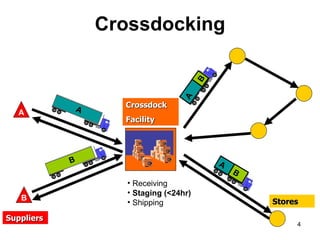
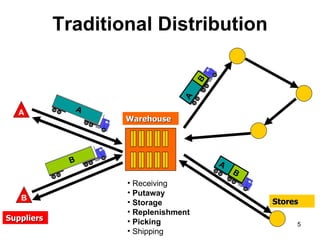
Cross docking is a logistics activity that reduces costs and lead time. It involves breaking down received items on the loading dock and immediately matching them with outgoing shipment requirements instead of storing items in a warehouse. This eliminates the need to place inventory in storage. Goods arriving from vendors already have a customer assigned, so workers simply move shipments from inbound to outbound trailers bound for the appropriate destination. There are two types - pre-distribution where items arrive tagged for transfer, and post-distribution where the crossdock allocates material to stores. Major retailers like Walmart have popularized crossdocking to reduce costs in their supply chains.