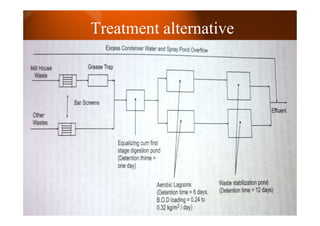
The sugar industry, primarily in countries like India, Cuba, and Jamaica, is crucial for rural development, supporting around 50 million farmers. The document discusses the manufacturing process of sugar, the characteristics of waste generated, and treatment alternatives, emphasizing the effectiveness of anaerobic treatment methods. It also highlights waste reduction practices and includes objective and theory questions related to the sugar production process and waste management.