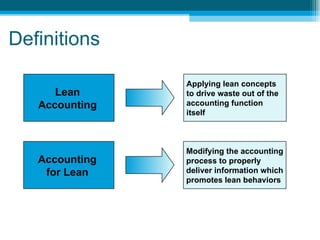
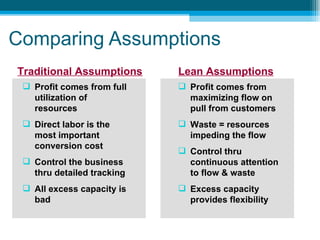
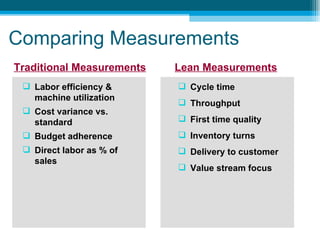
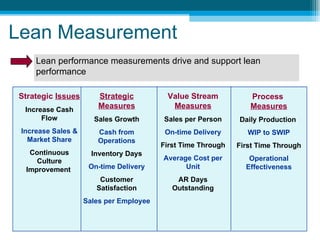
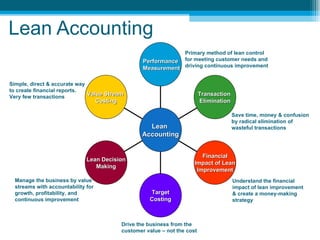
The document discusses lean accounting and how it differs from traditional accounting assumptions and measurements. Lean accounting applies lean concepts to reduce waste in the accounting function and modifies accounting processes to promote lean behaviors. It focuses on value stream costing, transaction elimination, and using lean metrics like flow, waste, and capacity rather than traditional metrics like labor efficiency. The primary goals of lean accounting are to understand the financial impacts of lean improvements, manage by value streams with a focus on growth and continuous improvement, and drive the business from customer value rather than costs.