Embed presentation
Downloaded 29 times




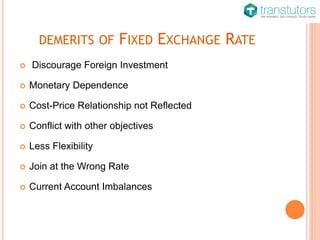

A fixed exchange rate, also known as a hard peg, is a currency regime where a country's exchange rate is tied to another currency or gold. It offers stability, promotes capital movement, and reduces speculation, but can discourage foreign investment and limit monetary flexibility. Overall, it has both merits and demerits that impact economic integration and growth.






