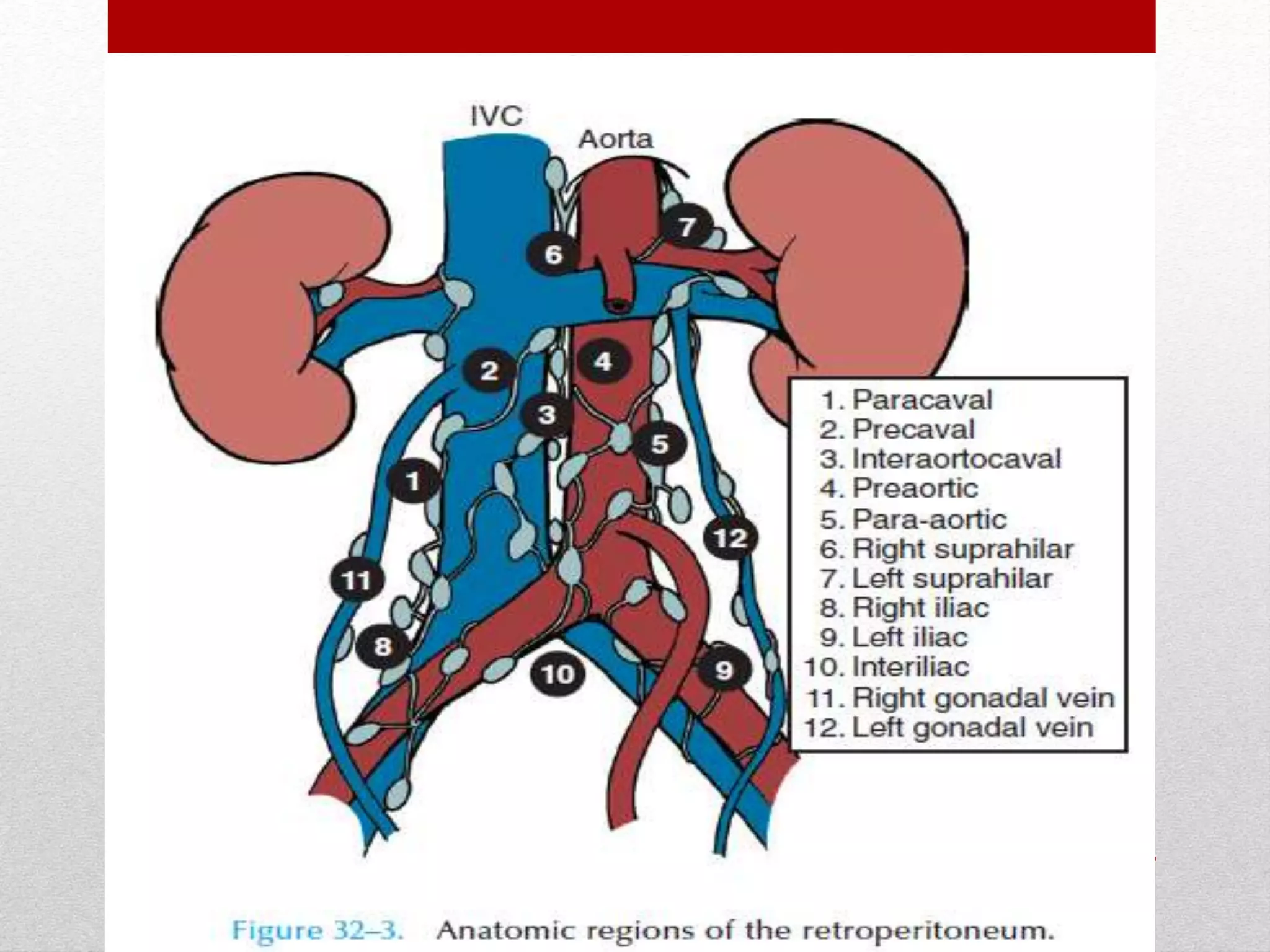
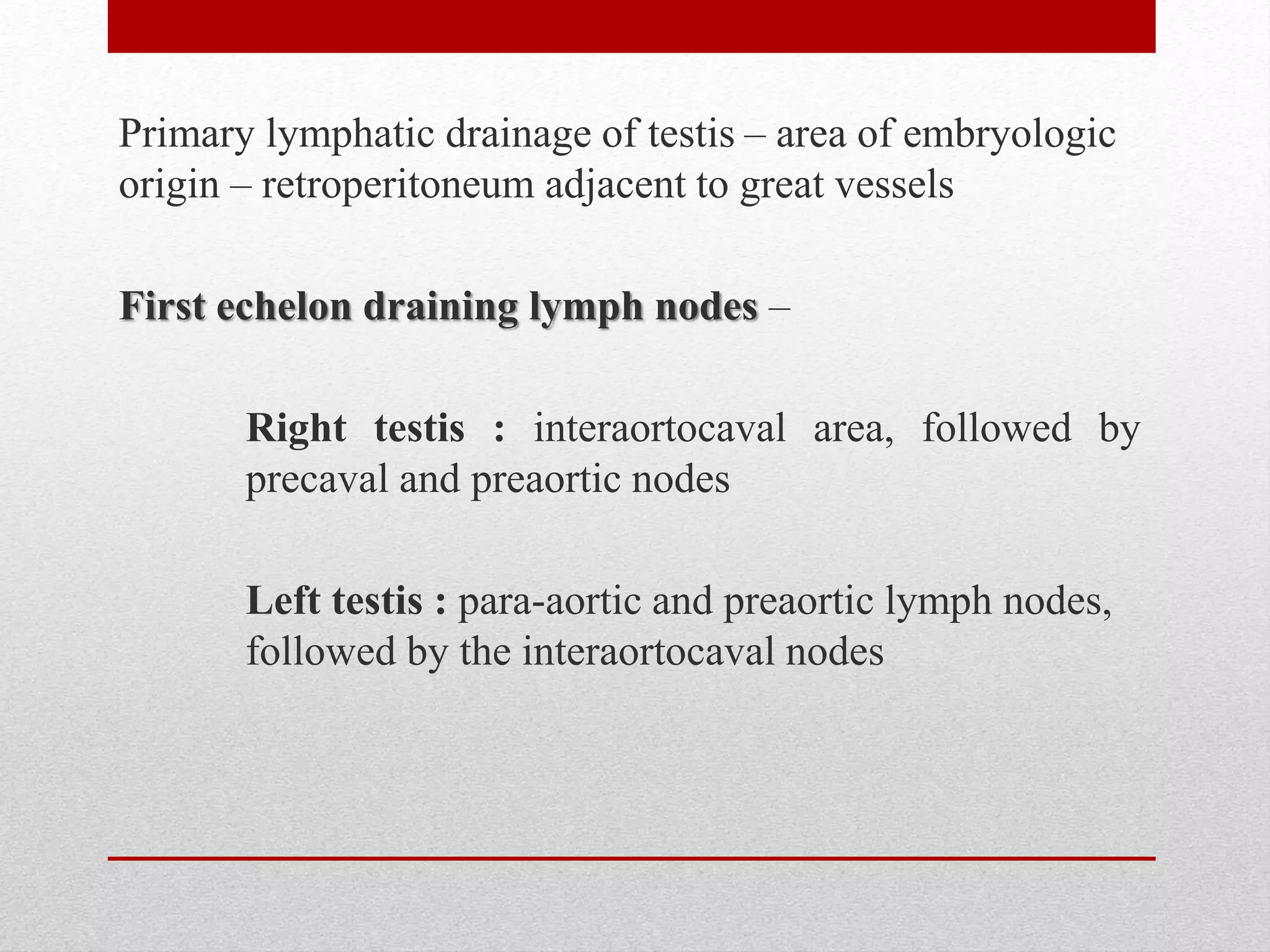
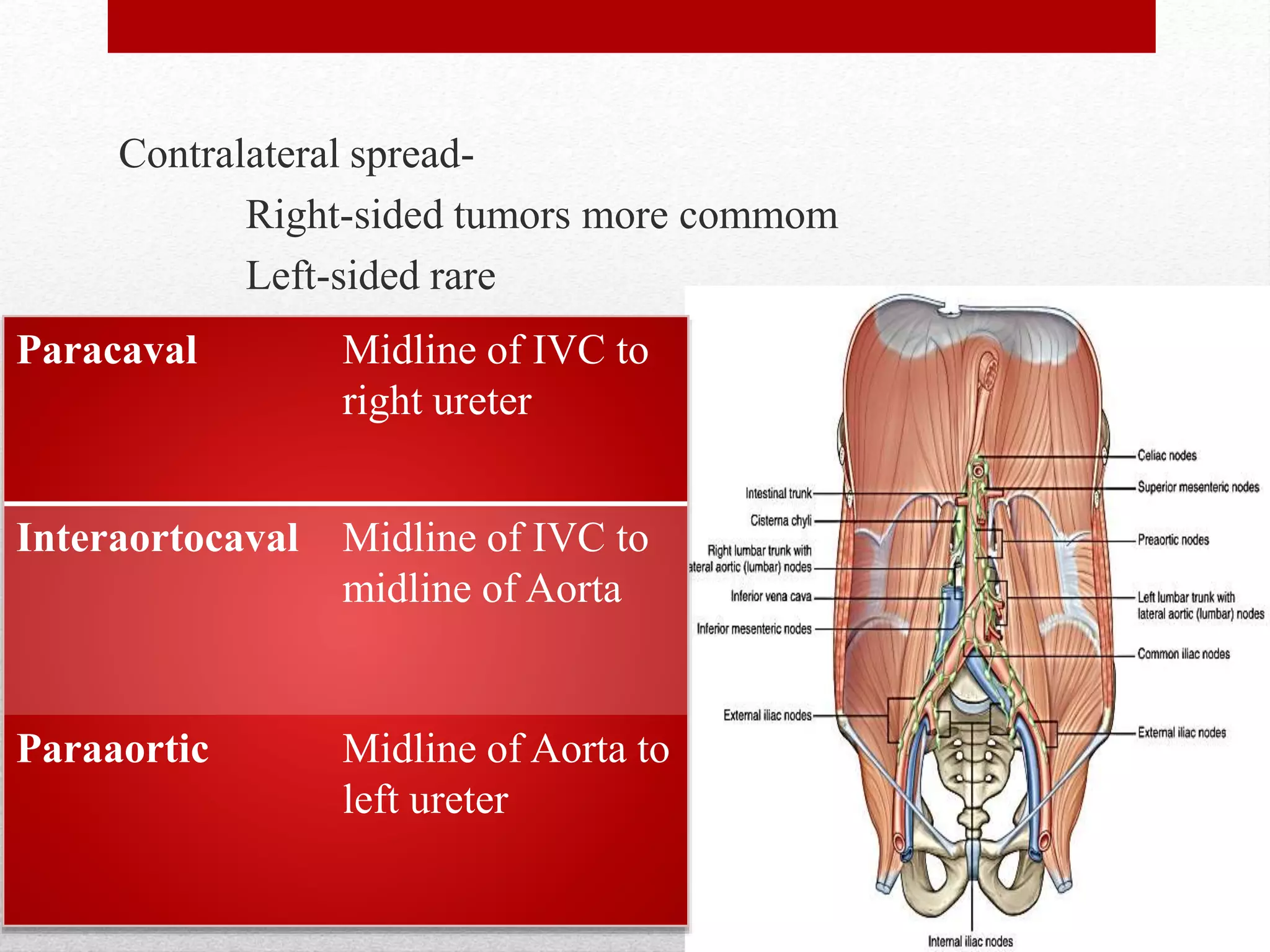
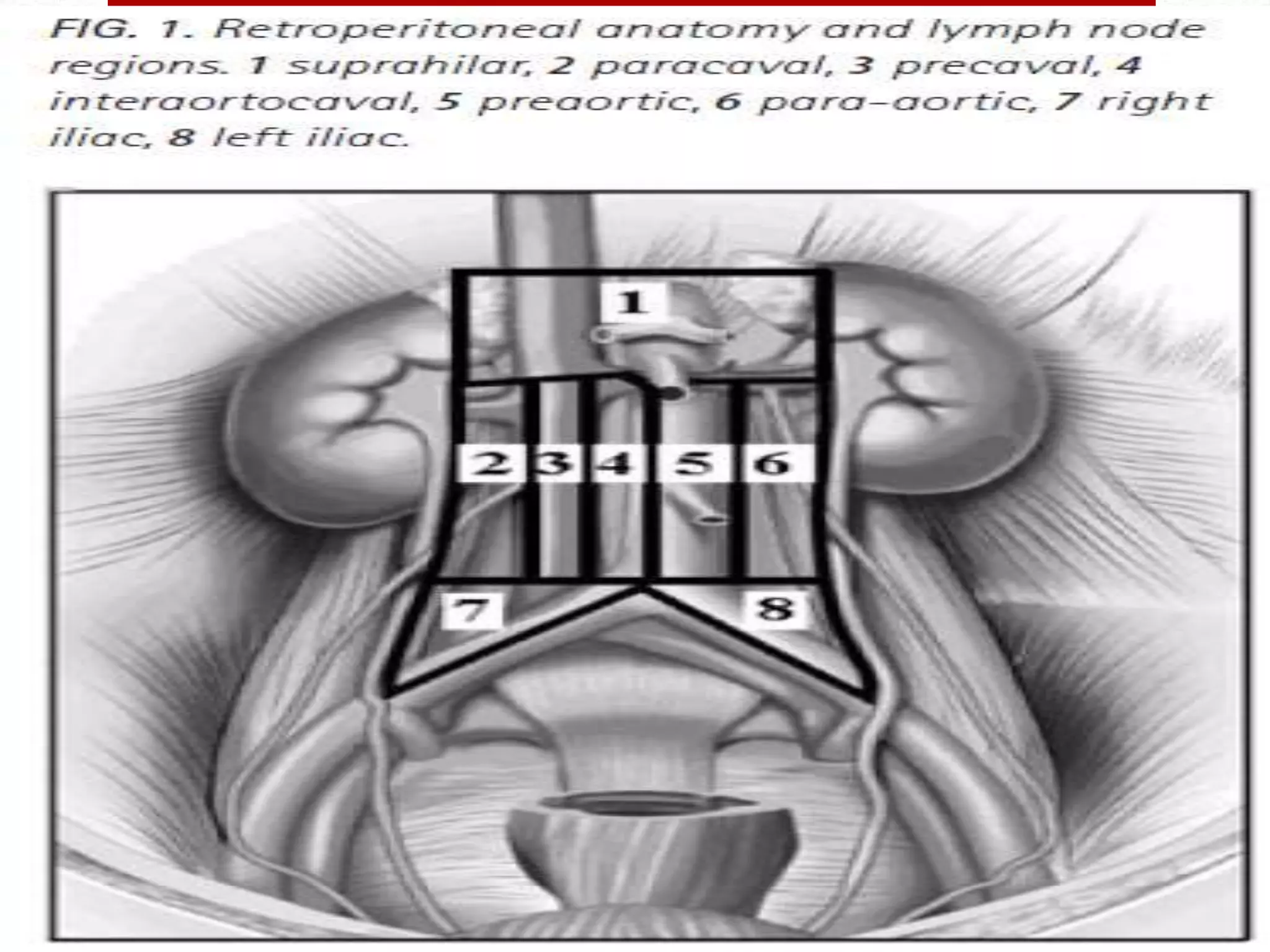
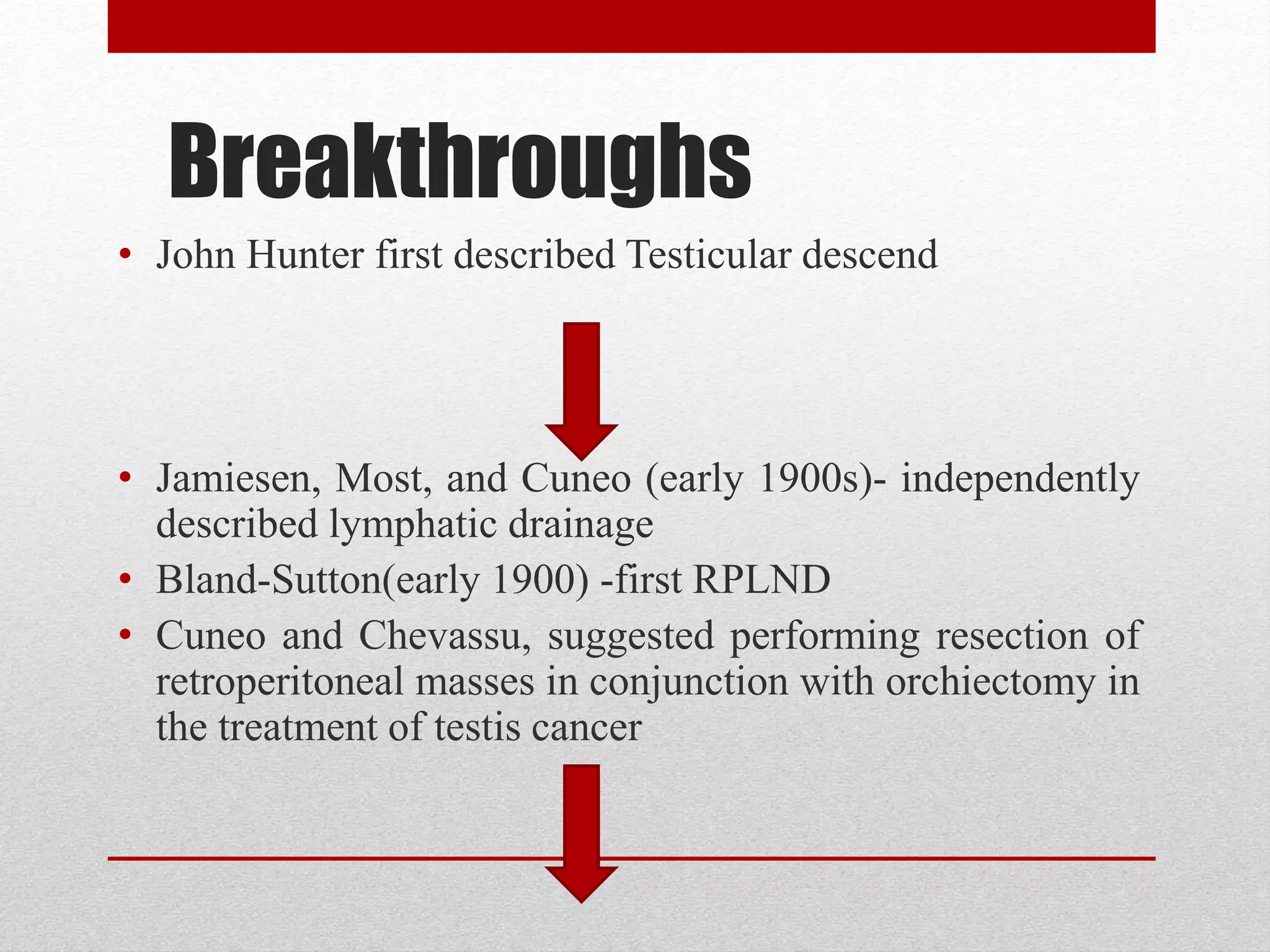
