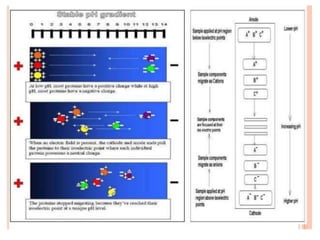
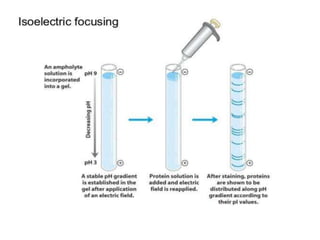
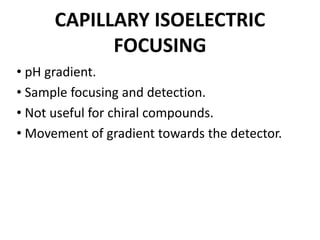
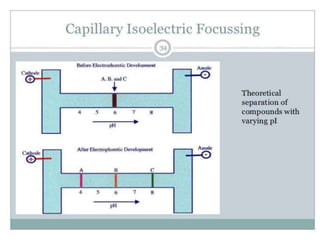
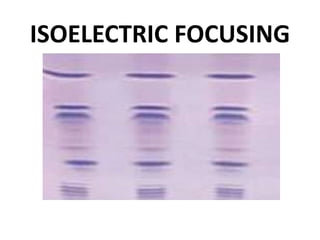
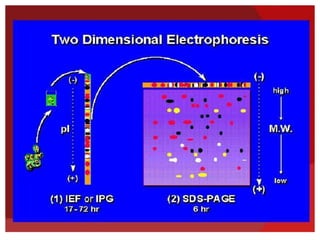
This document provides an overview of isoelectric focusing (IEF). IEF separates proteins in a gel according to their isoelectric point (pI), which is the pH at which a protein has no net charge. During IEF, proteins migrate through an immobilized pH gradient generated by ampholytes until they reach the pH that matches their pI and cease moving. IEF provides high resolution separation and is useful for research applications such as taxonomy, cytology, and immunology.