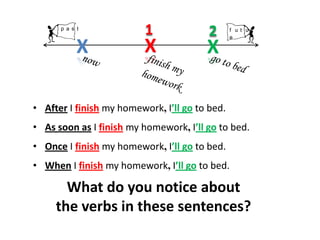
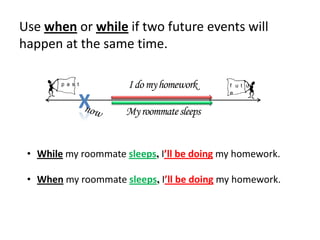
This document discusses future time clauses, which use words like after, as soon as, once, when, before, until, while to connect two future events. The verb following these time words should be in the simple present tense, even though both events will occur in the future. The time clause can come before or after the main clause. When placed first, it requires a comma. Present perfect can also be used to emphasize completion of the first event. When and while connect events that will happen simultaneously.