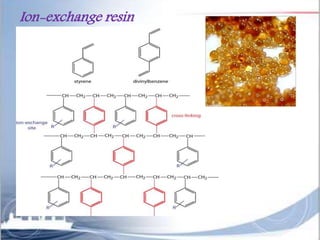
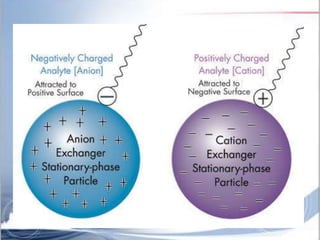
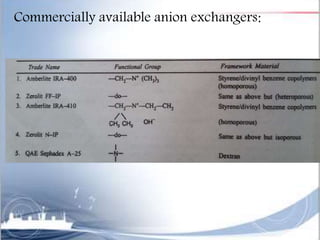
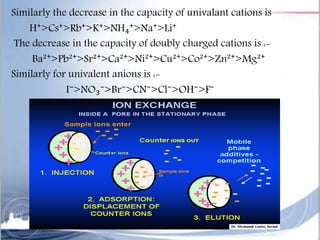
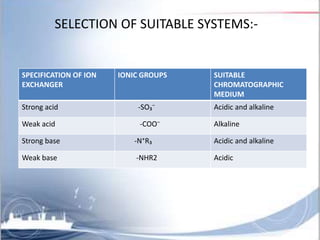
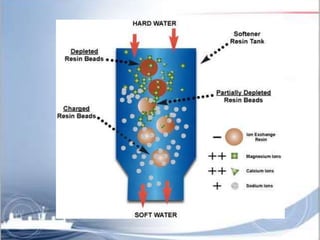
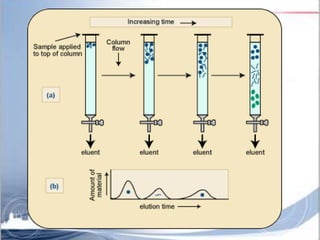
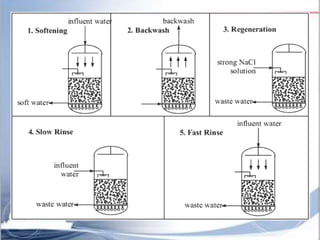
Ion exchange chromatography is a separation technique based on charge that can be used to separate a wide range of charged molecules like proteins, nucleotides, and amino acids. It works by exploiting ionic interactions between oppositely charged solute ions and the stationary phase. The stationary phase is typically a resin with covalently attached anions or cations. Cation exchange chromatography retains positively charged molecules, while anion exchange chromatography retains negatively charged molecules. Separation is achieved as molecules are differentially retained on and eluted off the column based on their affinity for the stationary phase. Ion exchange chromatography is widely used for applications like water softening, demineralization, and separation of molecules like amino acids, sugars, and lan