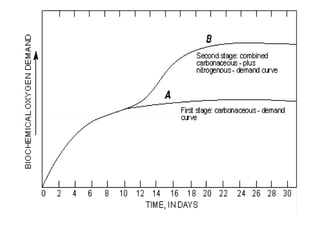
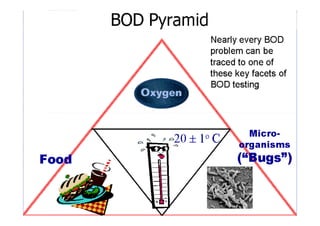
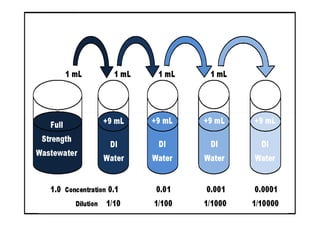
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) measures the amount of dissolved oxygen required by aerobic microorganisms to decompose organic material in water over a specified time at a set temperature, often used to assess water quality and organic pollution levels. The BOD testing process involves measuring the change in dissolved oxygen in water samples, with a focus on both the carbonaceous and nitrogenous stages of decomposition. Additionally, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) provides a broader measure of organic compounds in water, reflecting total oxidizable materials and usually yielding higher values than BOD.