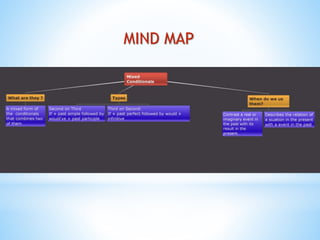
Mixed conditionals refer to conditional sentences where the time in the 'if' clause is different than the time in the main clause. There are two common types: mixed third/second conditionals refer to an imagined past condition and its present result, using the structure "if + past perfect" followed by "would + infinitive." Mixed second/third conditionals refer to an unreal present/ongoing condition and its probable past result, using "if + past simple" followed by "would have + past participle." Mixed conditionals are used to discuss different time frames and their conditional relationships.