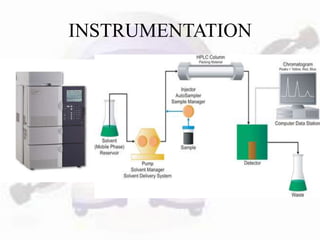
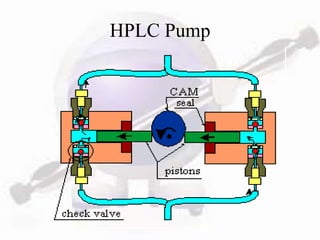
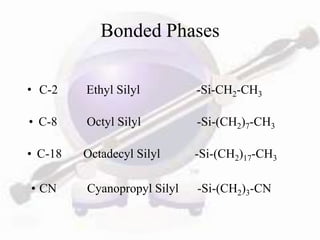
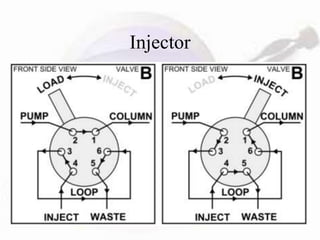
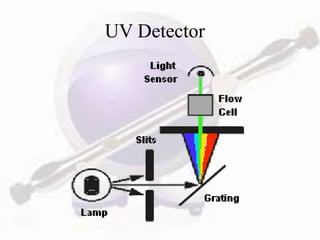
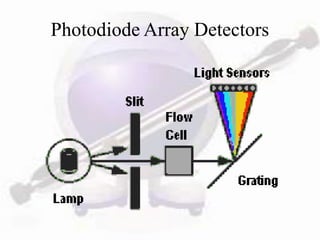
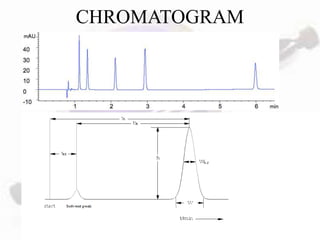
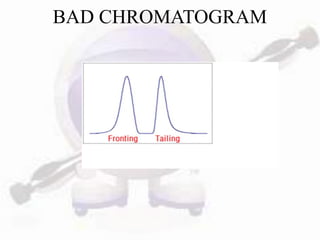
HPLC is a form of liquid chromatography used to separate compounds dissolved in solution based on how they partition between a stationary and mobile phase. The key components of an HPLC system are a pump, injector, column, and detector. Method development involves selecting parameters like the mobile phase, column type, detection method, and chromatography conditions to optimize separation of the sample components. HPLC offers advantages like high sensitivity, rapid analysis times, and use for both analytical qualitative and quantitative analysis.