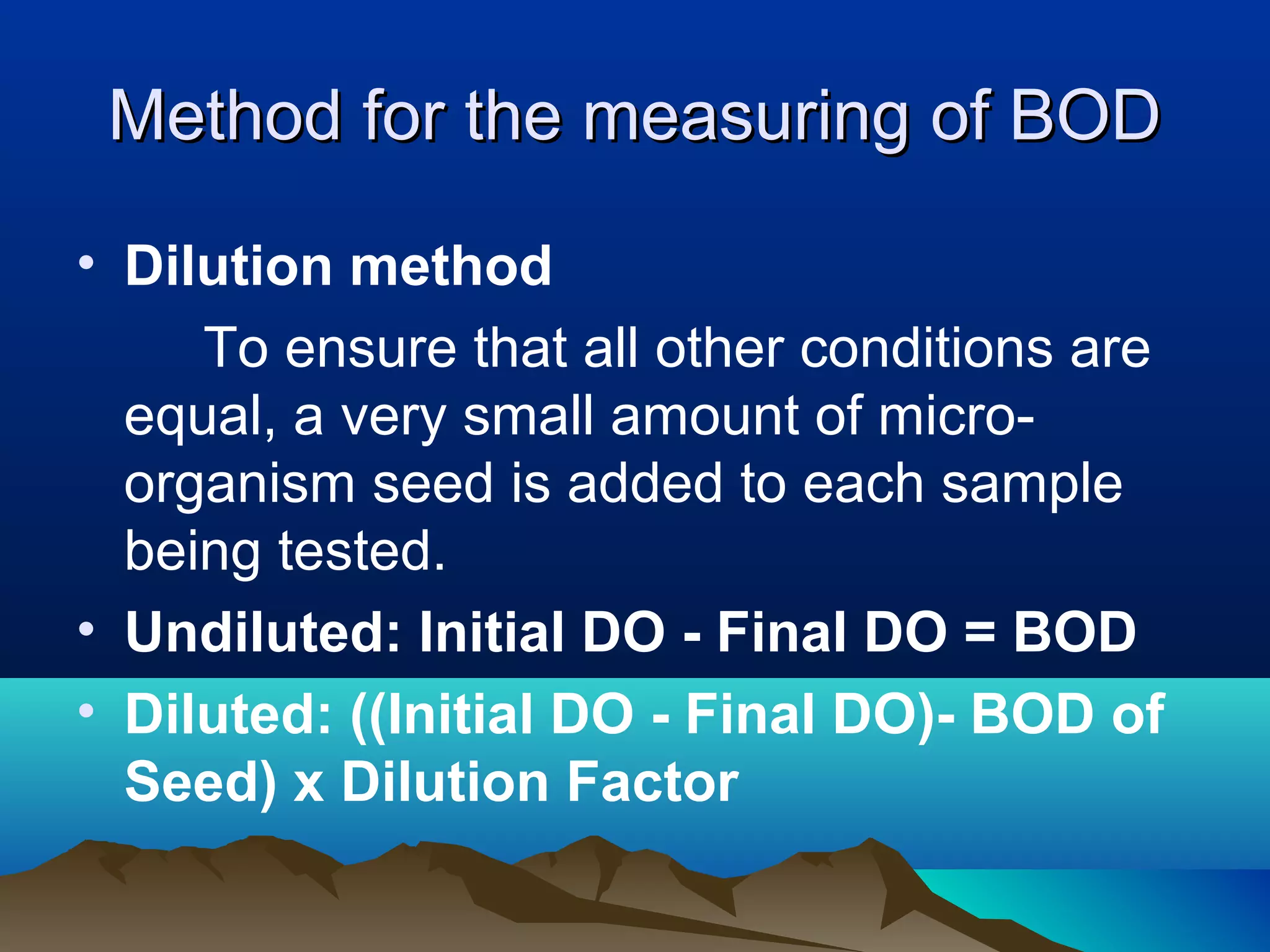
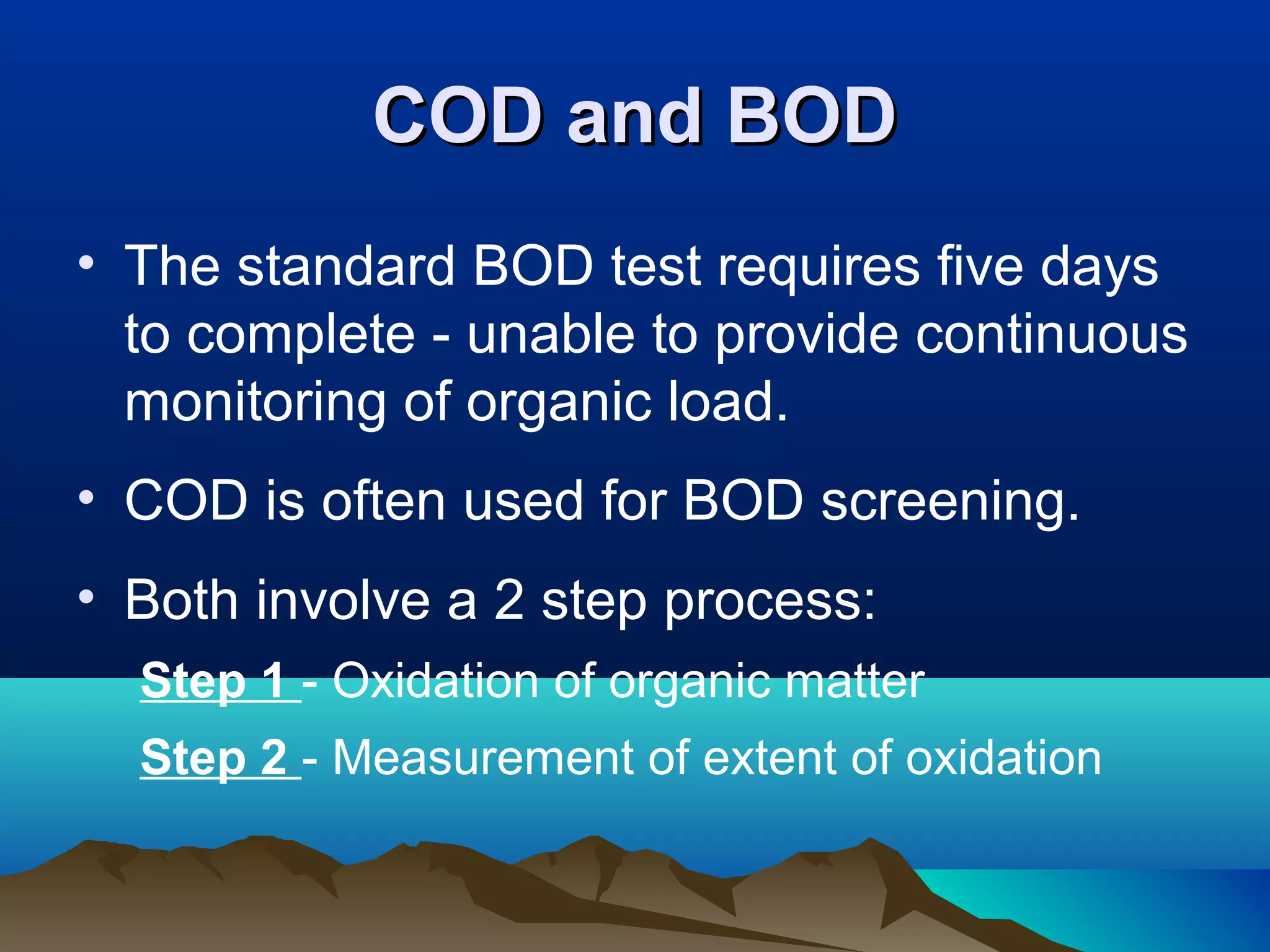
The document discusses biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and its importance as a measure of water quality. BOD is defined as the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material in a water sample over a 5 day incubation period at 20°C. A higher BOD indicates a higher level of organic pollution. BOD is used to assess the effectiveness of wastewater treatment plants and provides an indication of overall water quality. The standard BOD test involves measuring the dissolved oxygen in a sample before and after 5 days, with the difference representing the oxygen consumed during decomposition of organic compounds.