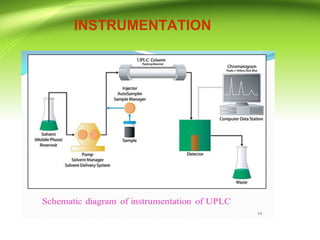
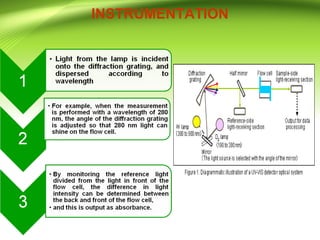
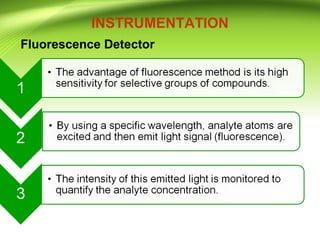
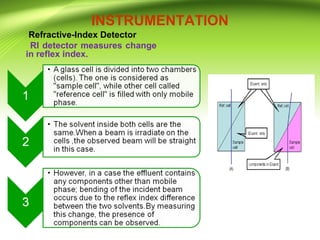
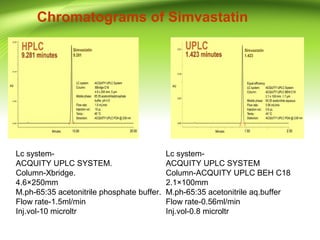
This document provides an overview of ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). It begins with an introduction to chromatography and defines UPLC. The main advantages of UPLC are listed as decreased run time, increased sensitivity, and maintaining resolution. The document outlines the basic principles, instrumentation, and differences between UPLC and HPLC. Applications discussed include drug discovery, herbal medicine analysis, and metabolomics studies. The document is presented by Mr. Atish Khilari and provides references for additional information.