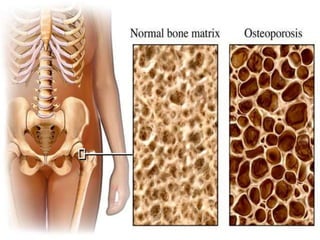
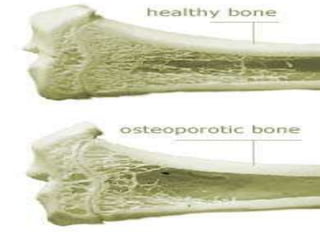
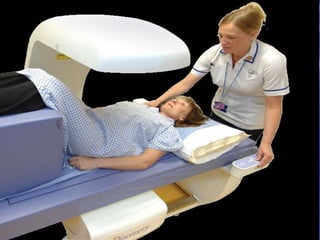
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and increased risk of fractures. It results from an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation, with a decrease in bone mass over time. Osteoporosis has two main types - type 1 occurs mainly in post-menopausal women due to estrogen loss, while type 2 is age-related and affects both men and women after age 70. Diagnosis involves bone mineral density tests and other exams to evaluate bone health and fracture risk. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to prevent further bone loss and increase bone strength.