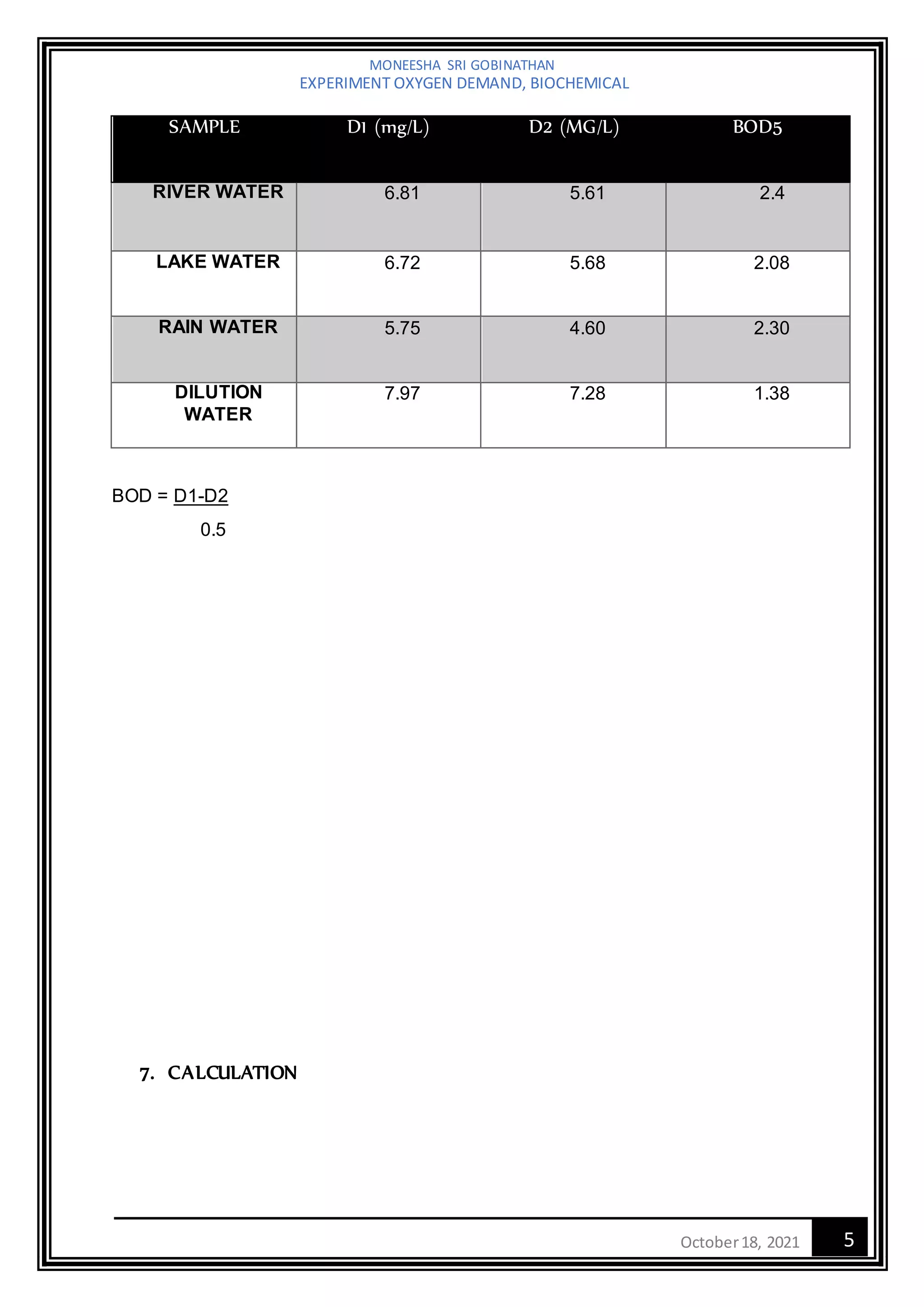
The document describes an experiment to measure biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of various water samples. BOD is a measure of the amount of oxygen consumed by microorganisms as they break down organic matter in water. The experiment involves taking water samples from a river, lake, and rain water, incubating them for 5 days, and measuring the dissolved oxygen levels initially and after 5 days. The BOD values were calculated and reported. The results showed that river water had the highest BOD at 2.4 mg/L, indicating more organic matter to be broken down by microbes. The conclusion discusses how BOD is used to understand how organic pollutants affect dissolved oxygen levels in water bodies.