Inversion means reversing the typical subject-verb word order in a sentence, usually for emphasis or effect. It is more common in formal writing and literary styles than everyday speech. Some instances when inversion is used include:
1) After place adverbials or adverbs of time at the start of a sentence.
2) In direct speech when the reporting verb follows the quoted statement.
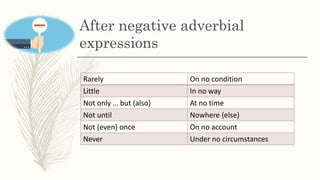
3) With certain negative adverbials like "hardly" or "scarcely" placed initially in a sentence.
4) With expressions like "so..." or "such..." starting a sentence to emphasize degree or quality.