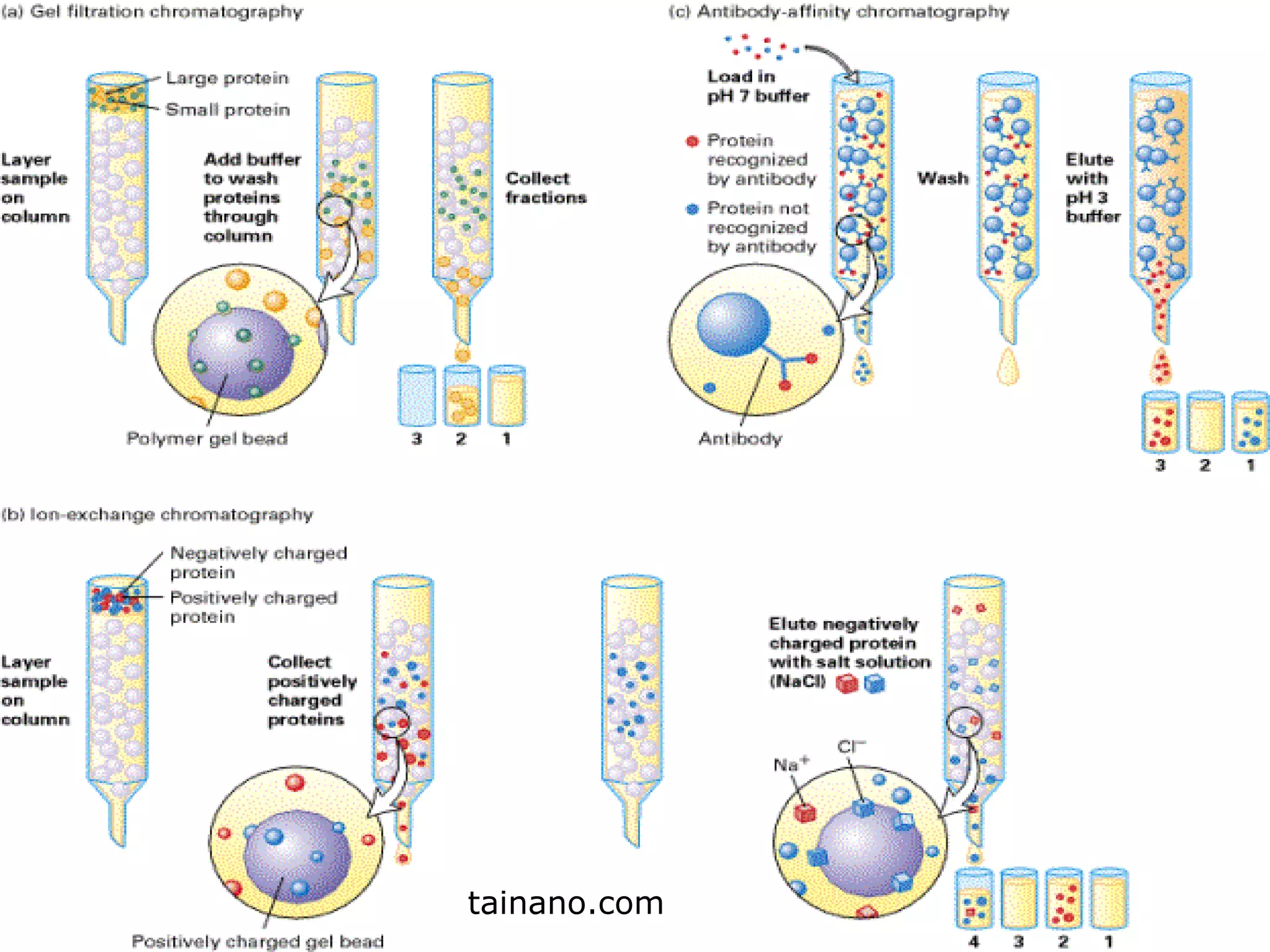
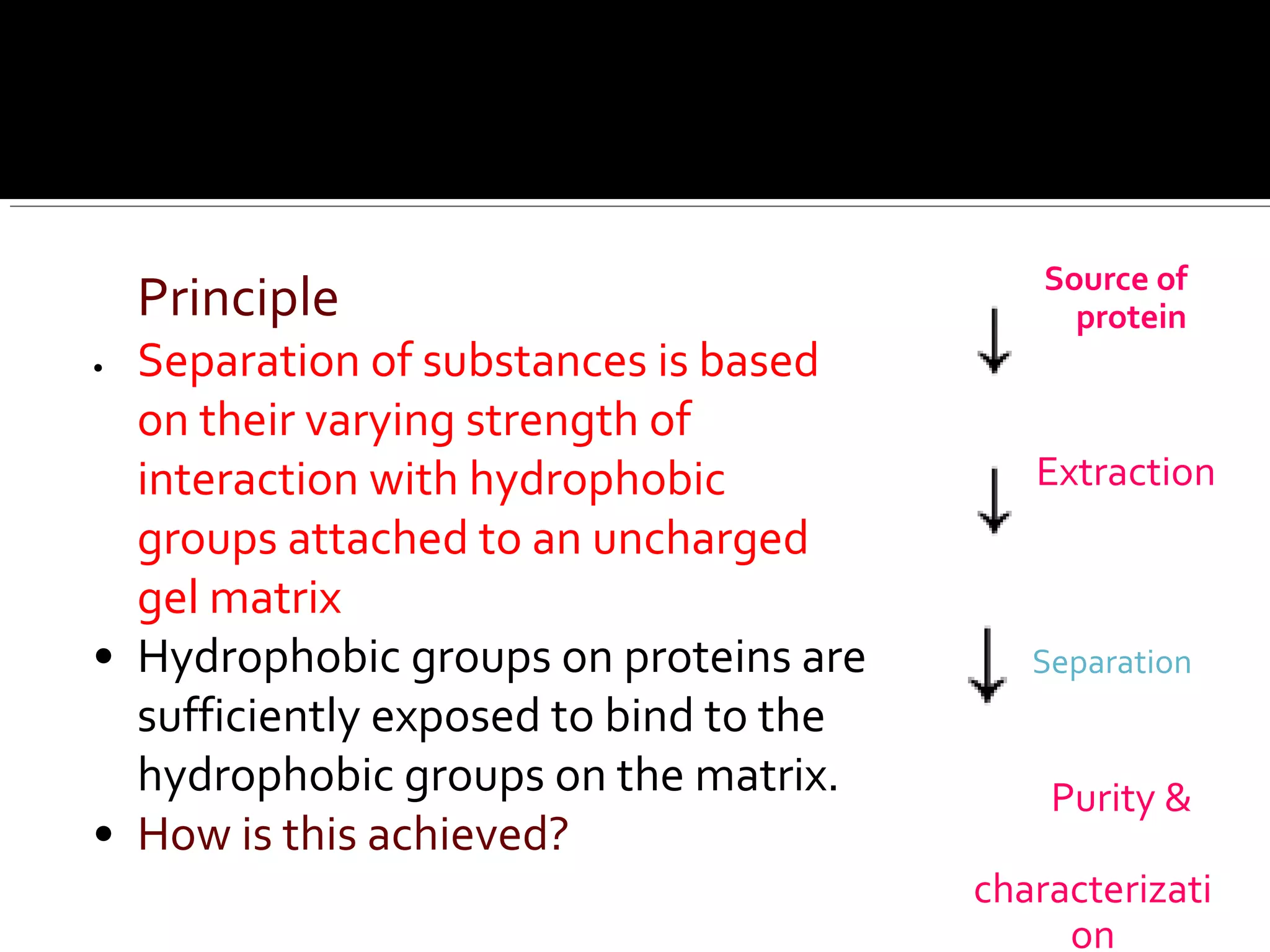
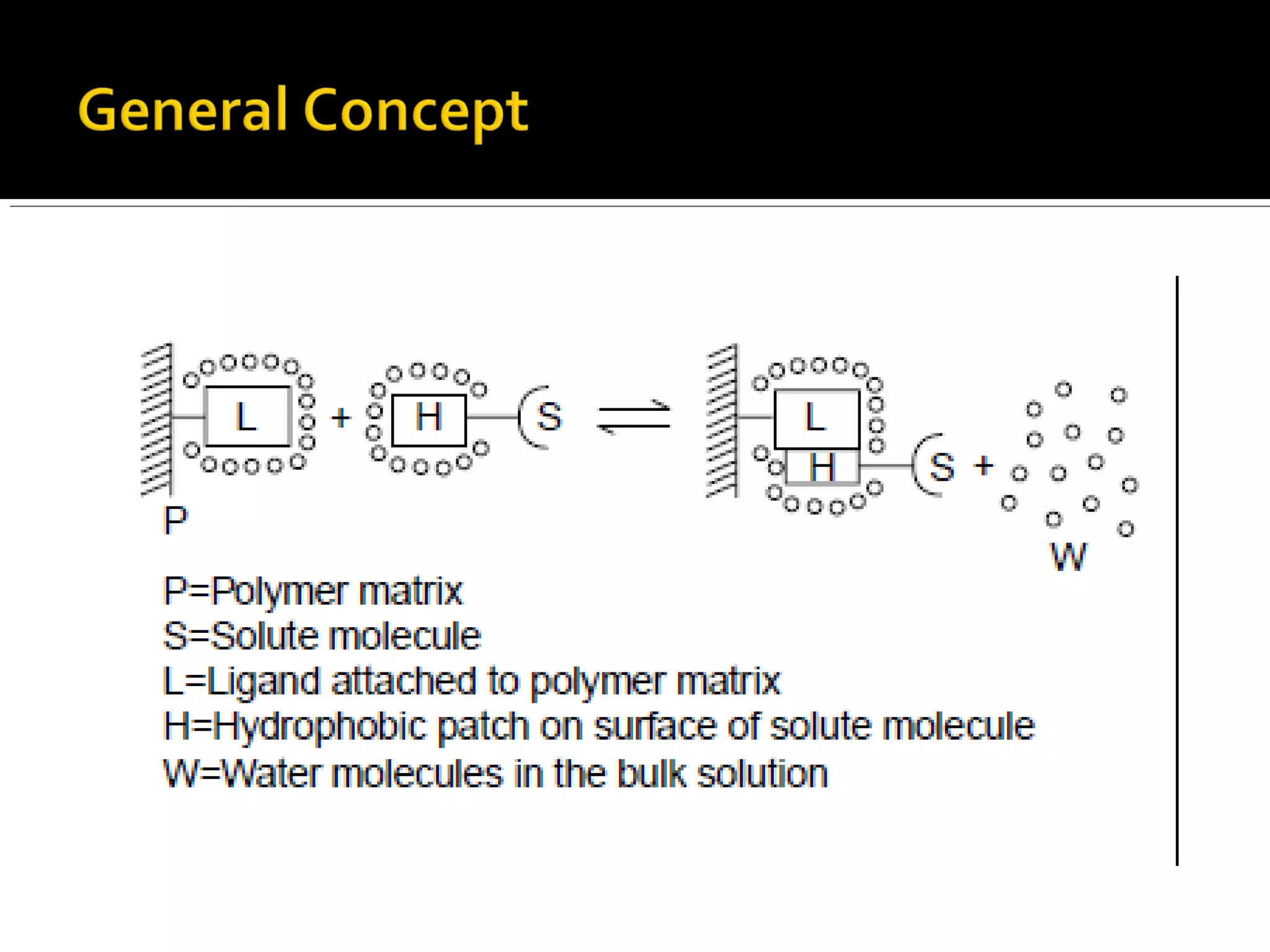
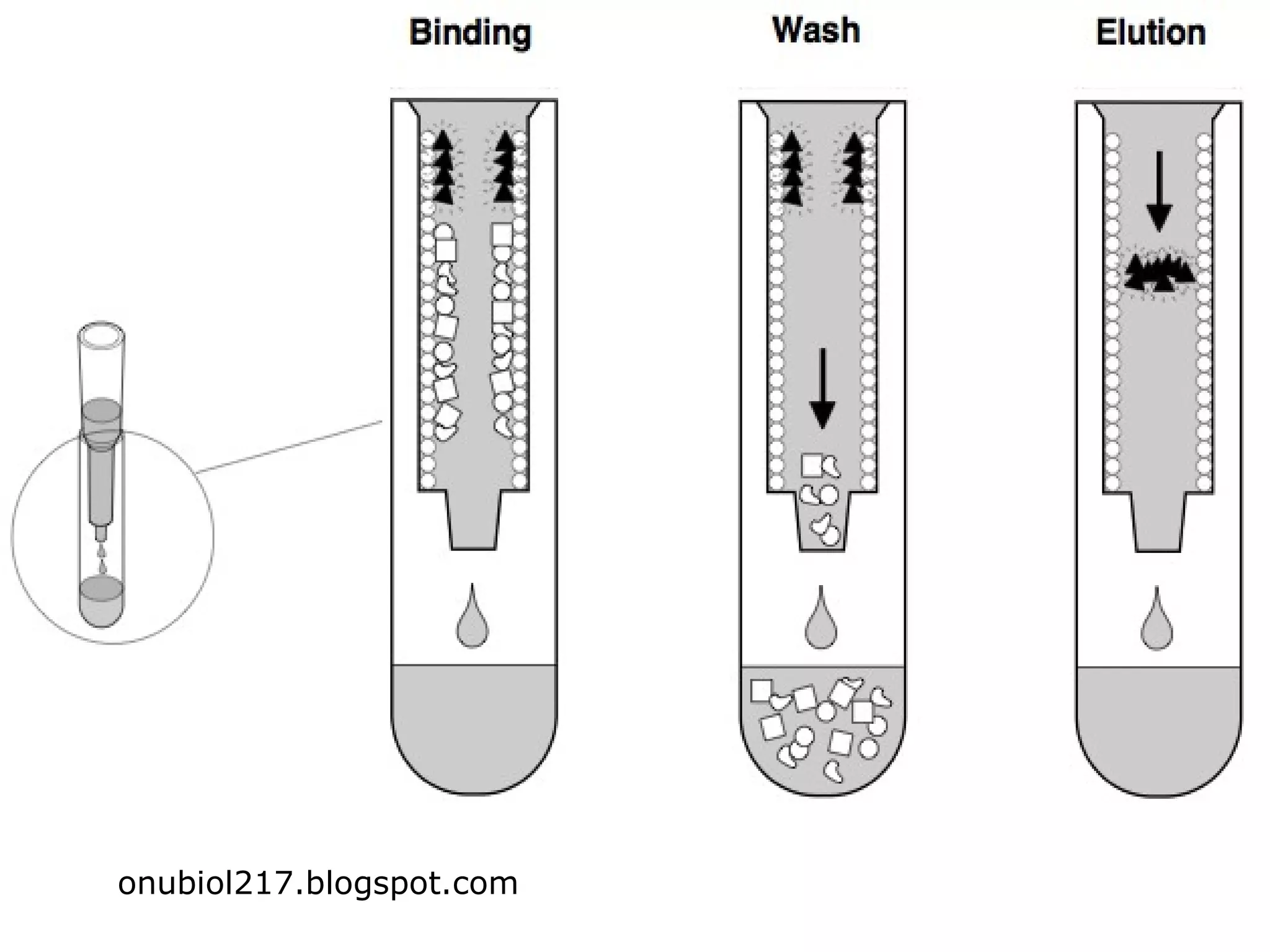
