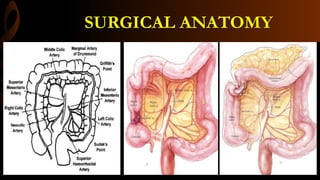
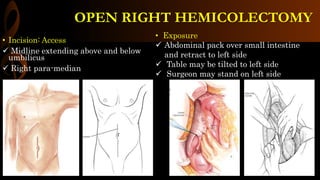
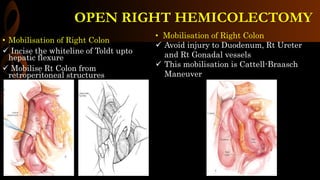
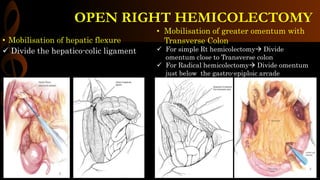
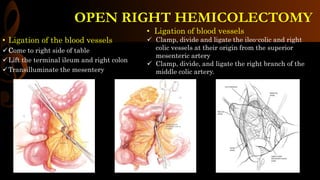
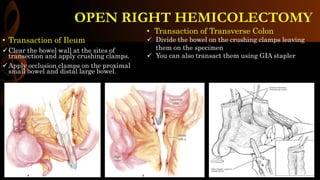
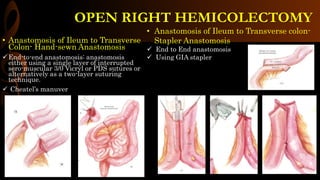
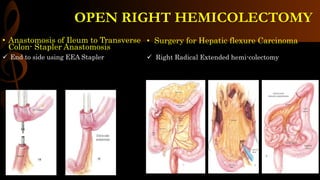
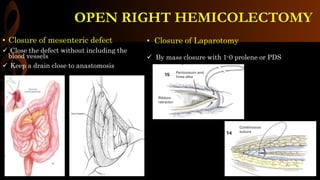
Open right hemicolectomy is performed to treat malignant tumors, polyps, and other conditions in the ileocecal region, ascending colon, and hepatic flexure. The procedure involves mobilizing the right colon, ligating blood vessels, resecting the involved bowel segments, and creating an ileocolic or ileotransverse anastomosis. Key steps include careful dissection to avoid injury to nearby structures like the duodenum and ureter, and ensuring a well-vascularized, tension-free anastomosis to minimize risks of leakage. Post-operative care focuses on early ambulation and advancing diet based on progress.