Embed presentation
Downloaded 44 times


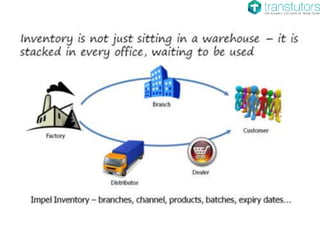

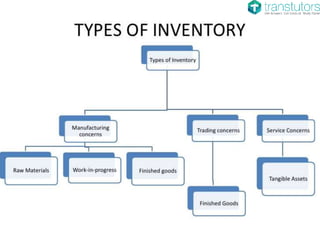
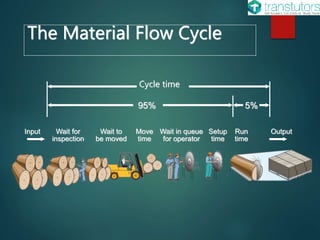




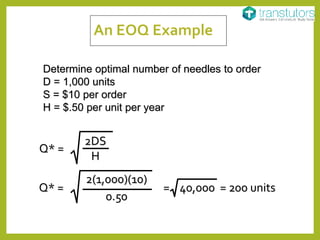



The document outlines the material flow cycle and introduces the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model for inventory management. It defines key variables such as annual demand, setup cost, and holding cost and lists important assumptions for the basic EOQ model. Additionally, it offers a calculation example to determine the optimal order quantity and discusses holding, ordering, and setup costs.