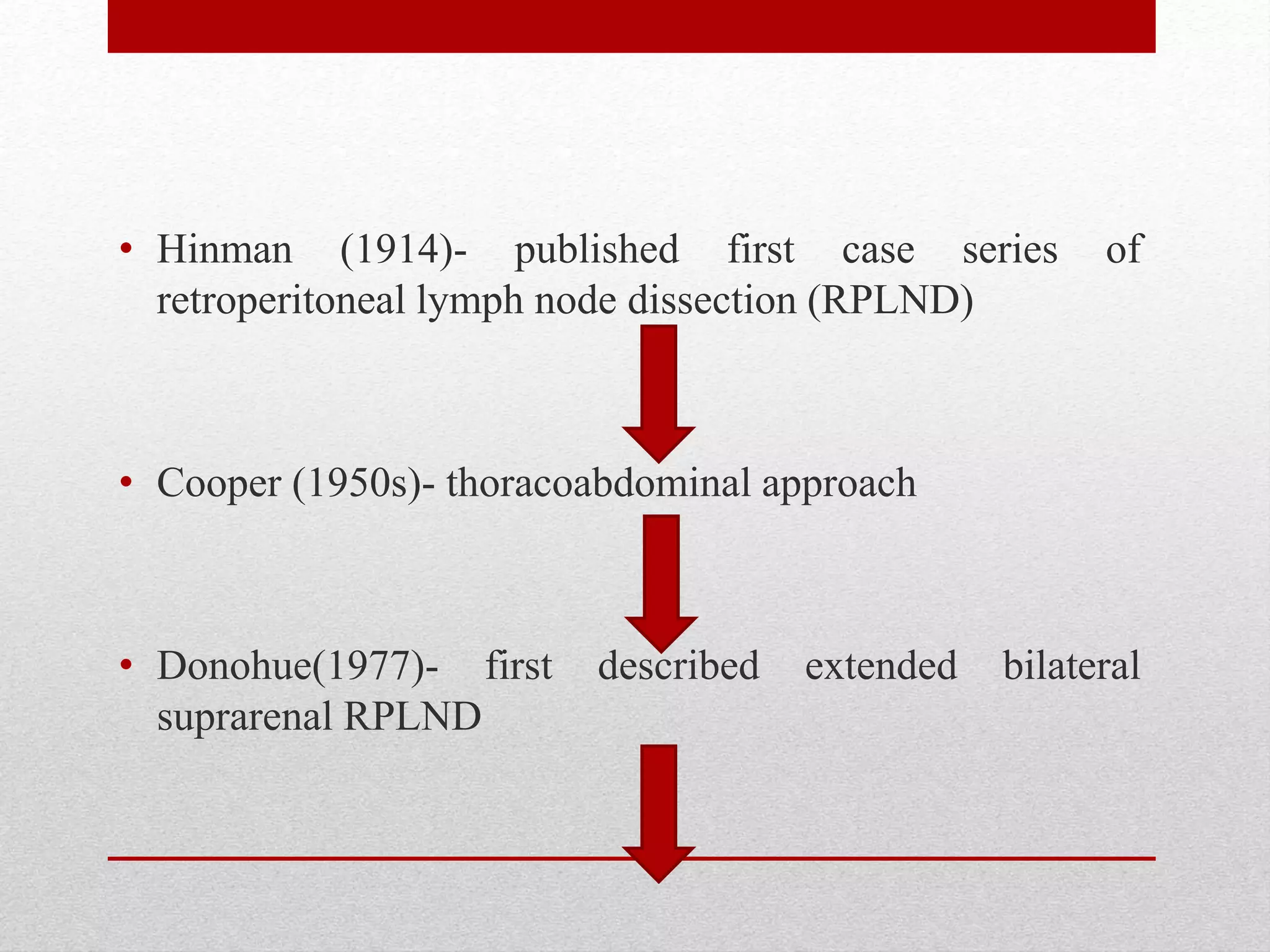
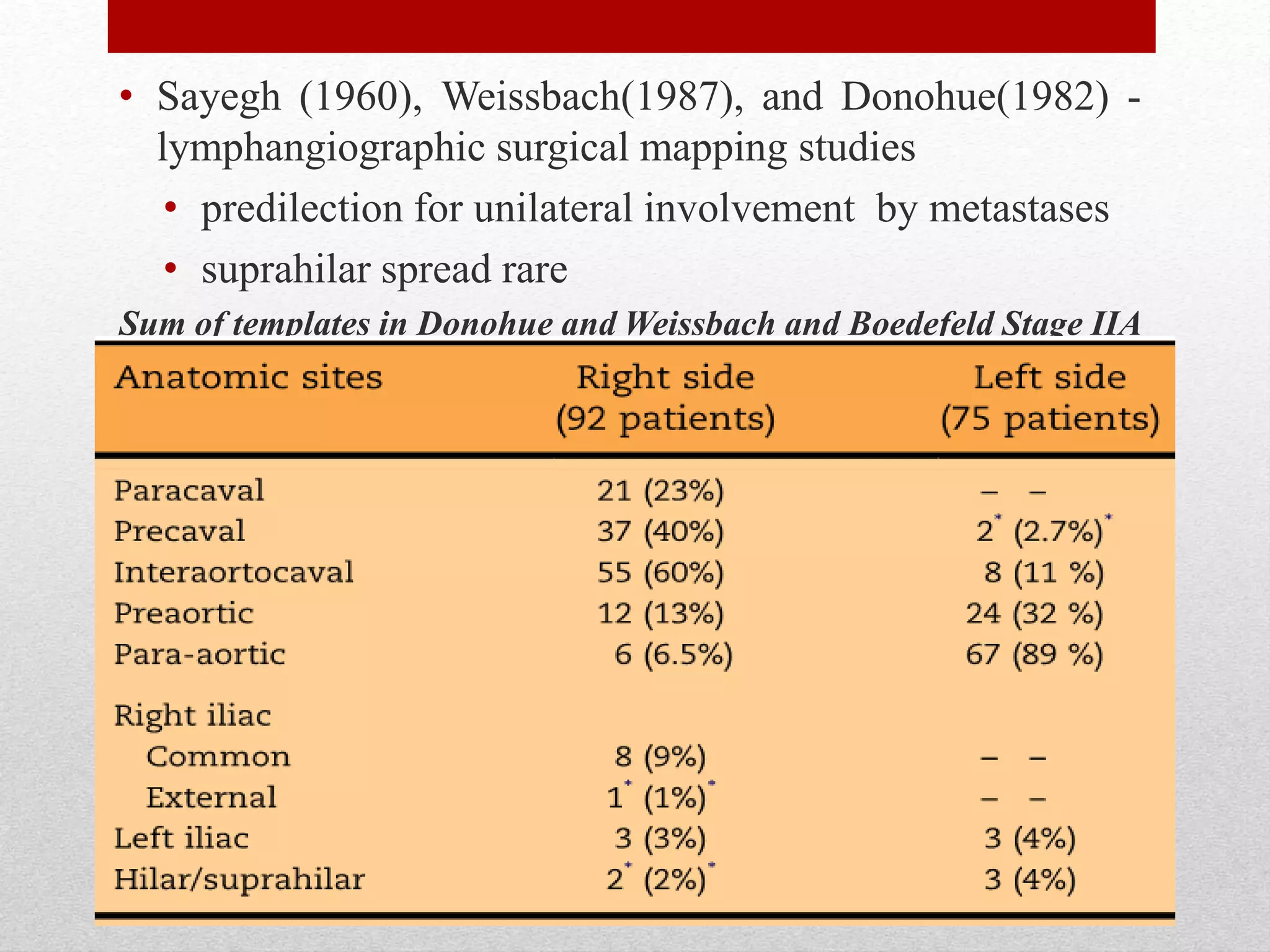
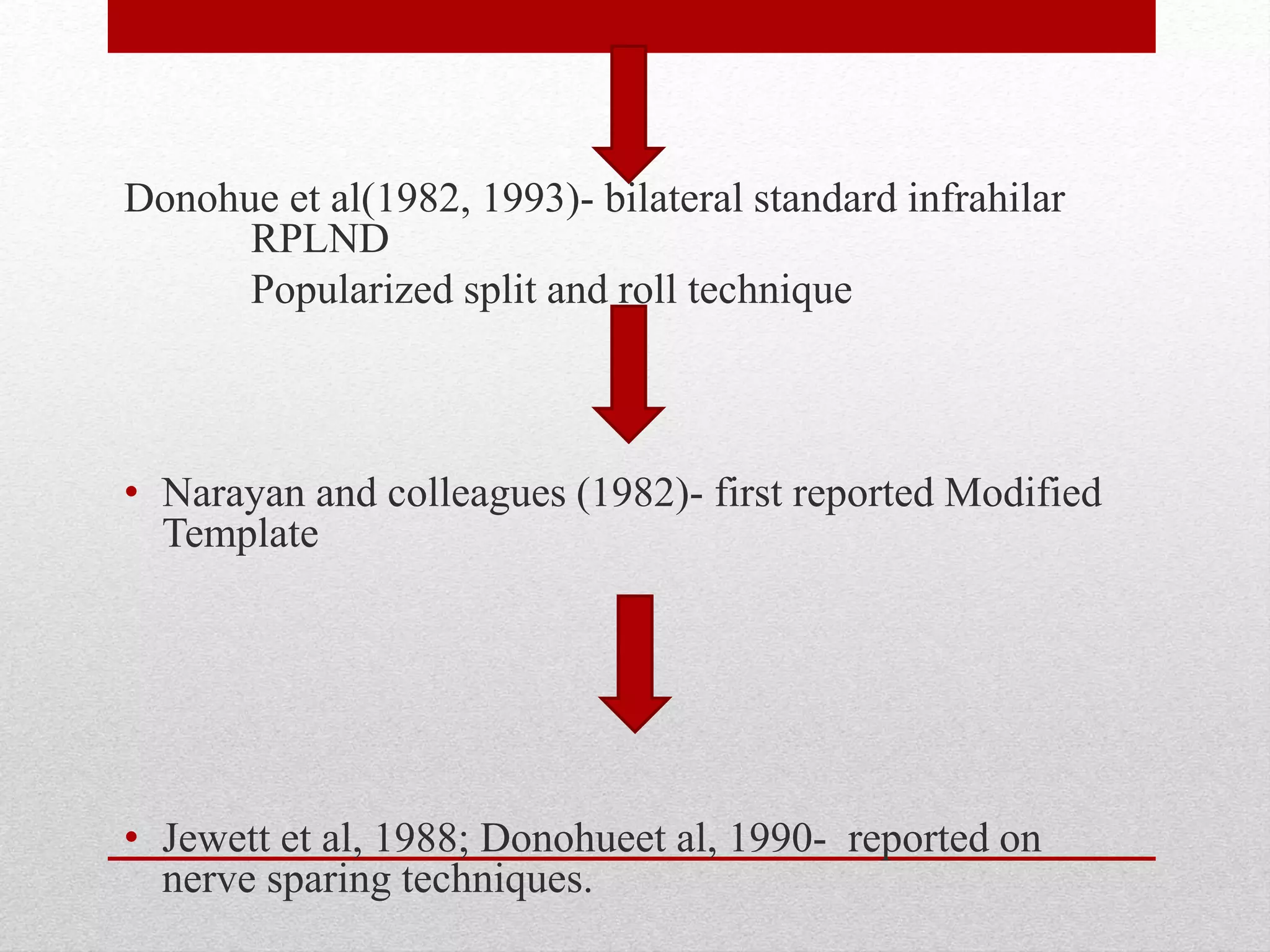
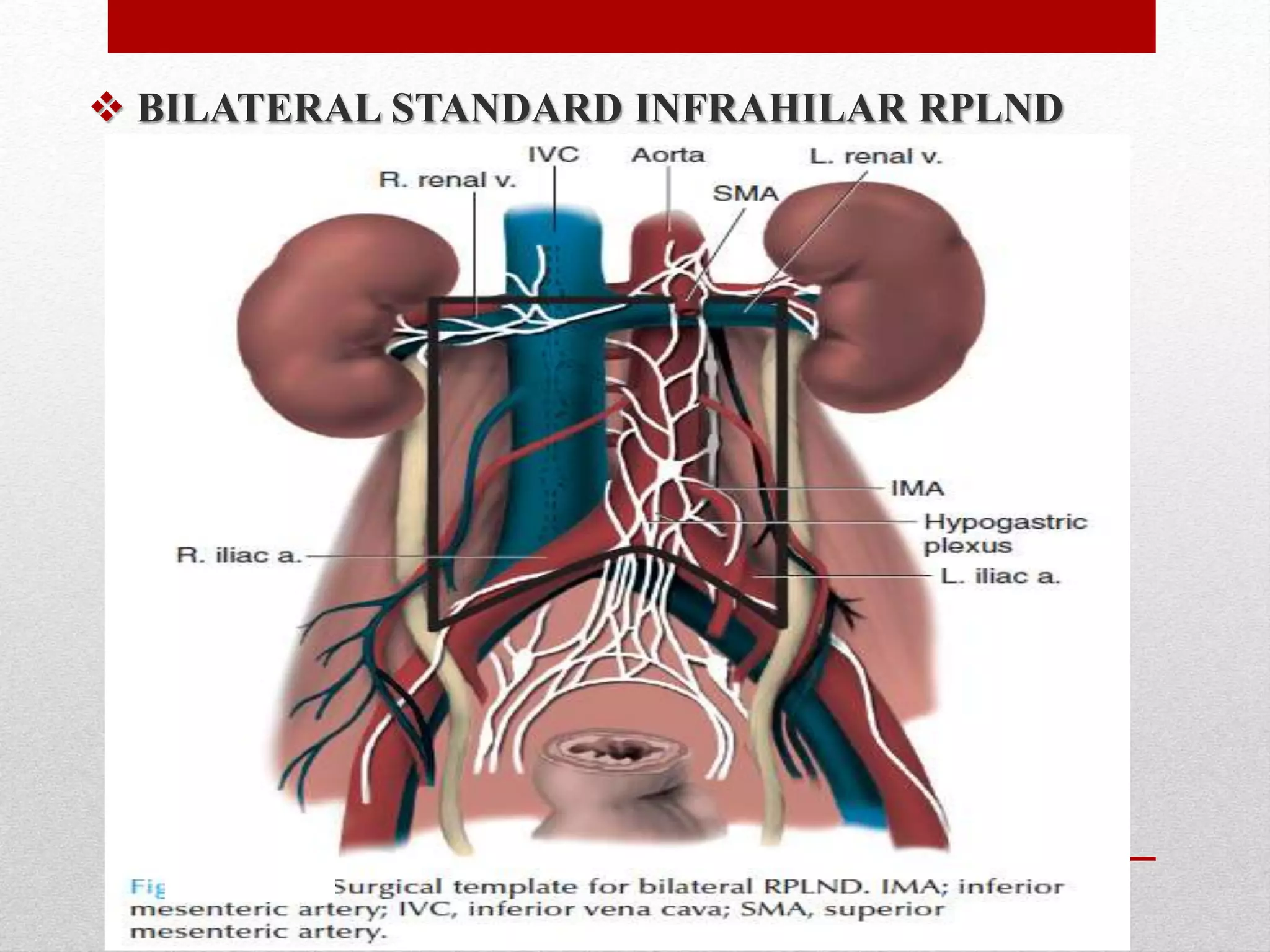
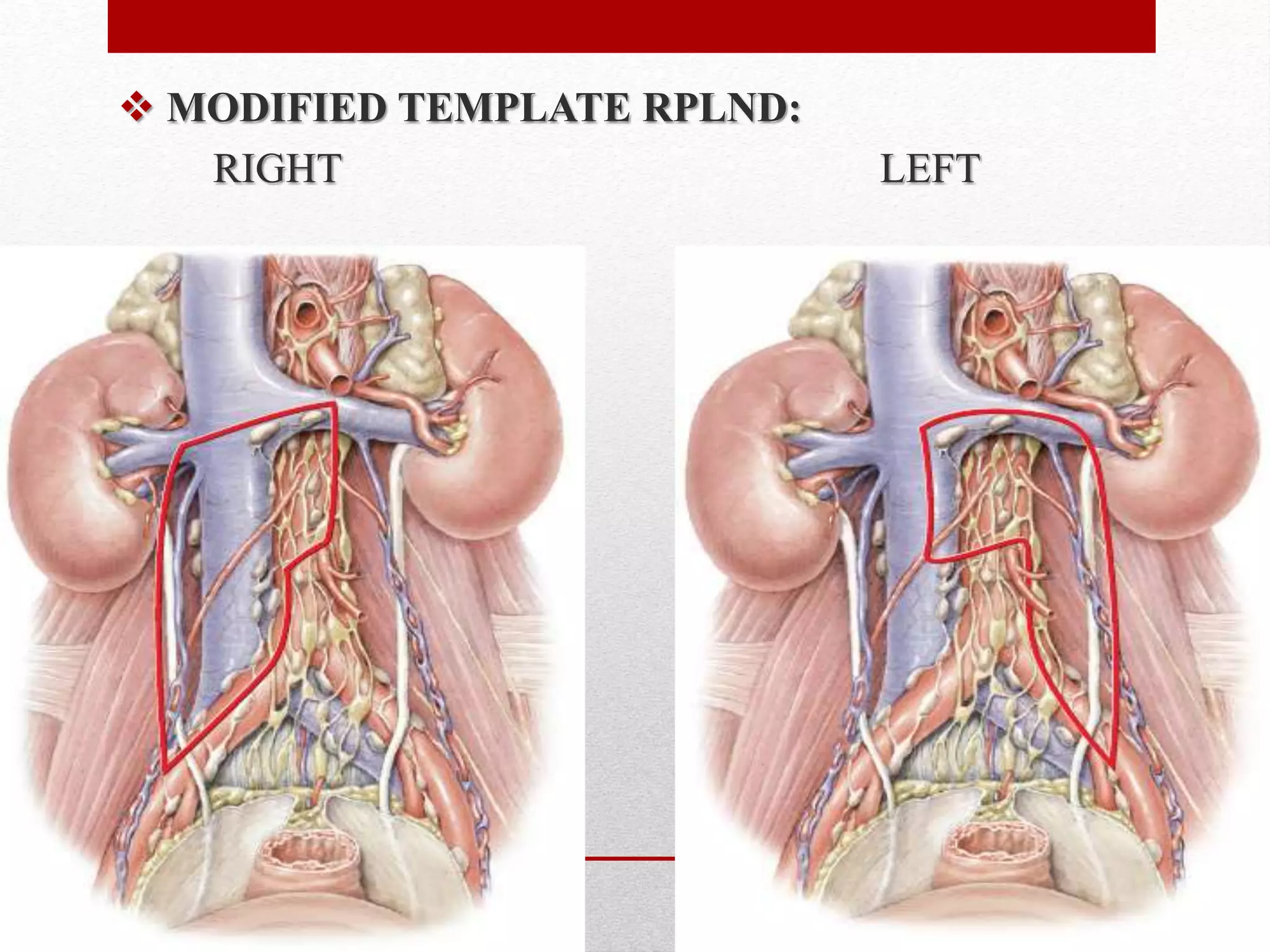