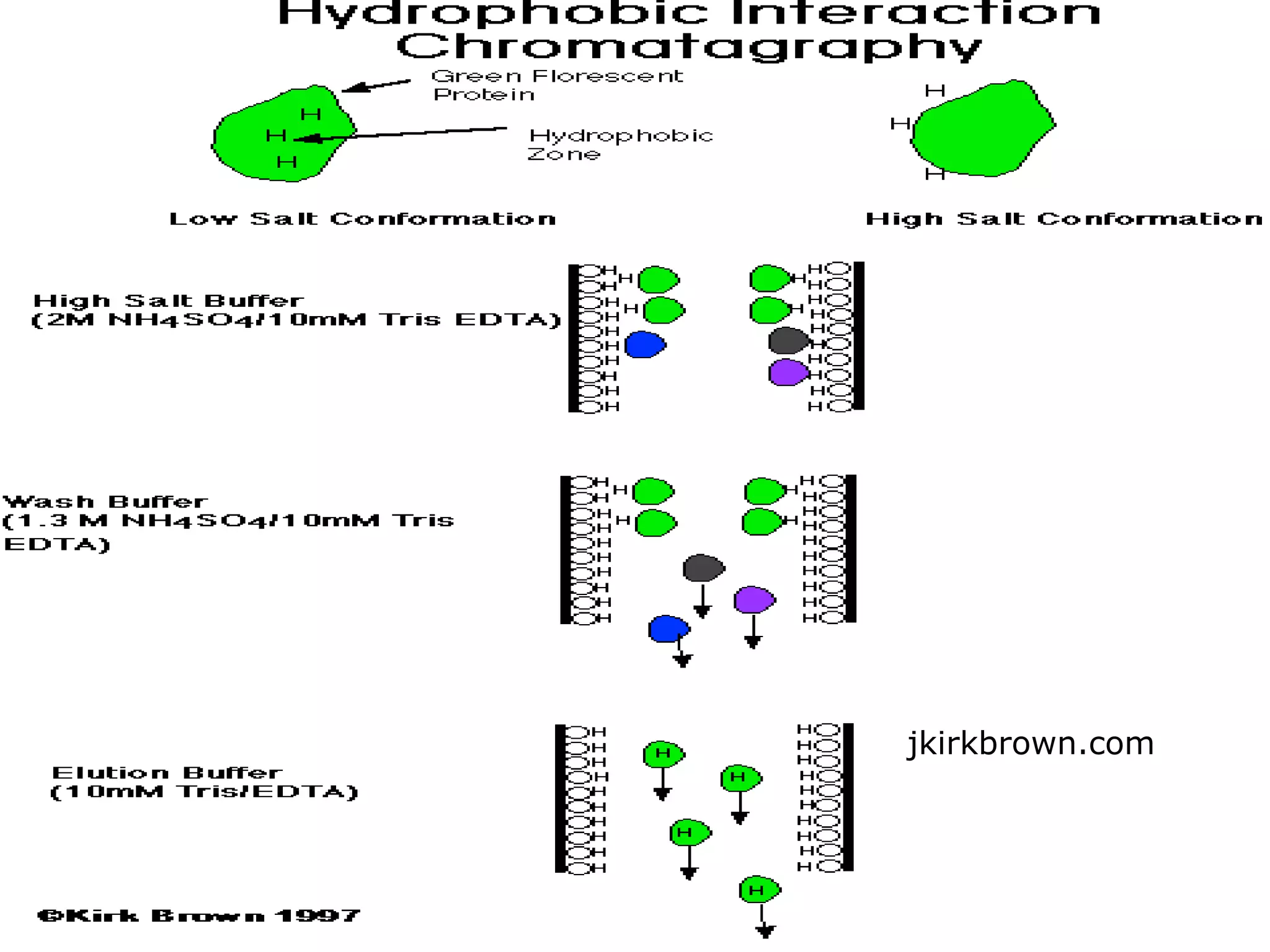
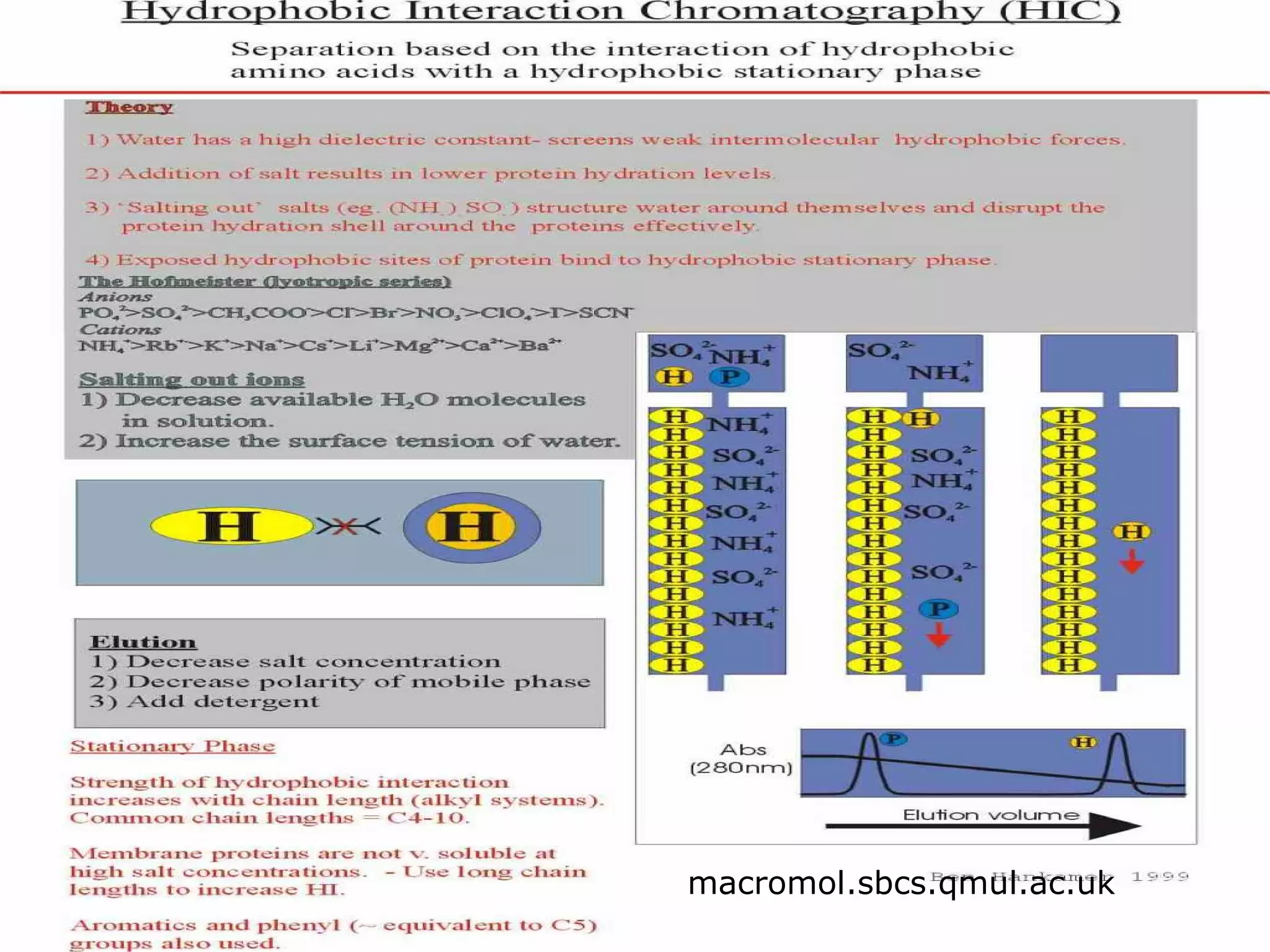
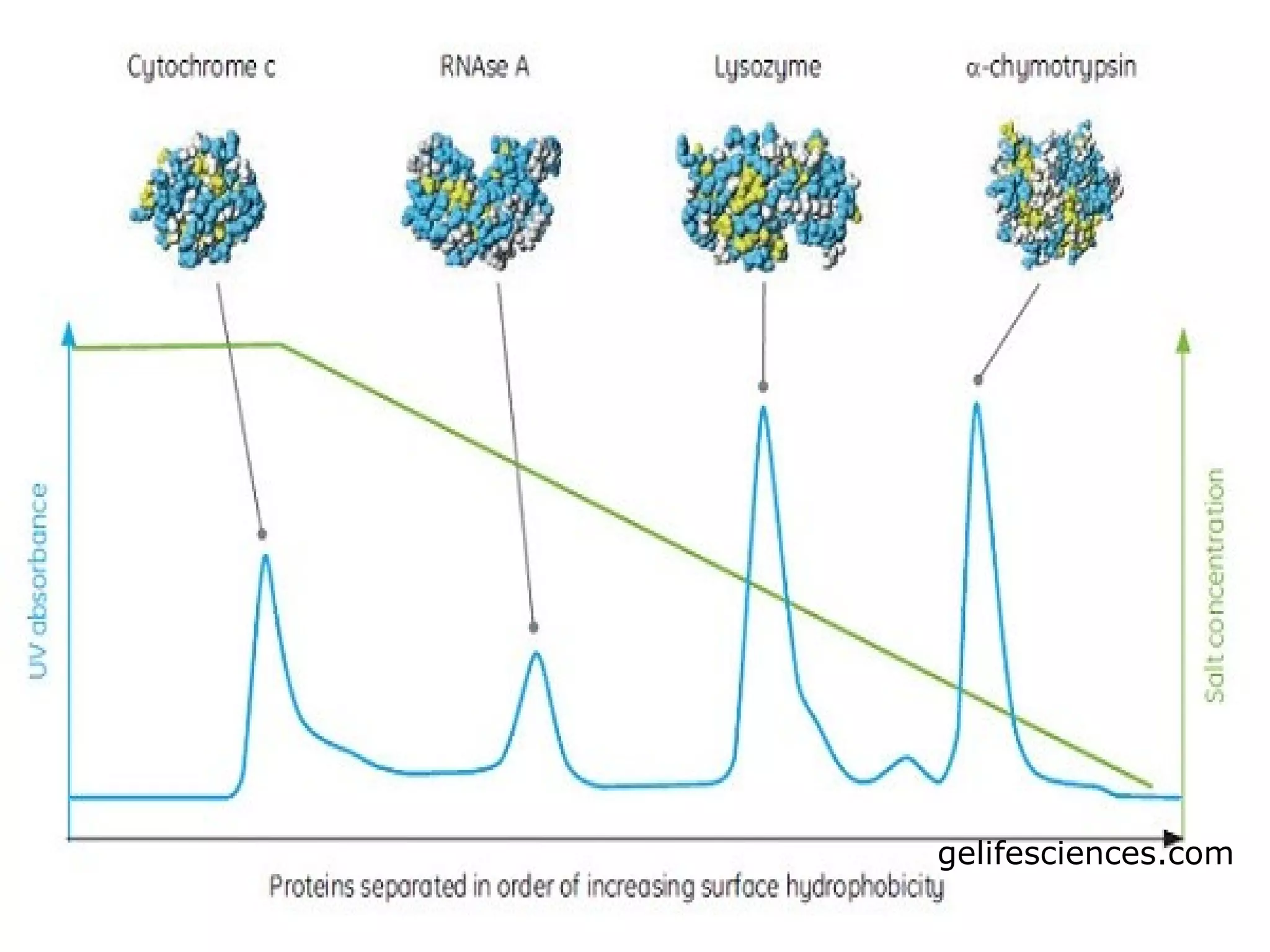
