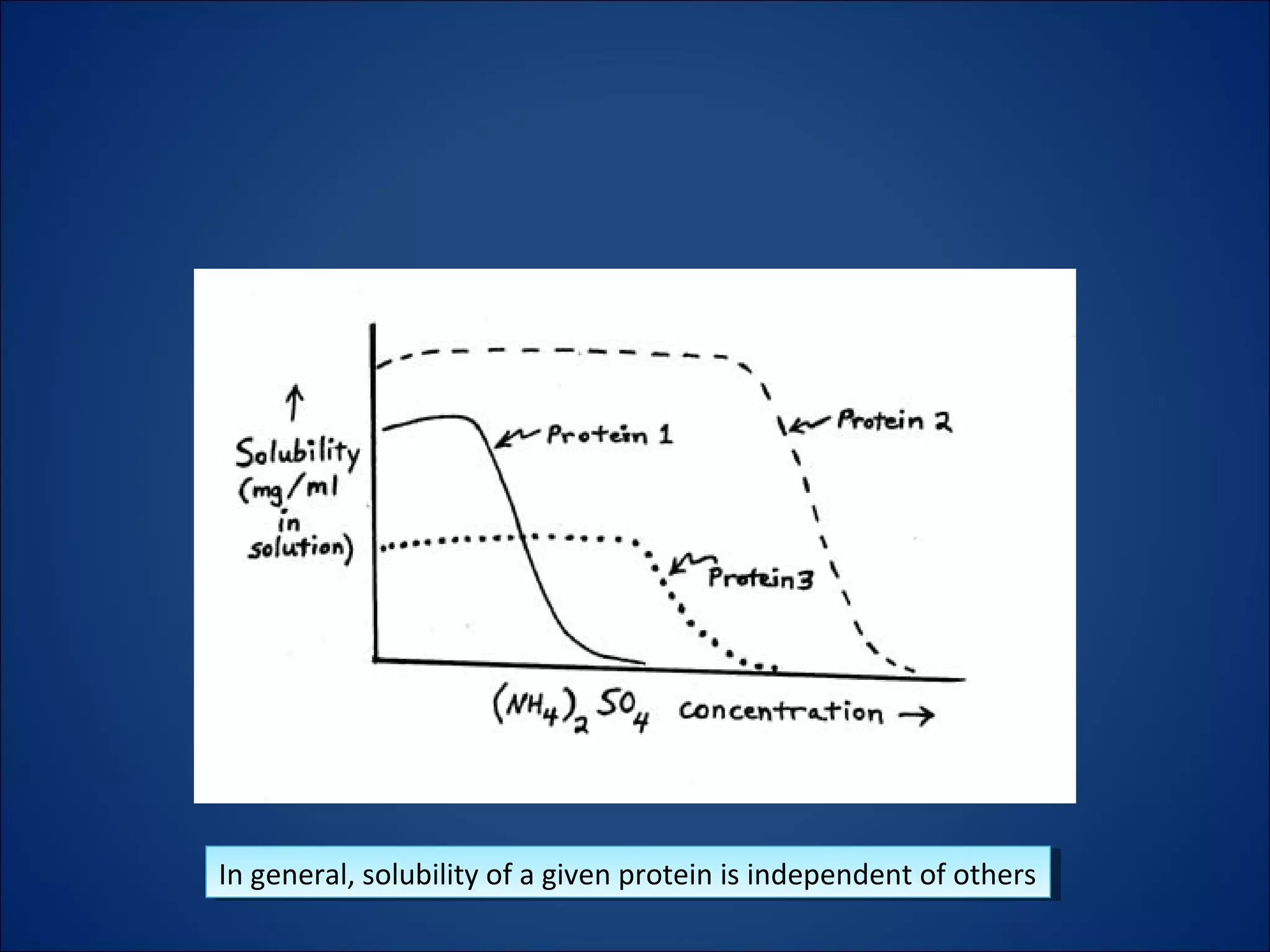
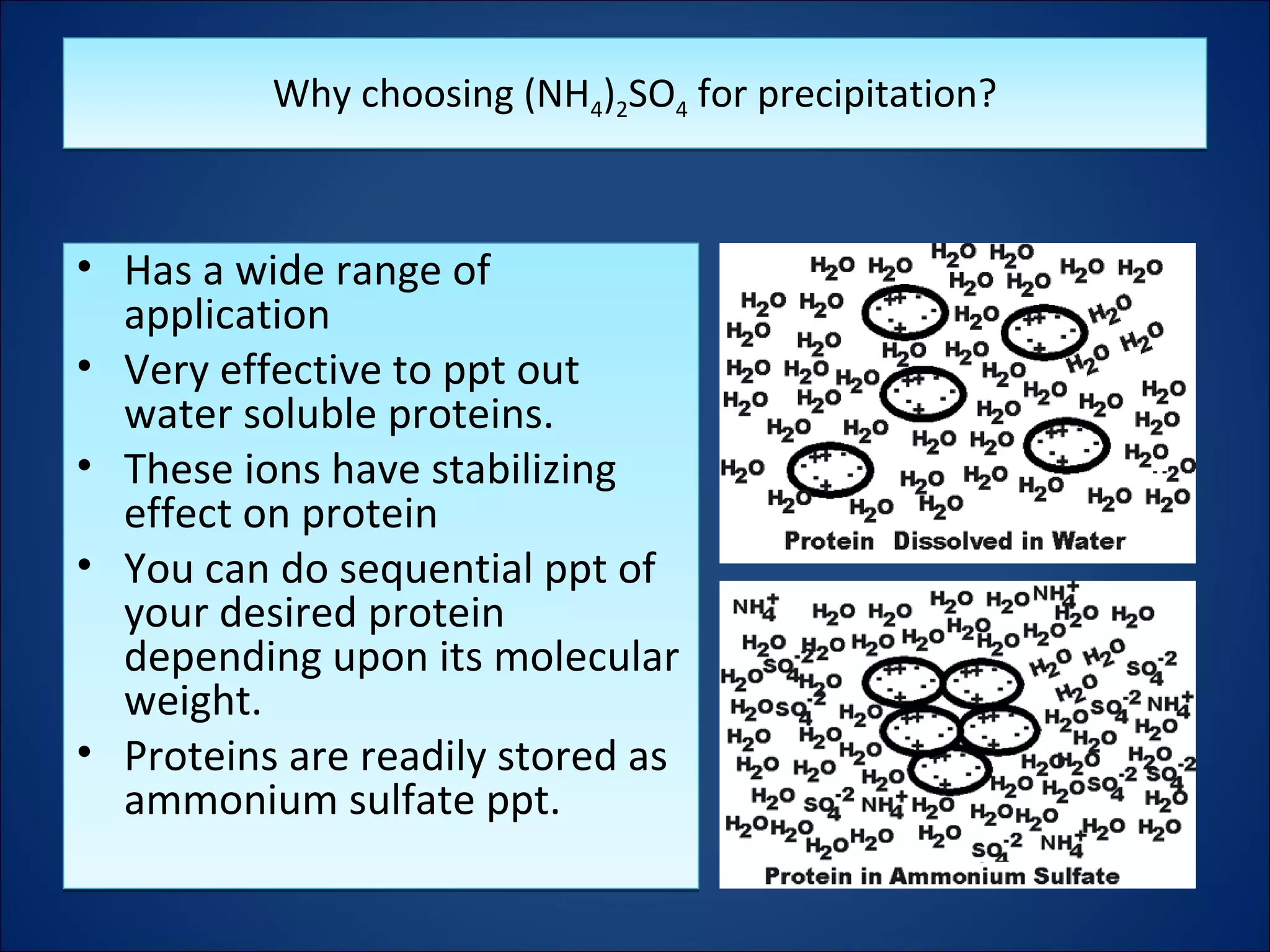
The document discusses the process of protein salting-out, where high concentrations of salts like ammonium sulfate are used to precipitate proteins out of solution. At low salt concentrations, solubility increases due to screening of charge-charge interactions, but at high concentrations the salt competes for water molecules needed to solvate proteins, removing their solvation sphere and causing precipitation. Fractional precipitation uses increasing ammonium sulfate concentrations to sequentially precipitate different proteins based on their individual solubility profiles.

![Salting in / Salting outSalting in / Salting out
• Salting IN
• At low concentrations,
added salt usually increases
the solubility of charged
macromolecules because
the salt screens out charge-
charge interactions.
• So low [salt] prevents
aggregation and therefore
precipitation.
• Salting IN
• At low concentrations,
added salt usually increases
the solubility of charged
macromolecules because
the salt screens out charge-
charge interactions.
• So low [salt] prevents
aggregation and therefore
precipitation.
• Salting OUT
• At high concentrations
added salt lowers the
solubility of macro-
molecules because it
competes for the solvent
(H2O) needed to solvate the
macromolecules.
• So high [salt] removes the
solvation sphere from the
protein molecules and they
come out of solution.
• Salting OUT
• At high concentrations
added salt lowers the
solubility of macro-
molecules because it
competes for the solvent
(H2O) needed to solvate the
macromolecules.
• So high [salt] removes the
solvation sphere from the
protein molecules and they
come out of solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-session-3-150414002807-conversion-gate01/75/Lab-session-3-2-2048.jpg)
![– Proteins require H2O molecules interacting with
surface groups, in order to stay in aqueous solution
(hydration).
– Salting out usually uses increasing concentrations of
ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4] to compete with the
protein groups for the available H2O.
– Like all purification methods, salt fractionation has to
be worked out empirically for each protein of interest
– Every protein in the solution has its own solubility
limits in ammonium sulfate, independent of the
other proteins in the mixture.
– Proteins require H2O molecules interacting with
surface groups, in order to stay in aqueous solution
(hydration).
– Salting out usually uses increasing concentrations of
ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4] to compete with the
protein groups for the available H2O.
– Like all purification methods, salt fractionation has to
be worked out empirically for each protein of interest
– Every protein in the solution has its own solubility
limits in ammonium sulfate, independent of the
other proteins in the mixture.
Fractional Precipitation ("salting out")Fractional Precipitation ("salting out")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-session-3-150414002807-conversion-gate01/75/Lab-session-3-4-2048.jpg)