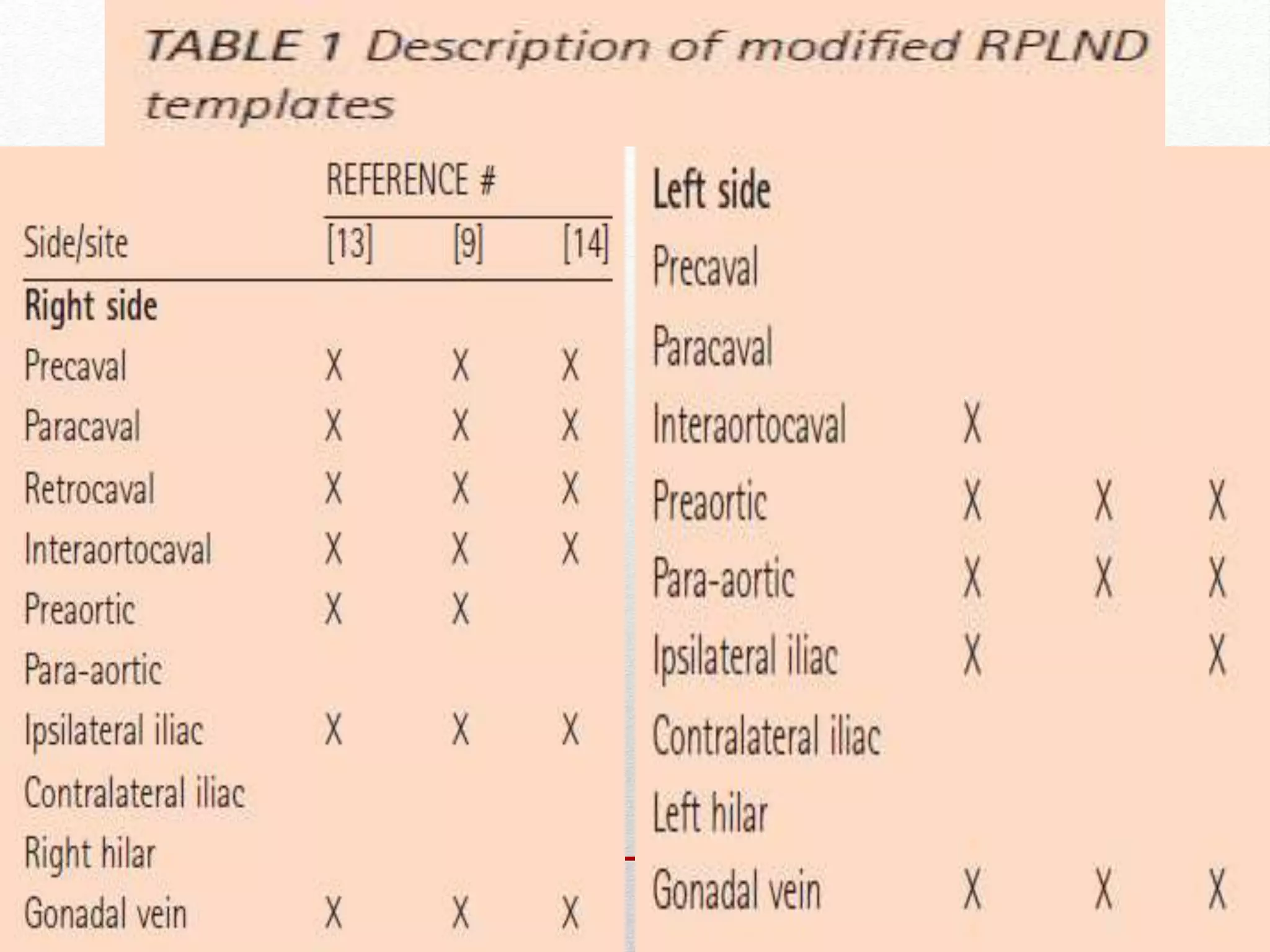
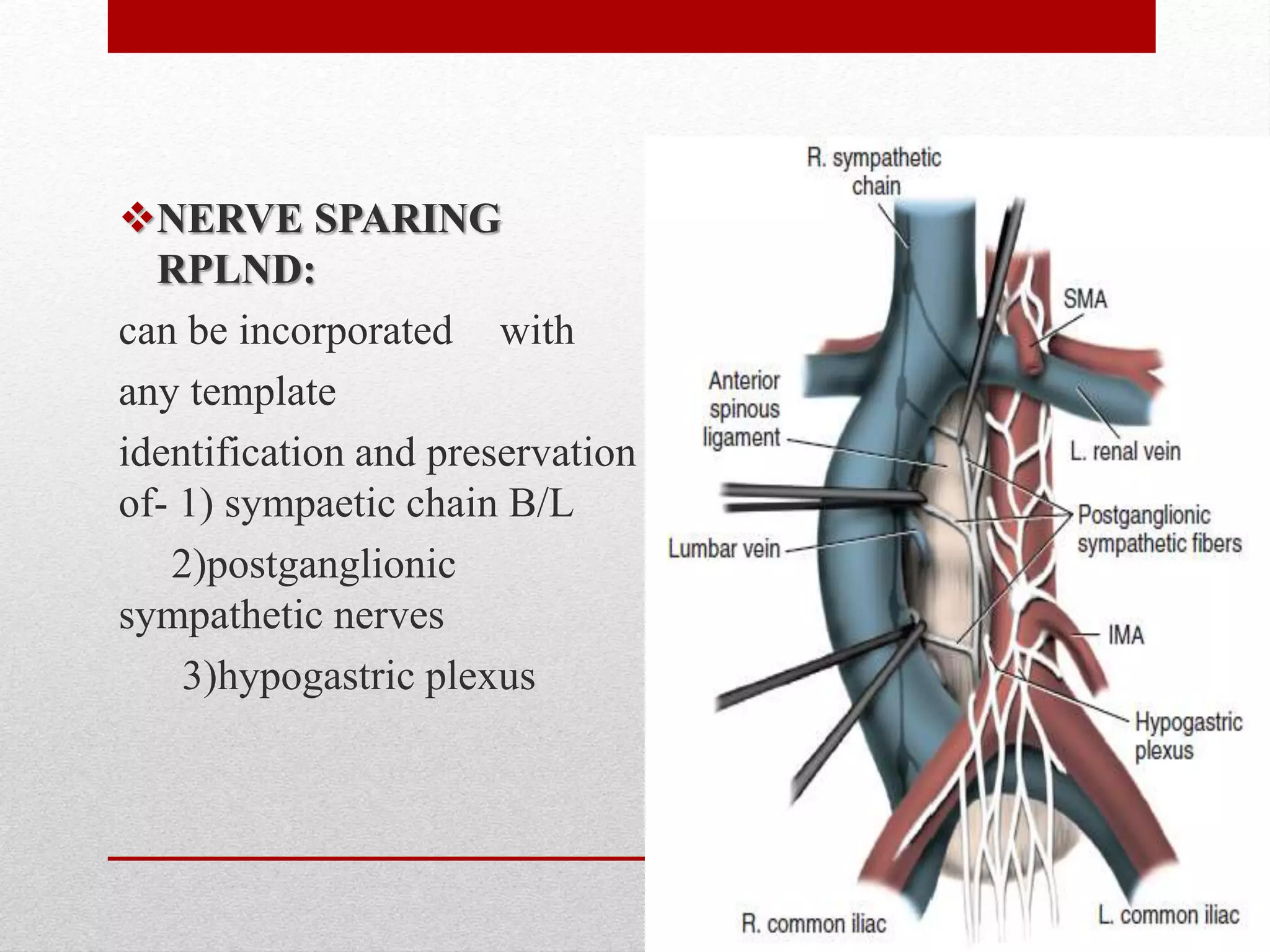
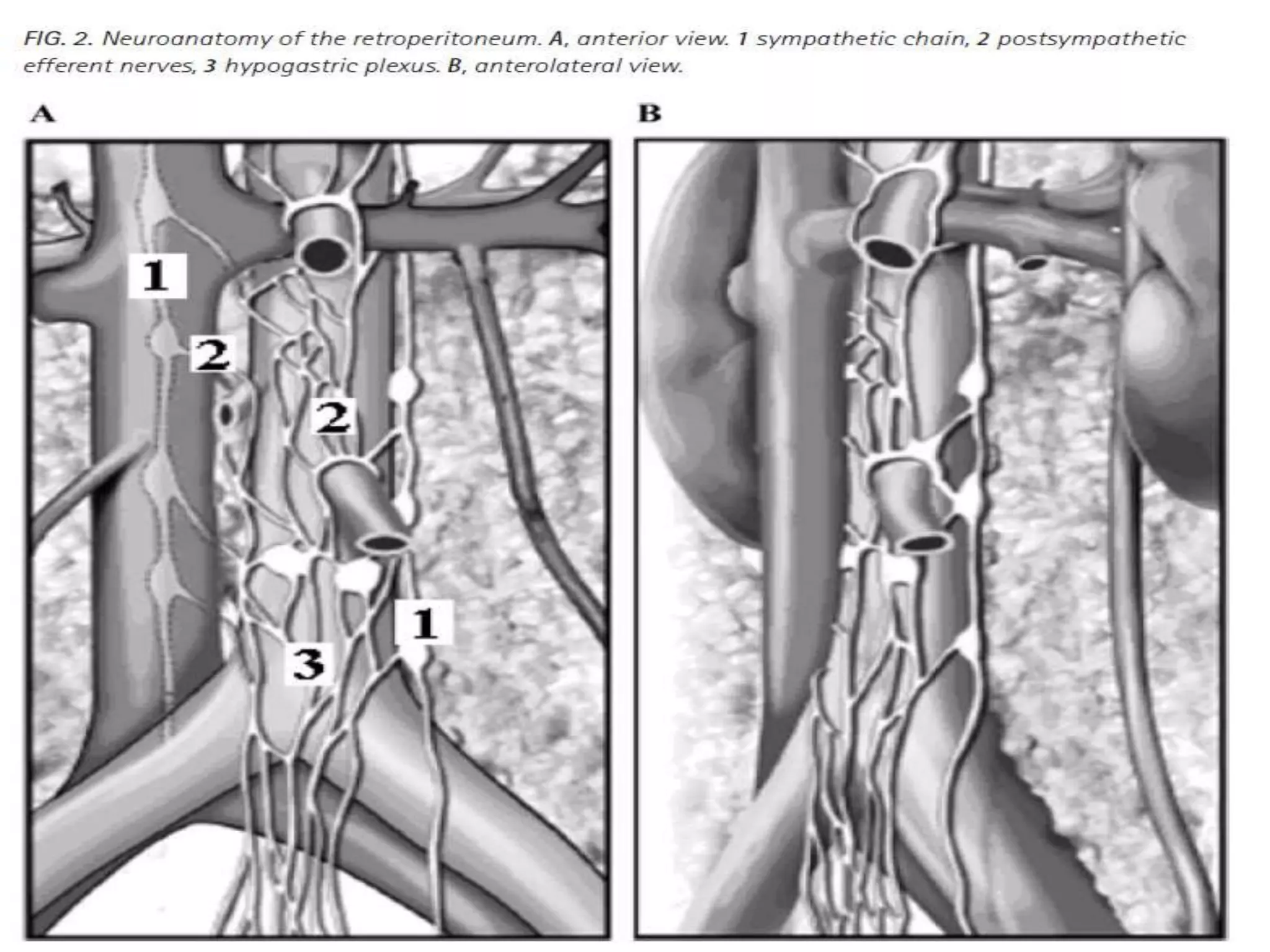
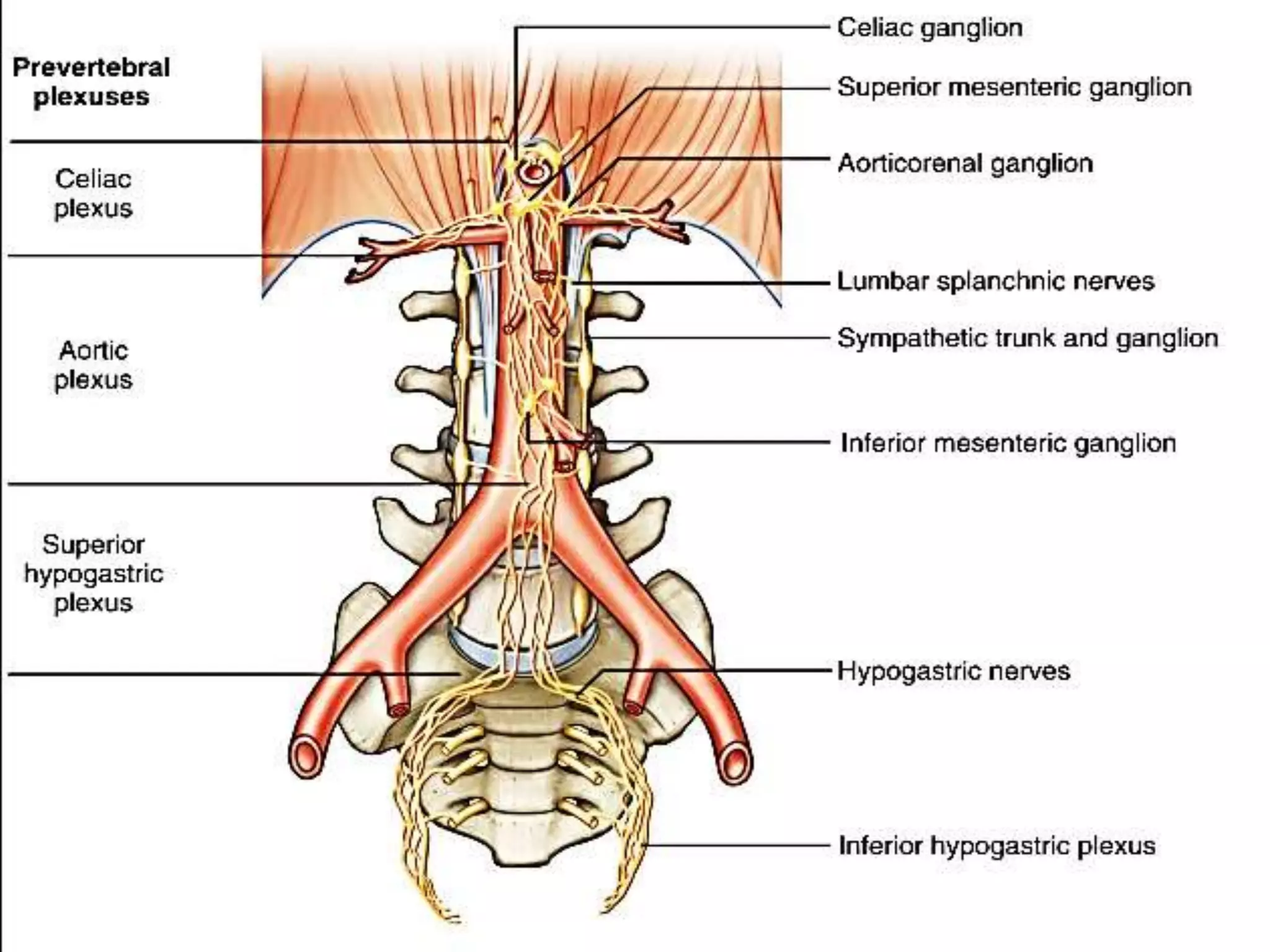
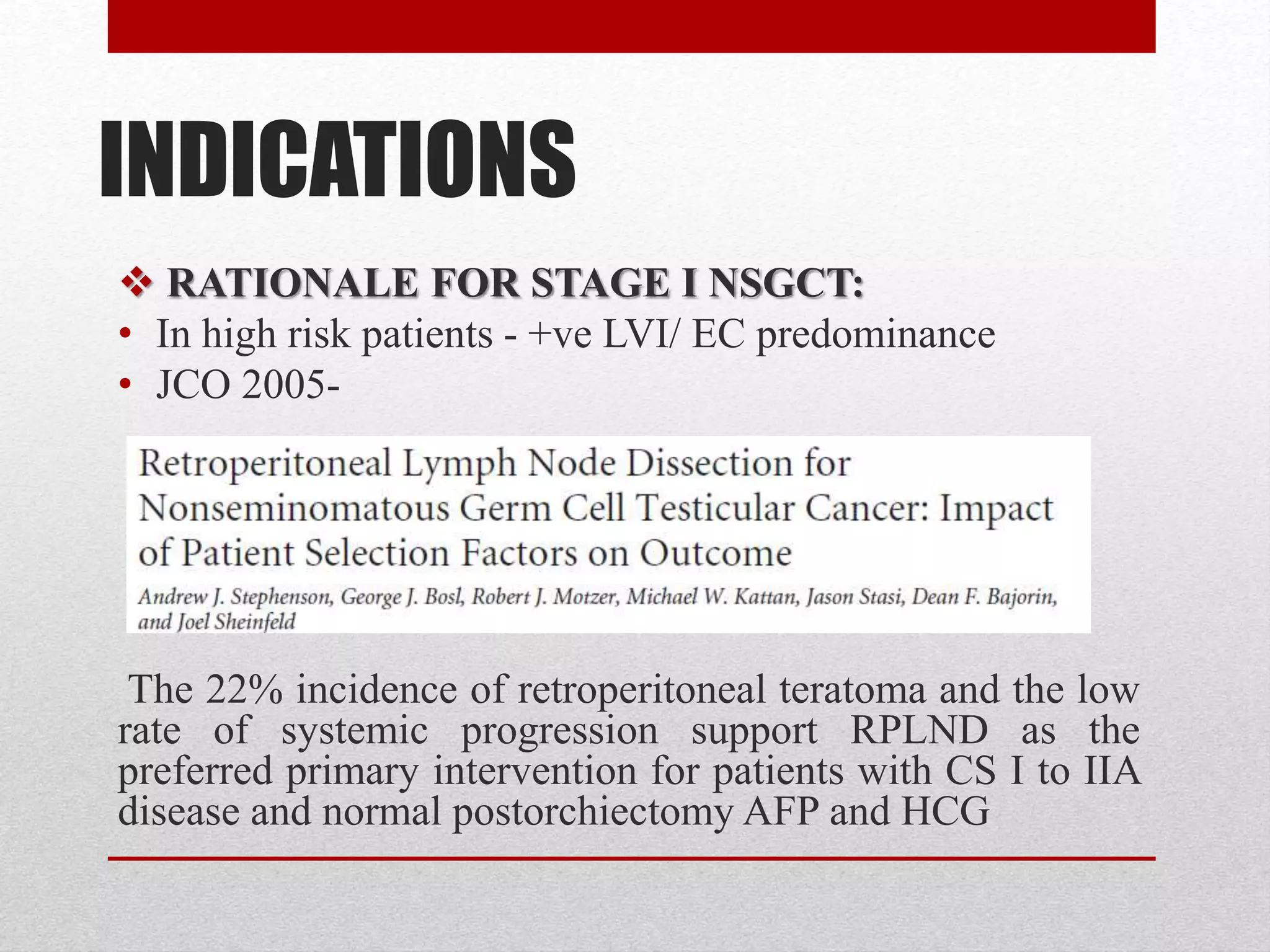
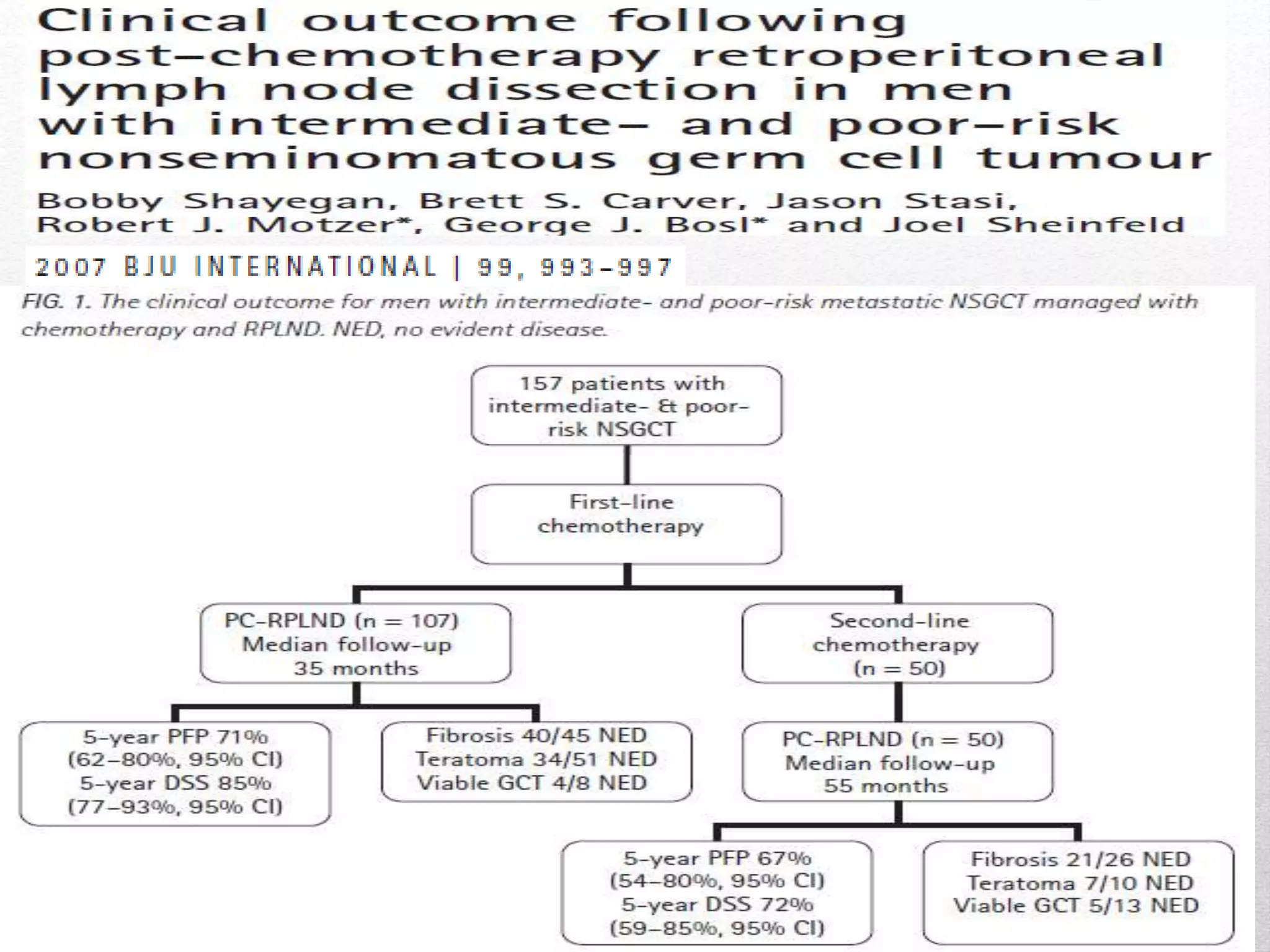
