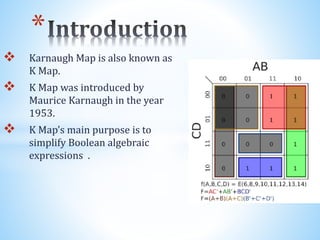
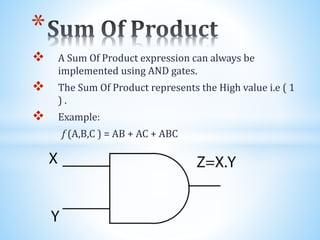
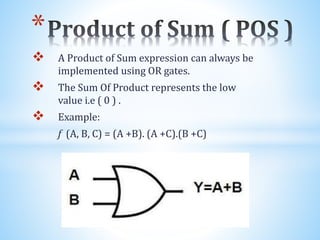
The document discusses Karnaugh maps, which are used to simplify Boolean algebraic expressions. It describes the basics of Karnaugh maps including their introduction in 1953, how they can simplify sum of products and product of sums expressions, their properties for two and three variable maps, and the rules for grouping cells in maps. Advantages are their simplicity and reducing costs. Applications include simplifying circuits.