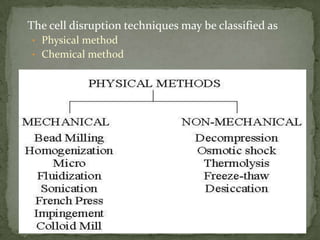
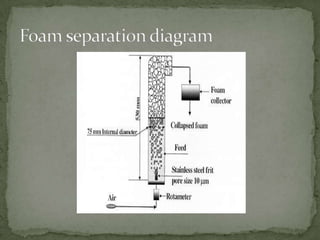
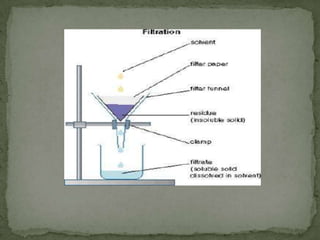
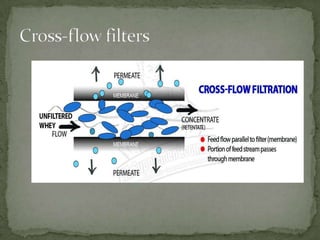
This document summarizes downstream processing steps in bioprocessing. It discusses various unit operations used for product recovery including cell removal, dewatering, protein purification through adsorption chromatography or immobilization, and protein packaging through sterilization. Methods for solid separation like filtration, sedimentation, centrifugation and foam separation are described. The document also provides details on precipitation, filtration processes, and different types of filters used.