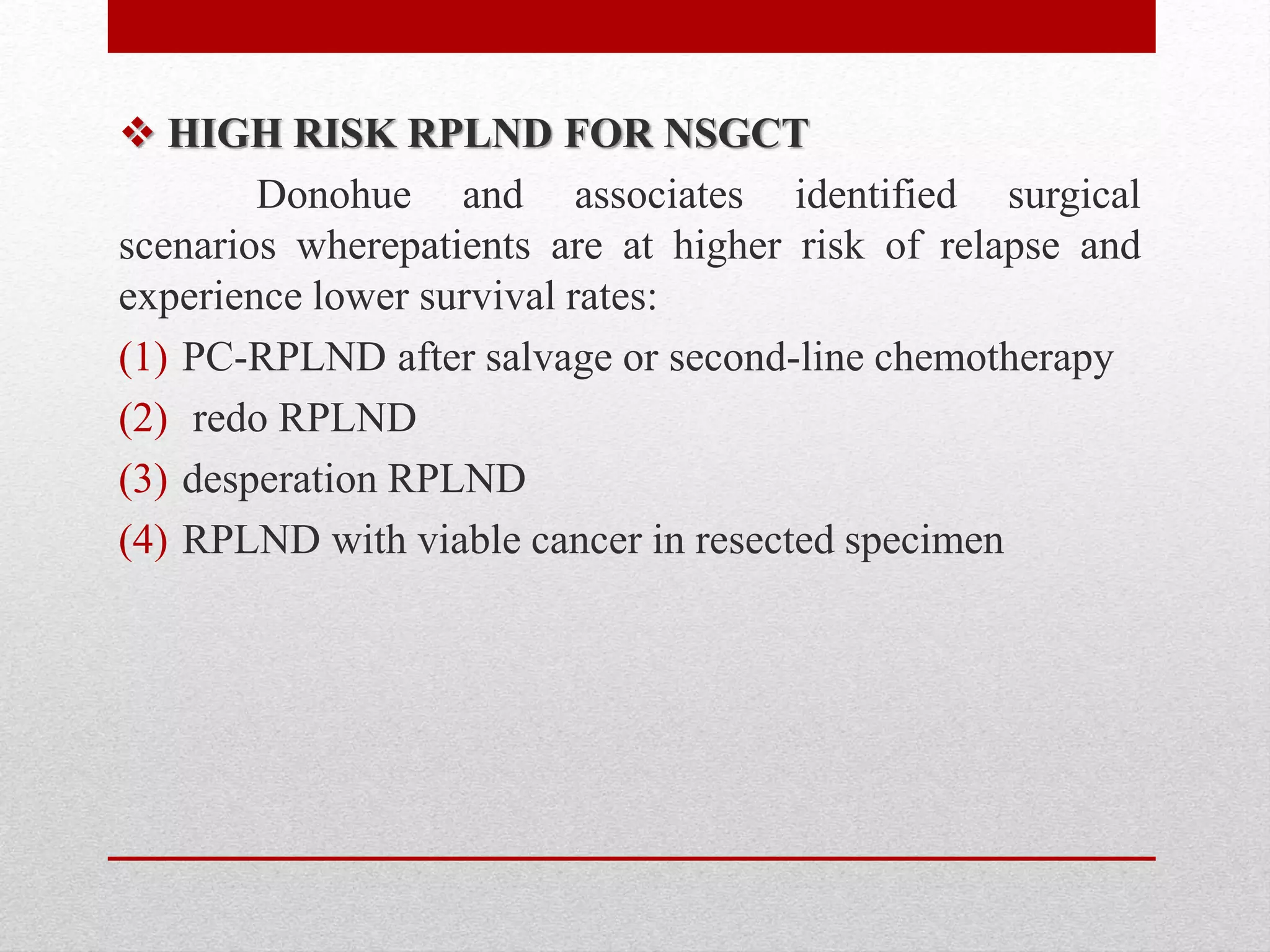
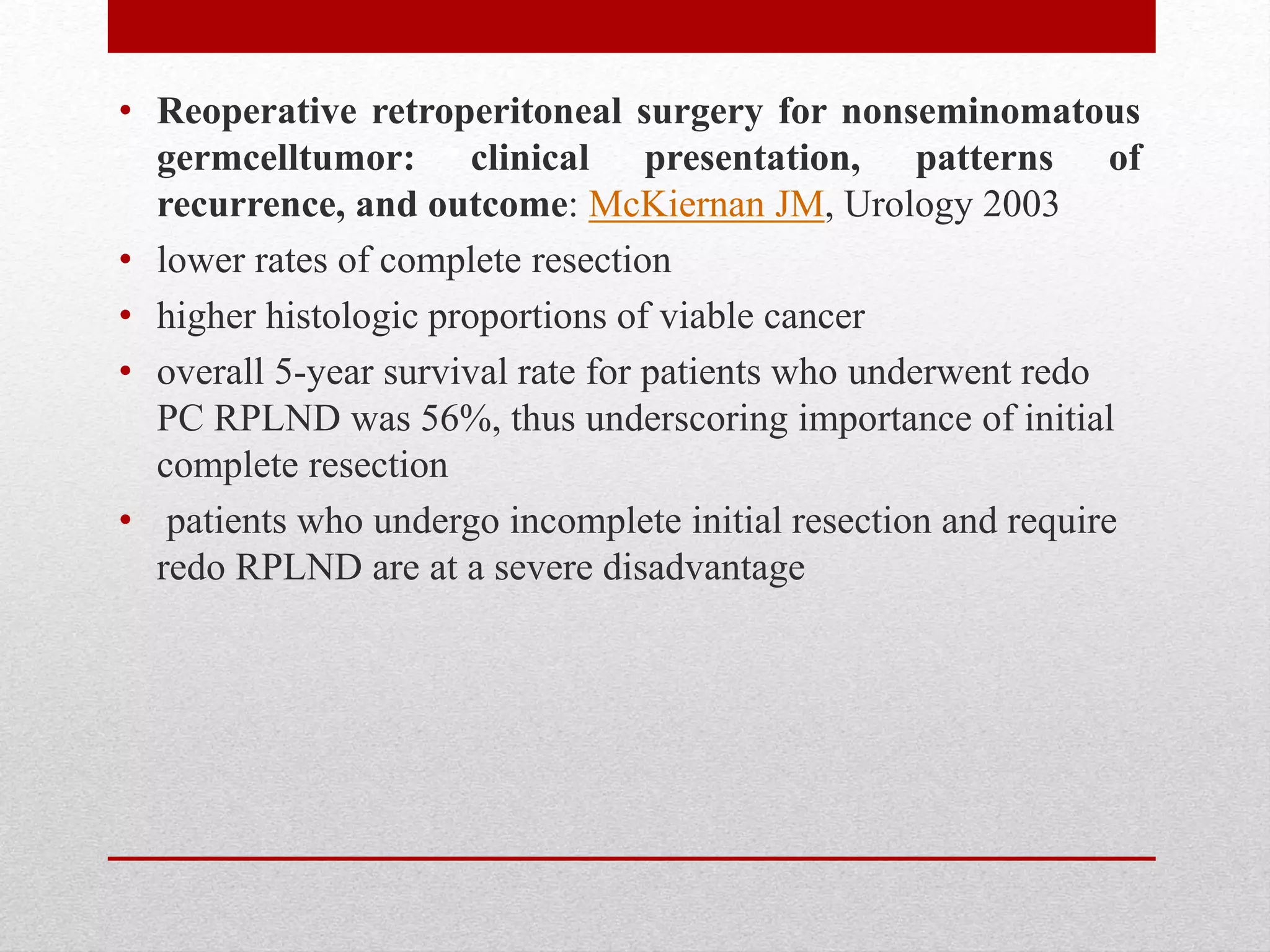
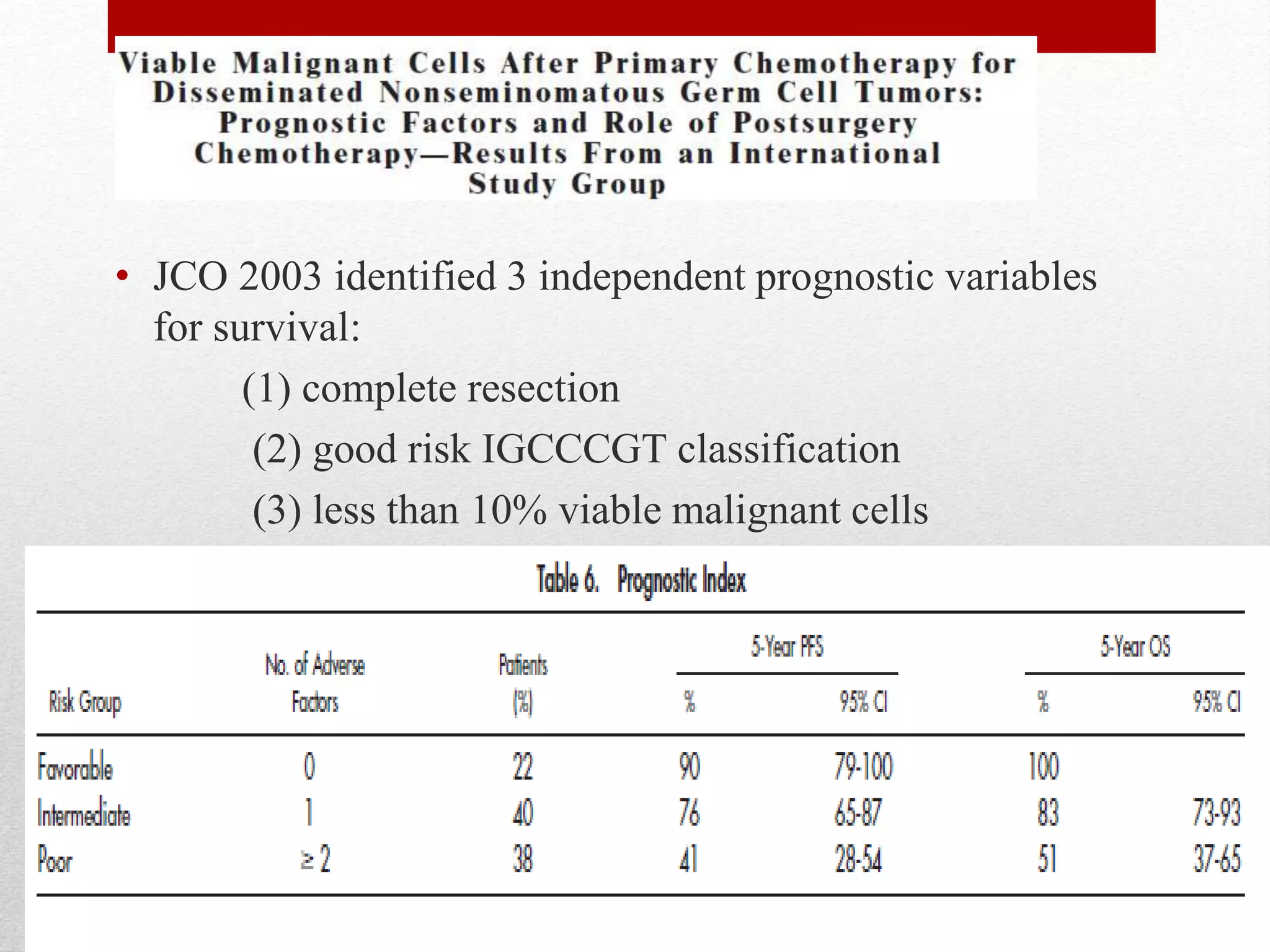
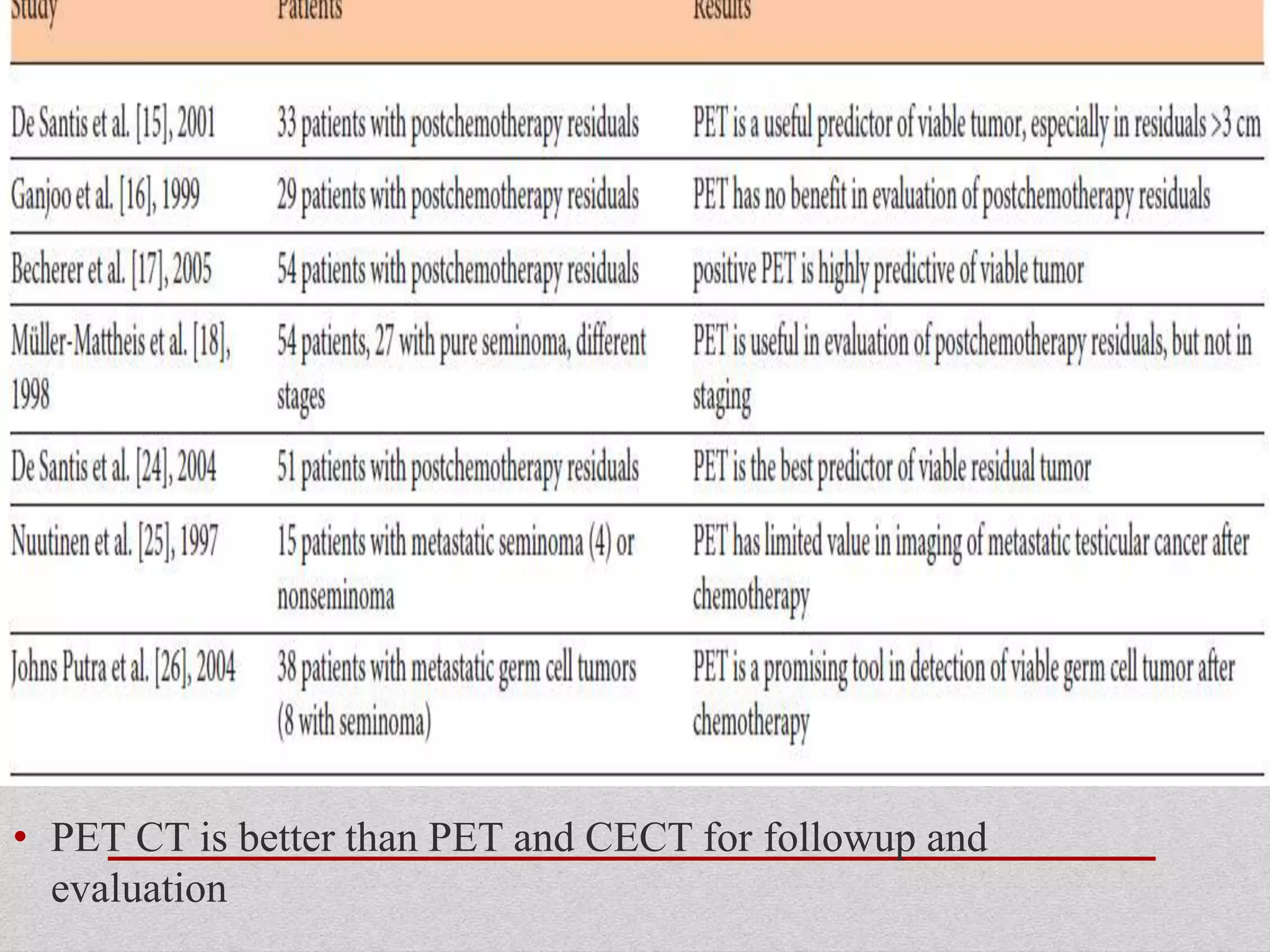
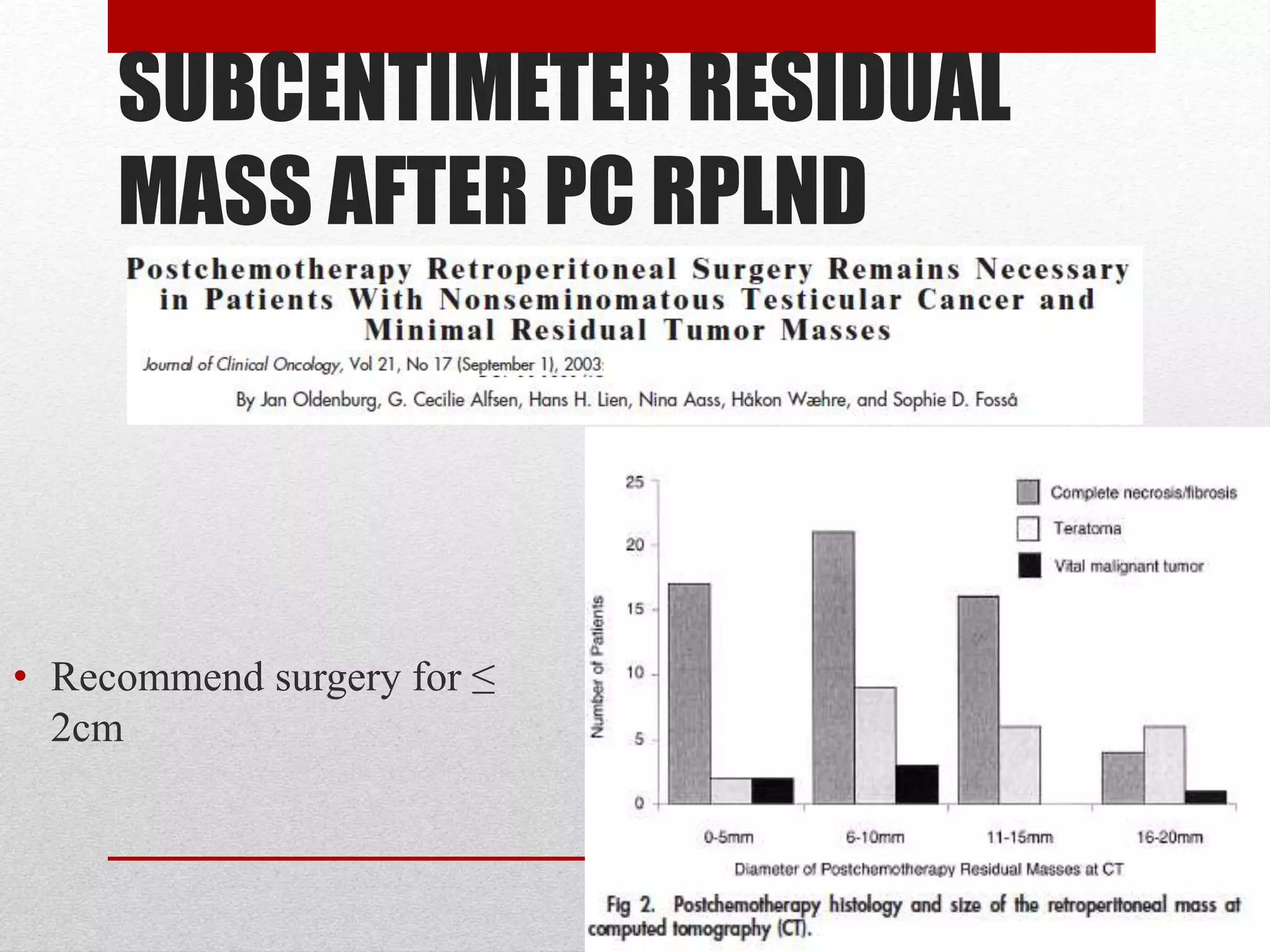
