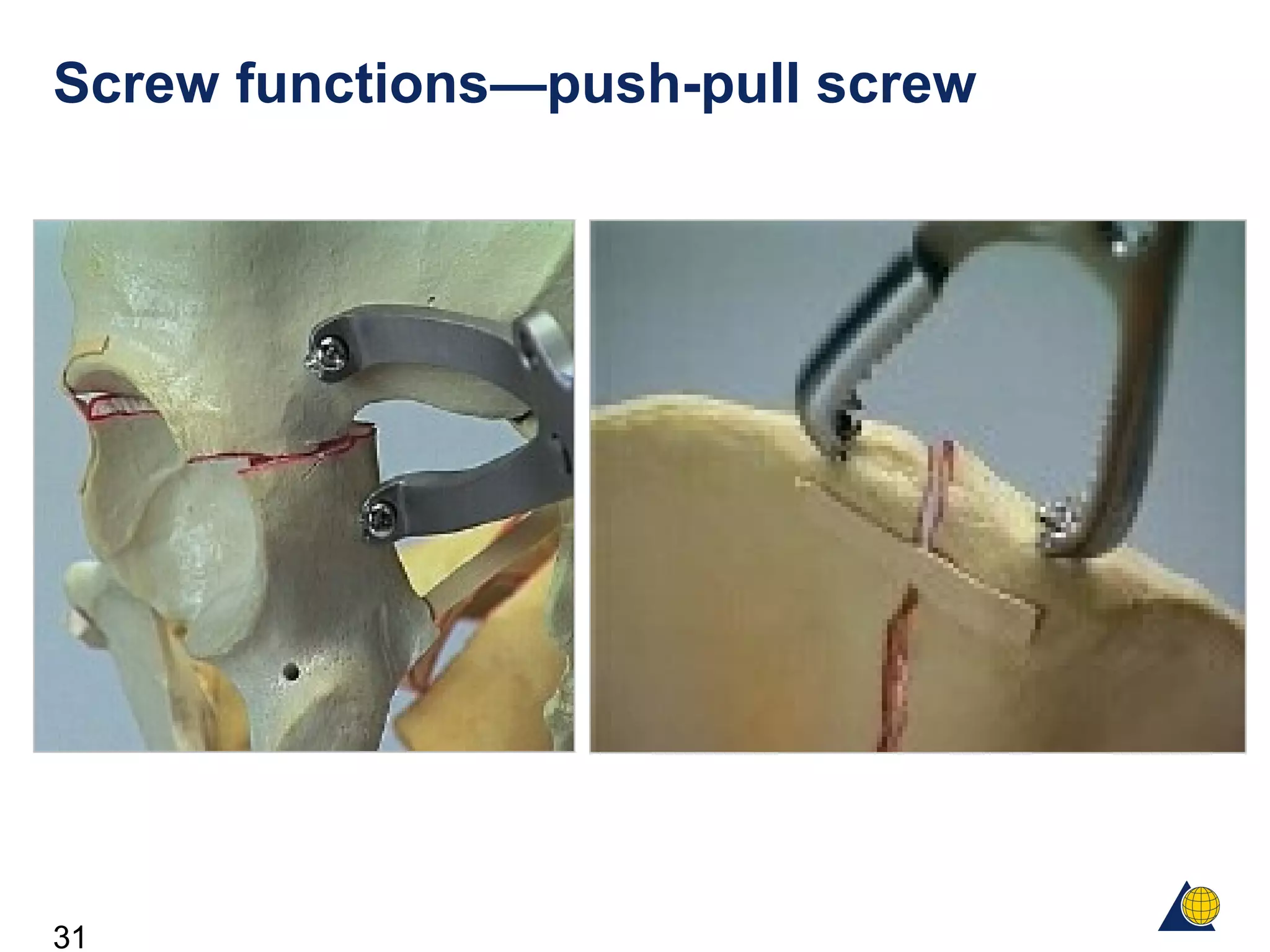
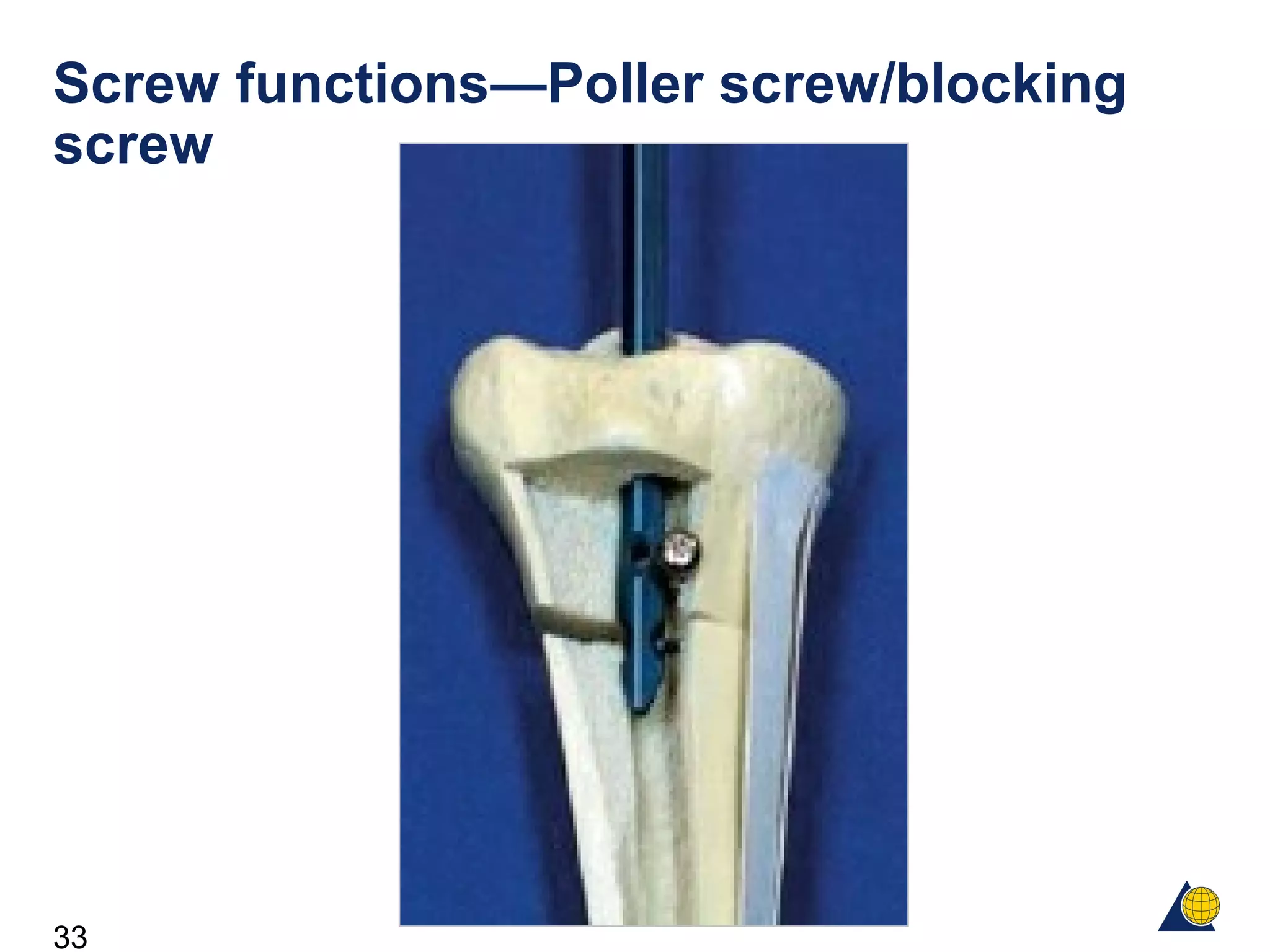
This document discusses the design and function of surgical screws. It defines what a screw is, describes the different types of screws including cortex screws and cancellous bone screws. It explains how screws work through turning rotational forces into linear motion. The key functions of screws are compression, both between a plate and bone and between two bone fragments. The lag screw technique provides interfragmentary compression and absolute stability by allowing the screw to glide through the near cortex while threading into the far cortex. Countersinking creates a seat for the screw head to maximize contact and minimize stress. Different screw functions include lag screws, compression screws, position screws, and more.