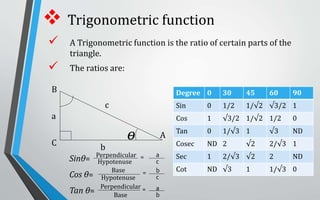
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics used to define relationships between sides and angles of triangles, especially right triangles. It has applications in fields like architecture, astronomy, geology, navigation, and oceanography. Trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent are ratios that relate sides and angles, and trigonometry allows distances, heights, and depths to be easily calculated. Architects use trigonometry to design buildings, astronomers use it to measure distances to stars, and geologists use it to determine slope stability.