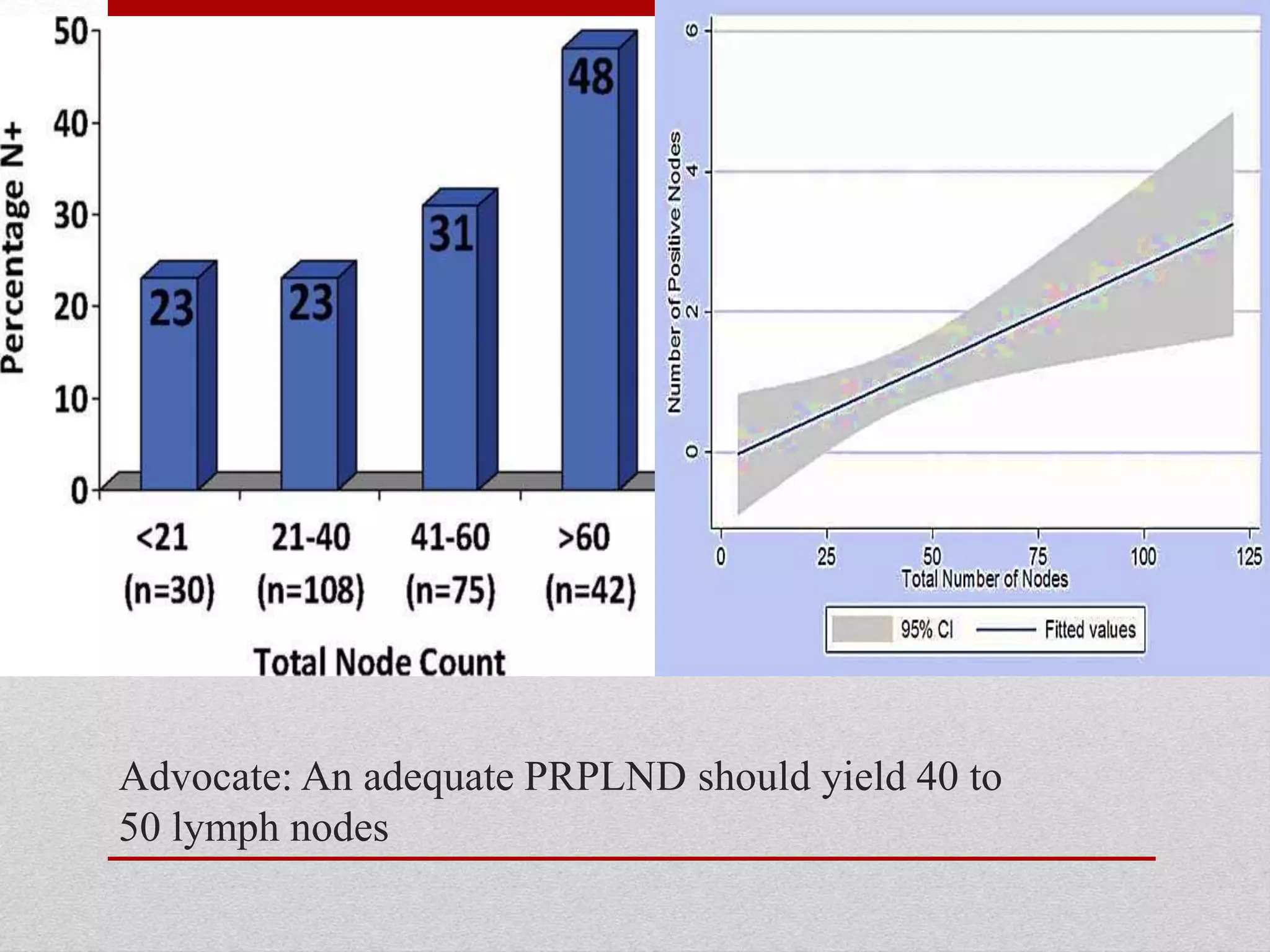
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) is a surgical procedure used to treat testicular cancer. It involves removing lymph nodes in the retroperitoneum which are the first draining sites of metastasis from testicular cancer. Over time, the procedure has evolved from open approaches to minimally invasive techniques. Key developments included mapping of lymphatic drainage patterns, adoption of nerve-sparing approaches to preserve ejaculation, and use of modified or extended templates based on tumor staging. While RPLND remains an important treatment option, ongoing debates include its role compared to surveillance for very small residual masses after chemotherapy and optimal surgical extent. Complication rates also vary based on whether performed for primary staging or post-