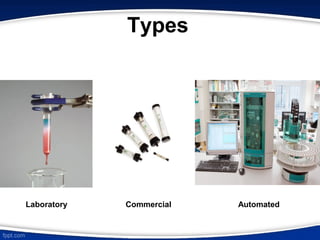
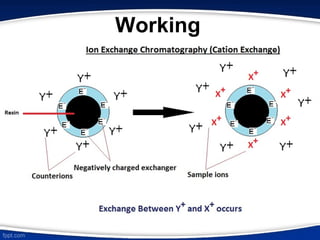
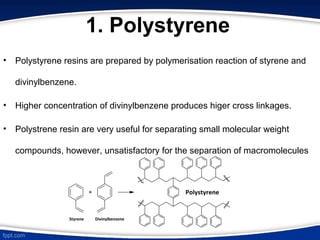
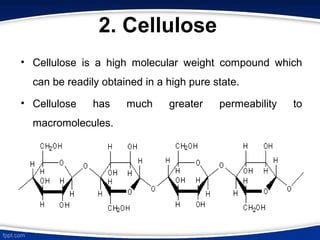
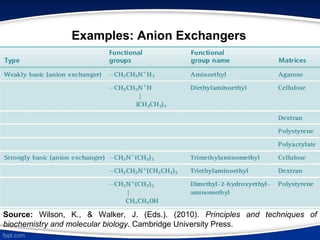
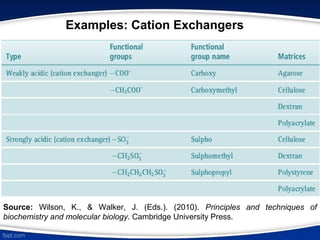
The document discusses ion exchange chromatography, which separates charged molecules by exchanging them for ions attached to an insoluble matrix. It describes the principle of reversible ion exchange between oppositely charged molecules and the matrix. The document outlines the types of ion exchange resins used, including polystyrene and cellulose. It also discusses cation and anion exchangers, preparation of ion exchangers, factors affecting separation, and applications such as water softening and analyzing nucleic acids.