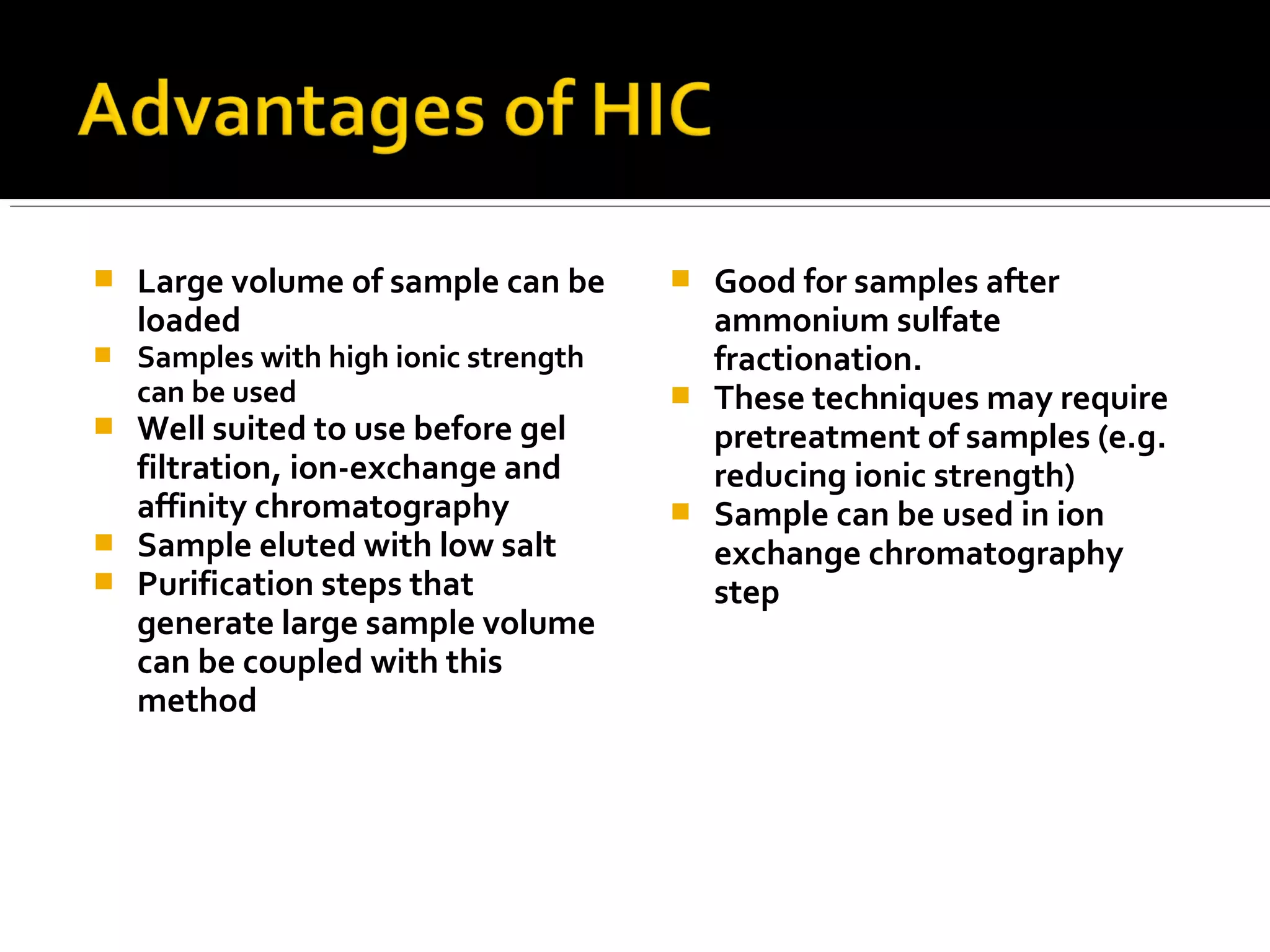
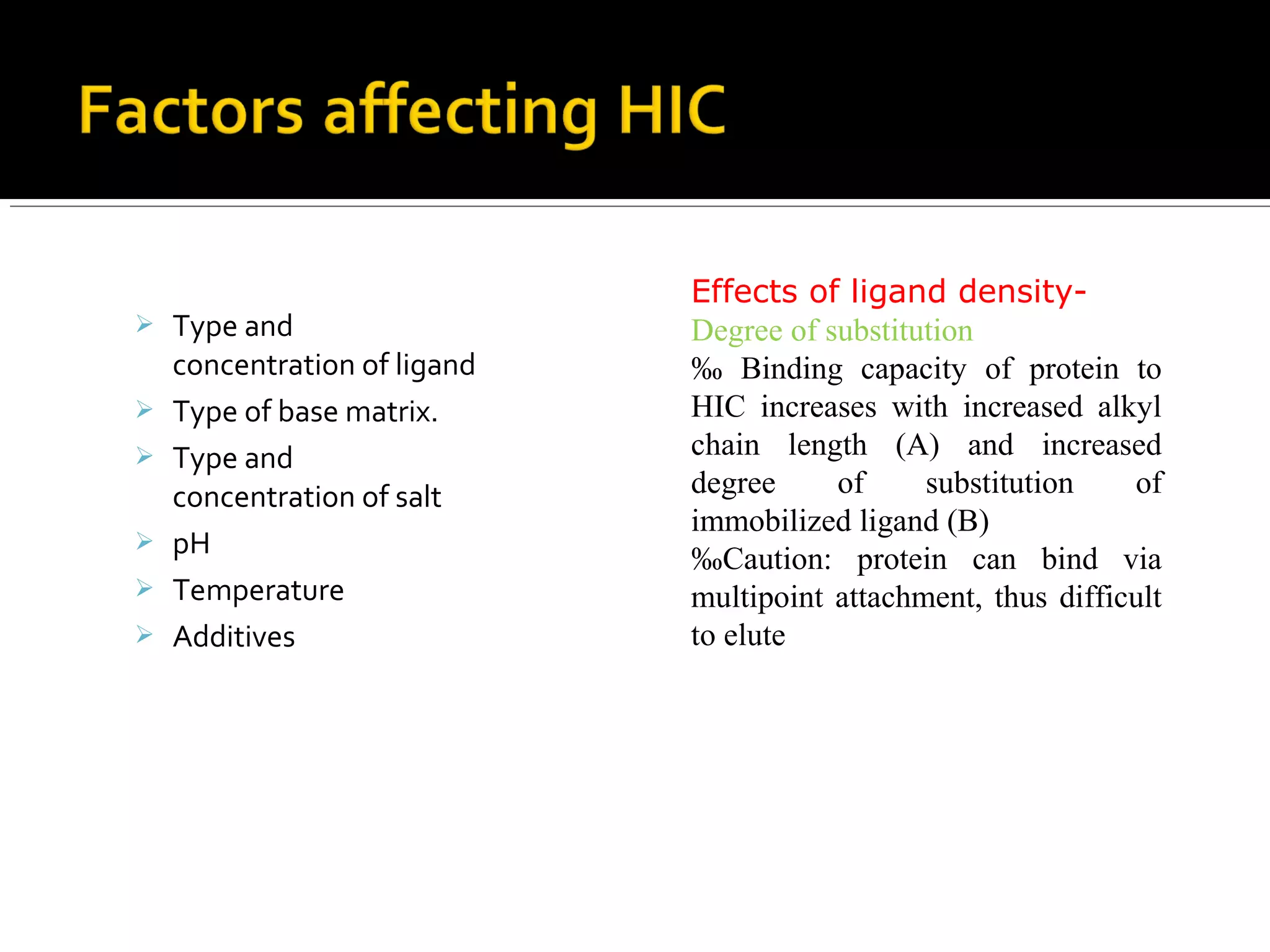
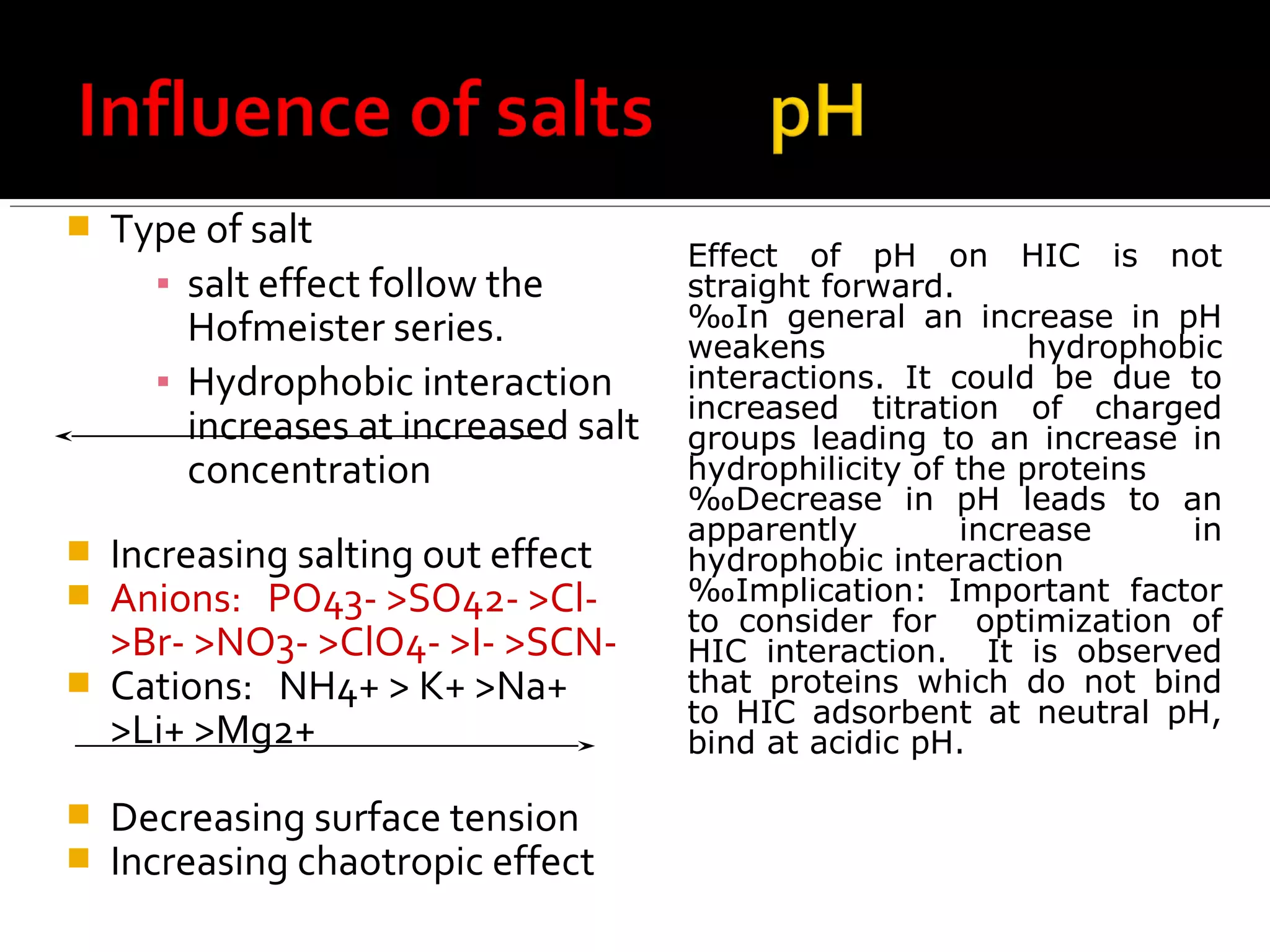
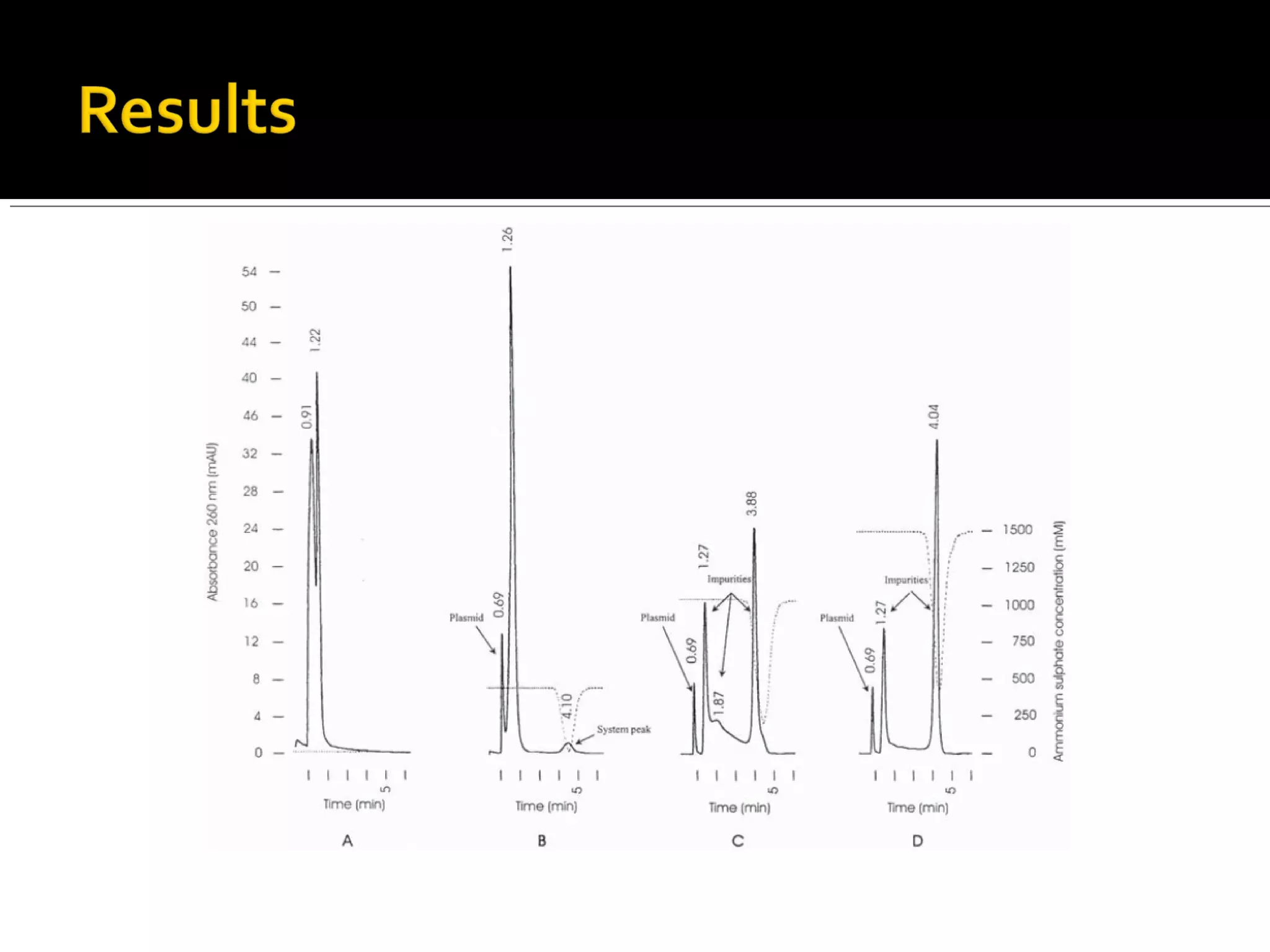
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is used to purify biomolecules like proteins by exploiting differences in hydrophobicity. It works by separating substances based on their varying strength of interaction with hydrophobic groups attached to an uncharged gel matrix. HIC is useful for downstream purification as it can handle large sample volumes with high salt concentrations and is gentler than other methods, maintaining protein activity. Factors like ligand type, salt concentration, pH, and temperature affect HIC separation. The document evaluates HIC for monitoring plasmid DNA purification, finding it is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to assess purity.