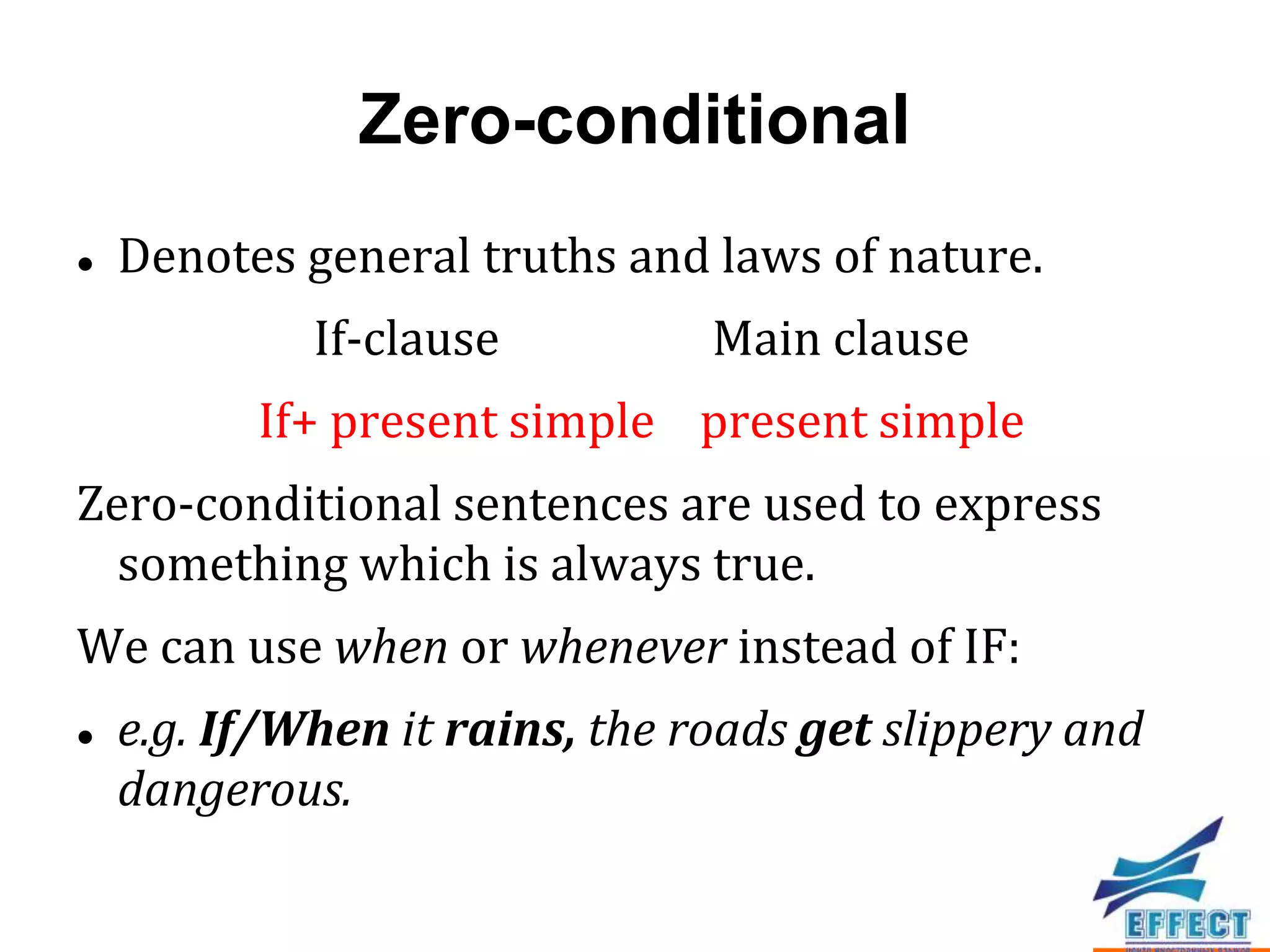
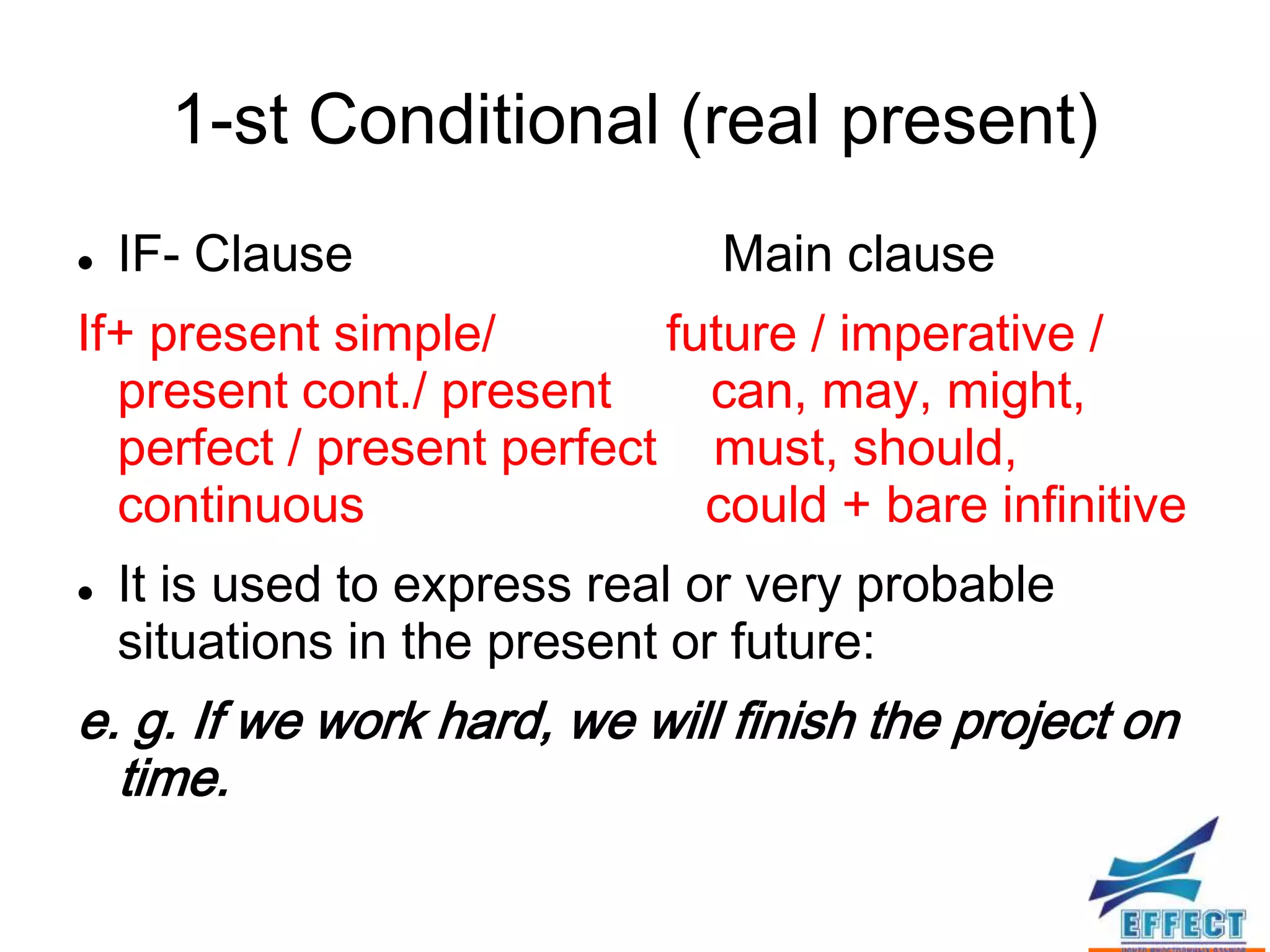
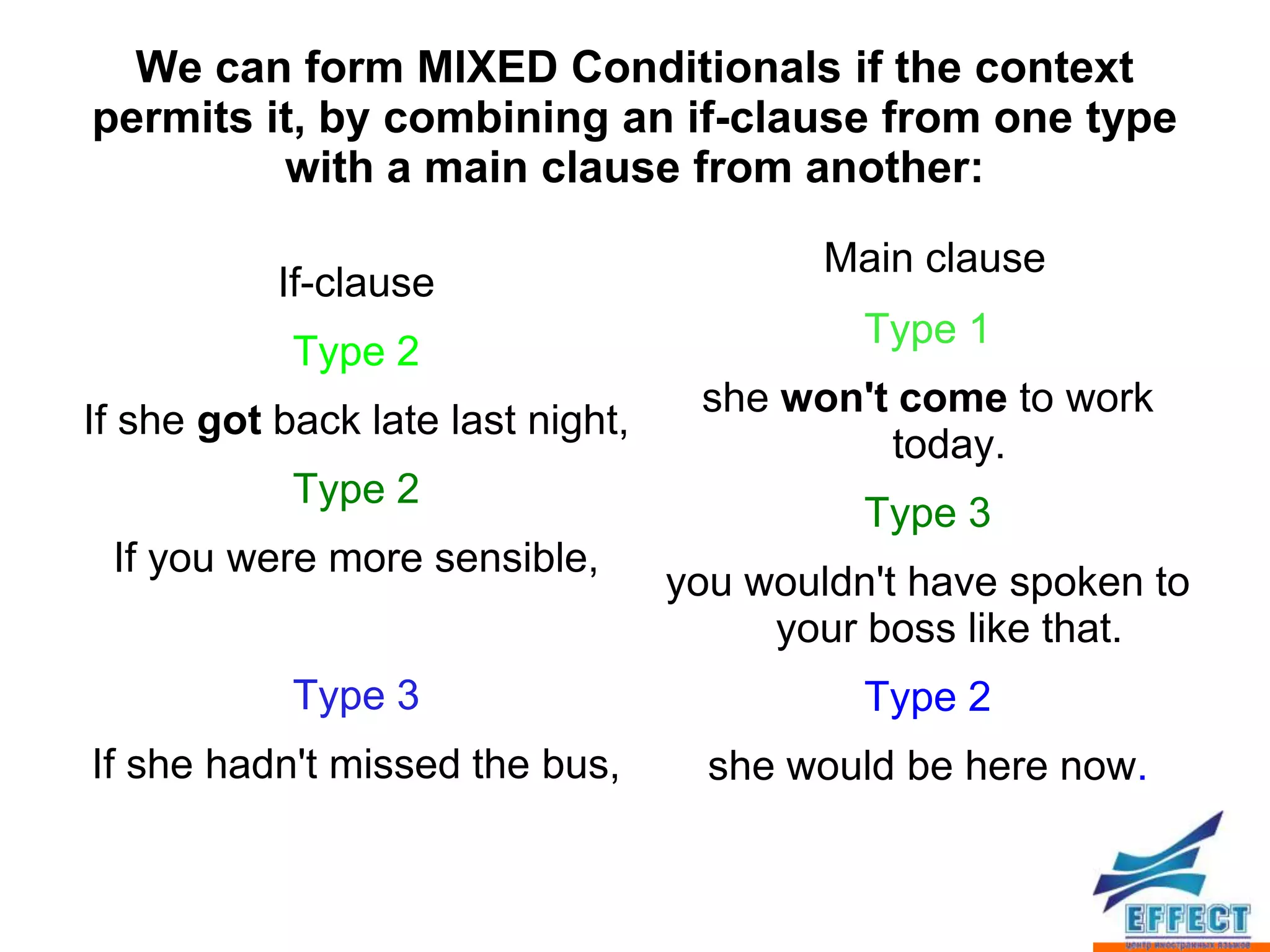
The document discusses the four types of conditional sentences in English: zero-conditional, first-conditional, second-conditional, and third-conditional. It also covers how to form mixed conditionals using elements from different conditional types, and how to express wishes using "wish" or "if only" followed by various verb tenses.