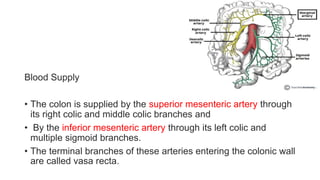
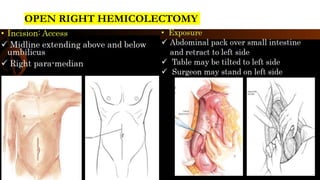
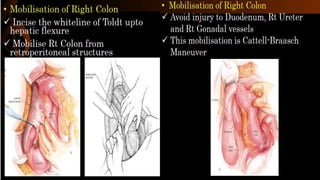
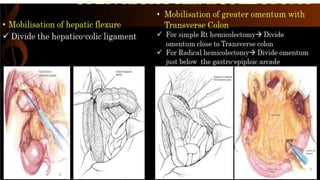
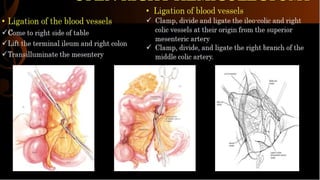
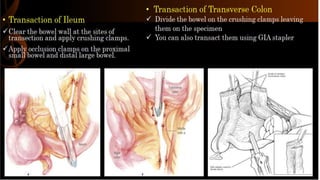
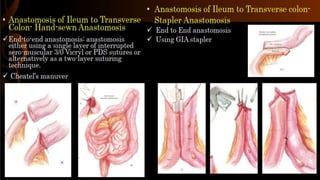
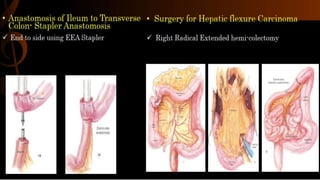
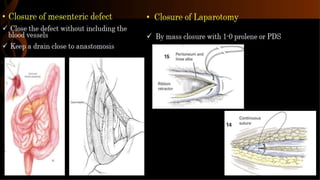
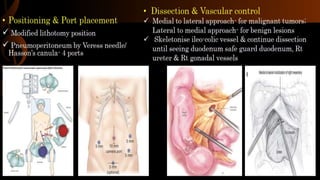
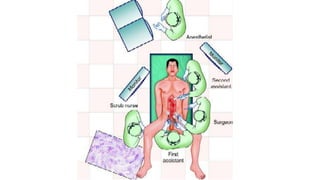
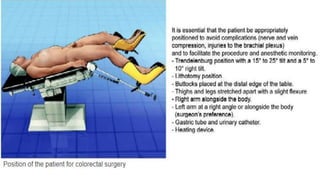
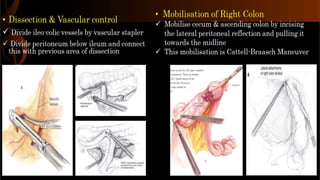
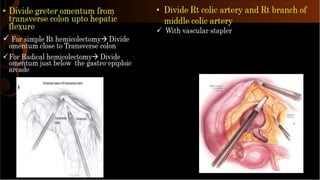
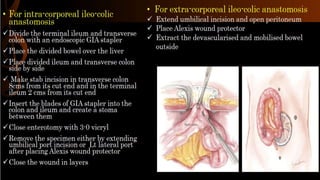
Right hemicolectomy involves removing part of the colon, cecum, terminal ileum, and lymph nodes. It is the standard treatment for right colon cancers. The procedure removes the cecum, ascending colon, first part of the transverse colon, and lymph nodes. Indications include adenocarcinoma of the right colon, adenomatous polyps that cannot be removed endoscopically, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticulitis. Risks include anastomotic leak, hemorrhage, bowel obstruction, and injury to nearby organs. Pre-op preparation includes bowel cleansing and antibiotics.