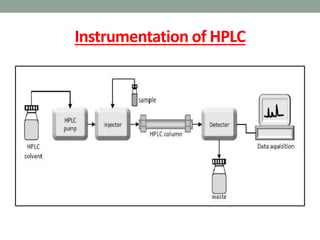
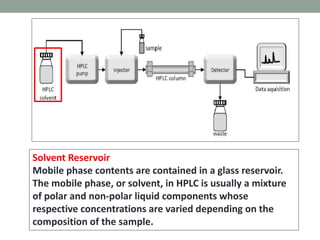
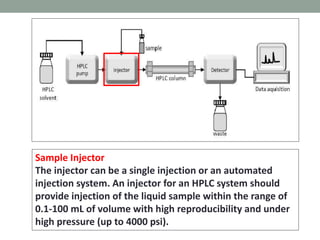
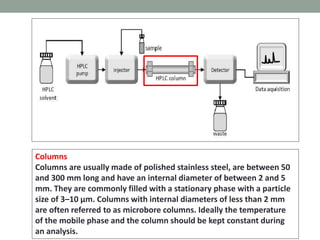
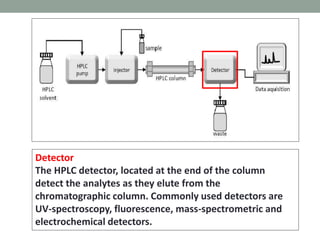
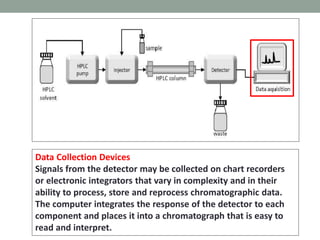
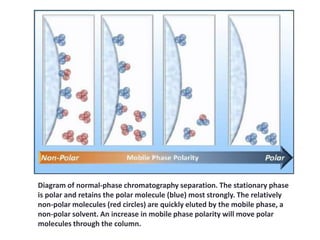
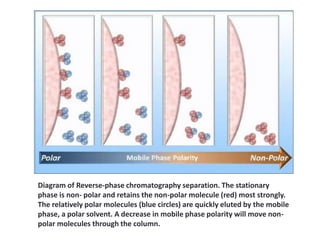
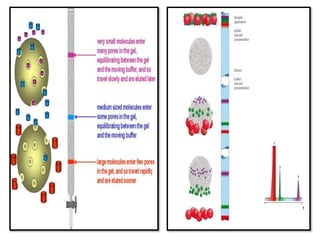
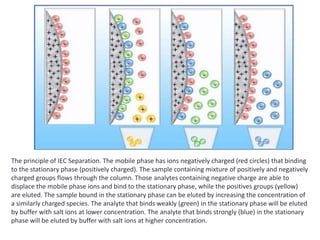
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique that forces a solvent through a column under high pressure to separate samples into their constituent parts. HPLC uses a pump to force a mobile phase through a column containing a stationary phase, and a detector measures the analytes as they elute from the column. There are several types of HPLC that separate samples based on polarity (normal phase), hydrophobic interactions (reverse phase), molecular size (size-exclusion), or ionic charge (ion-exchange). HPLC has many applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, forensics, food and flavors, and clinical testing.