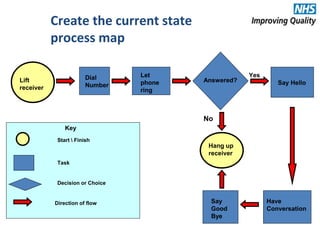
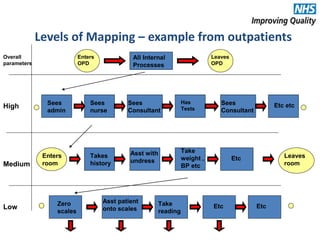
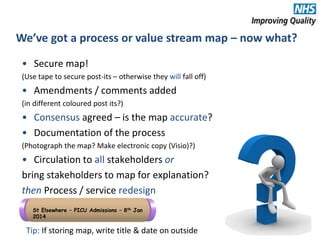
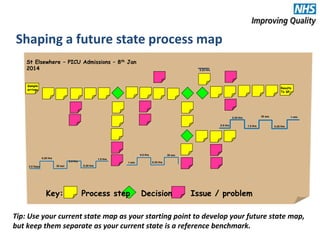
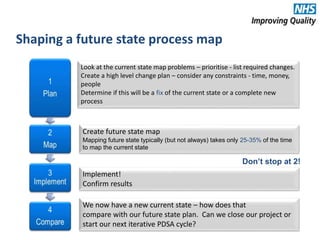
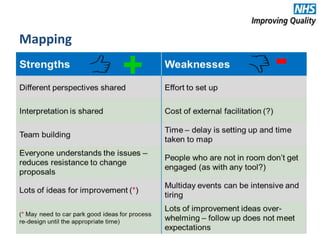
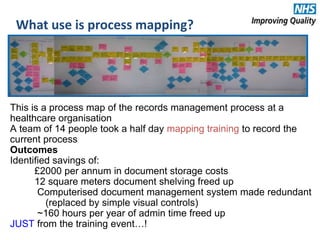
The document provides an agenda and overview for an e-seminar on process mapping. It discusses what process mapping is, how to create current and future state maps, common tools and techniques used in mapping, and how to analyze and improve maps. The goal of process mapping is to identify opportunities to streamline workflows and eliminate waste and inefficiencies in order to improve processes and services.