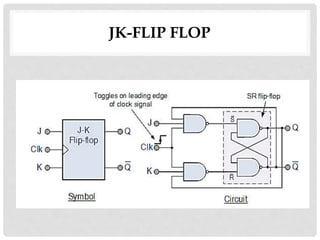
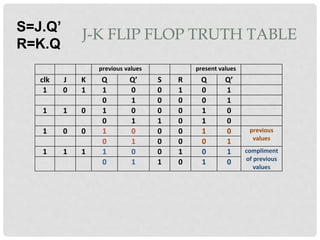
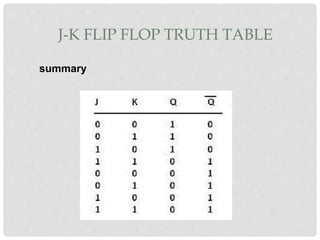
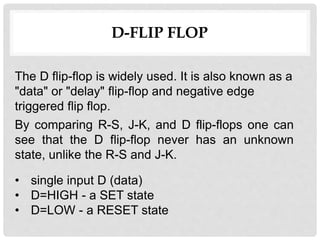
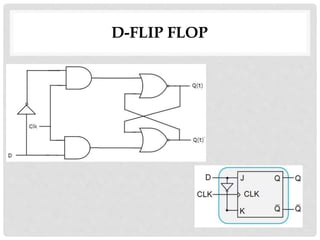
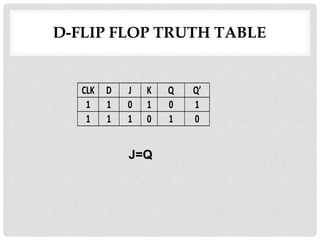
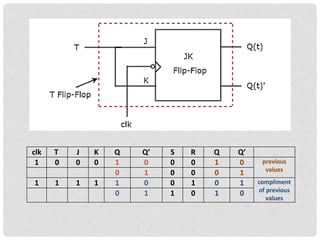
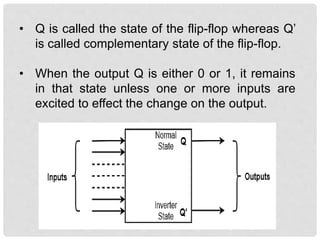
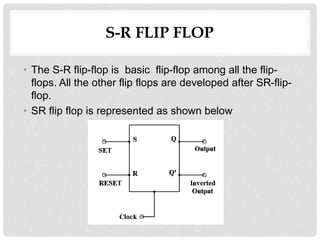
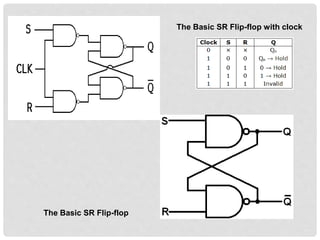
This document discusses different types of flip-flops including SR, JK, D, and T flip-flops. It explains that flip-flops have two stable states (high and low) and can switch between these states under a control signal like a clock. The document provides truth tables and diagrams to illustrate the working of each flip-flop type and their applications in storing data and transferring data between registers.





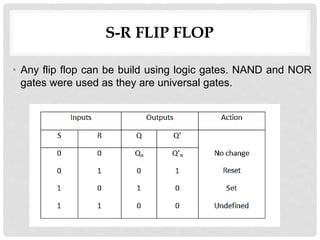
![S=0, R=0 — Q & Q’= Remember
If both the values of S and R are switched to 0,
then the circuit remembers the value of S and R in
their previous state.
S=1, R=1—Q=0, Q’=0 [Invalid]
• This is an invalid state because the values of
both Q and Q’are 0.
• They are supposed to be compliments of each
other. Normally, this state must be avoided.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9flipflopsupdated-191016140658/85/flip-flops-12-320.jpg)