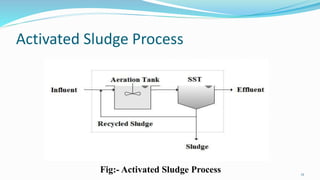
This document discusses the process of sewage treatment. It begins by defining sewage and its characteristics such as being mostly water with small amounts of waste matter. It then outlines the various steps of sewage treatment including preliminary treatment using screens and grit chambers, primary treatment using sedimentation to remove solids, and secondary treatment using activated sludge processes with microorganisms to reduce organic content before final treatments like anaerobic digestion and chlorination. Flow diagrams and tables with treatment details are provided.