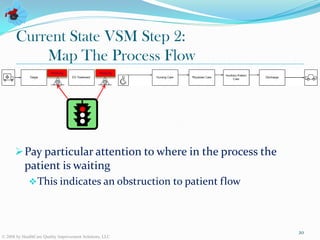
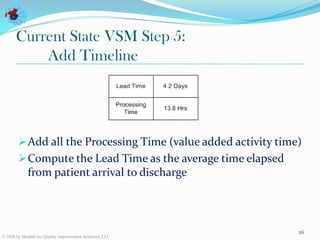
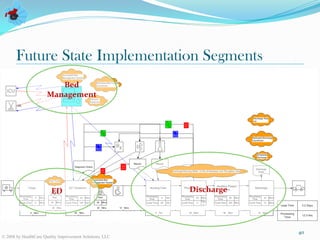
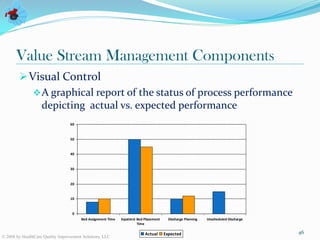
The document discusses value stream management in healthcare. It defines a value stream as all the activities involved in treating patients from arrival to discharge. It describes mapping value streams using current and future state value stream maps to identify waste and improvements. The goal is to link processes in a smooth continuous flow without interruptions. Key components of value stream management include selecting a value stream manager, using visual controls, and conducting real-time problem solving and continuous process improvement.