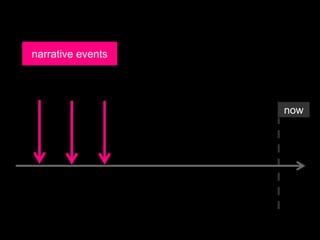
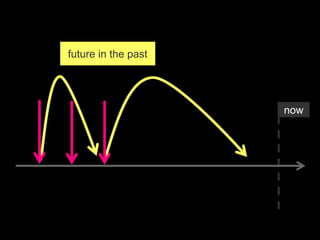
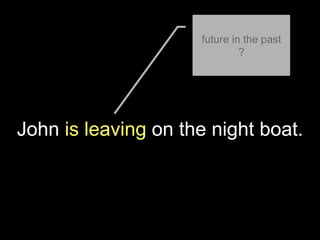
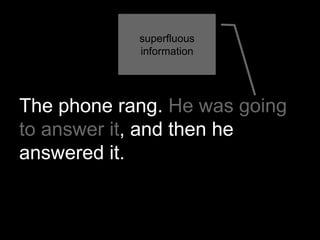
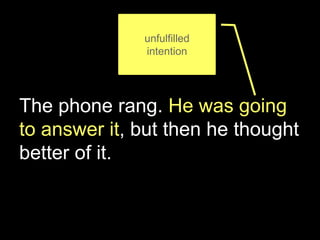
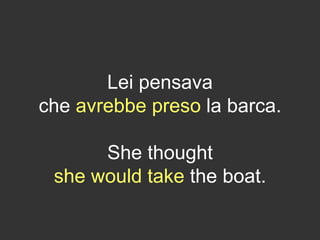
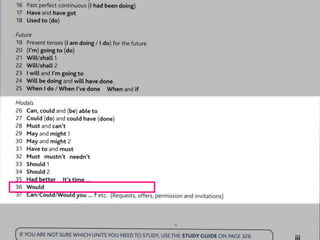
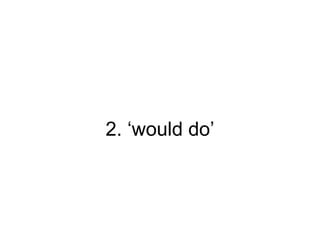The document explores the concept of 'future in the past' in English using the character John, who is leaving on a night boat. It discusses various grammatical forms such as past continuous, 'would do', 'about to', and 'going to', illustrating how they relate to intentions and actions that did not occur in the past. Additionally, it includes examples and translations to highlight the complexities of expressing unfulfilled intentions and reported speech.