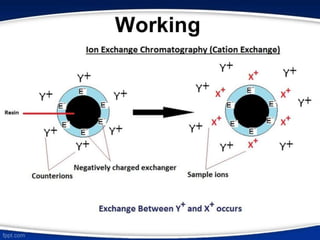
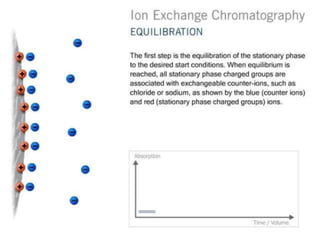
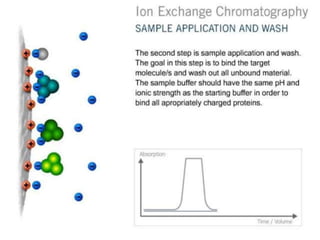
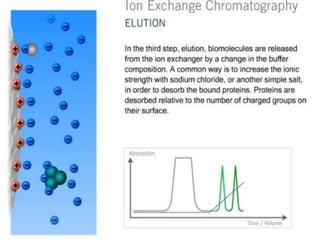
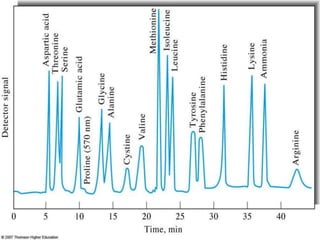
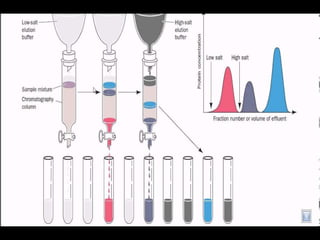
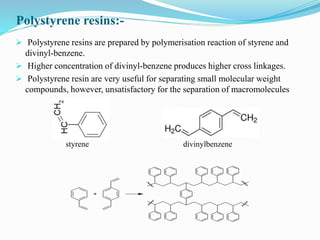
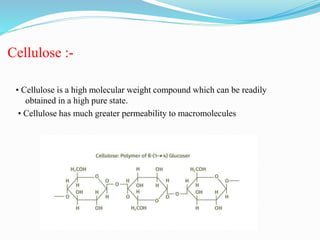
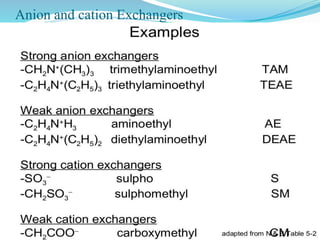
The document discusses ion exchange chromatography, which separates charged compounds by reversible ion exchange between ions in solution and ions bound to an insoluble matrix. It works by binding either the compound of interest or contaminants to the column. The document covers the principle, working, types, requirements, and applications of ion exchange chromatography. It discusses cation and anion exchangers used as the stationary phase and factors that affect separation like pH, ionic strength, and temperature.