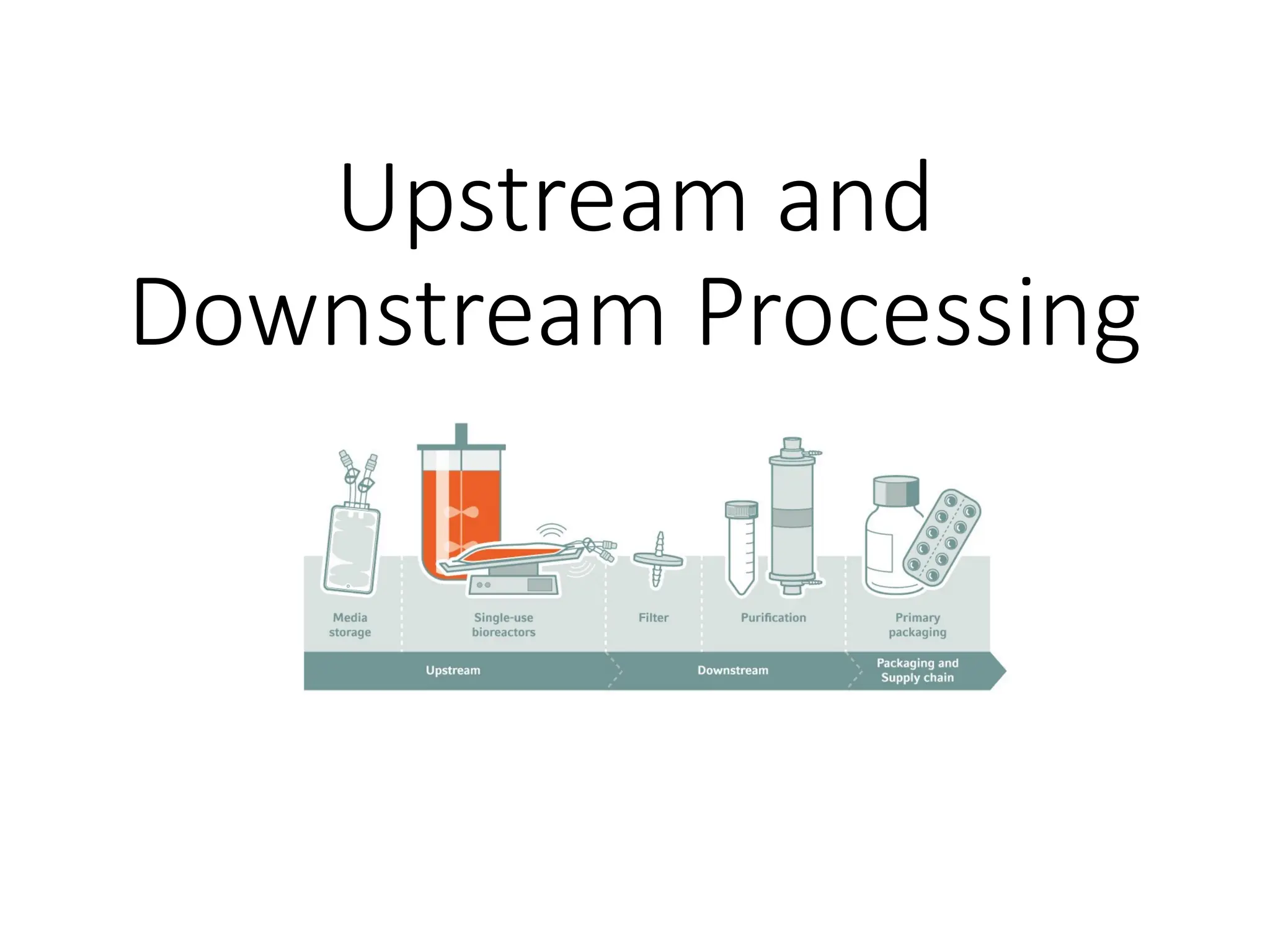
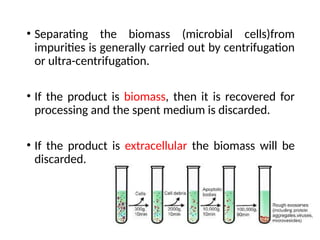
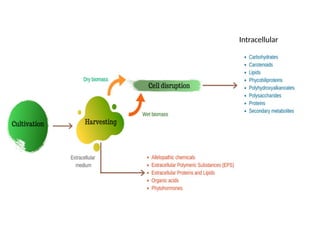
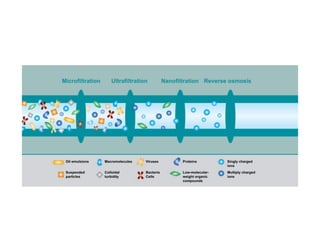
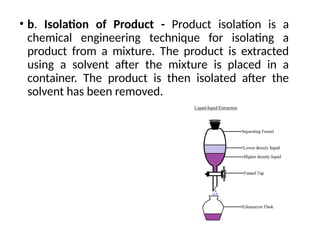
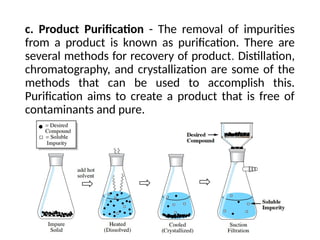
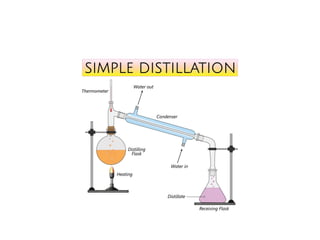
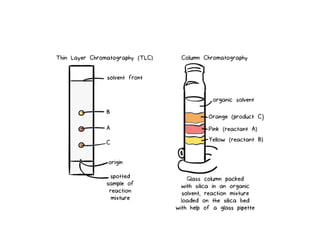
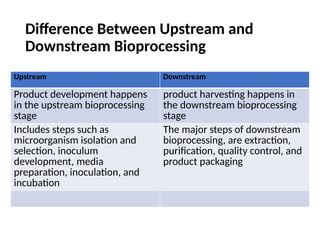
The document describes the two main segments of bioprocessing: upstream and downstream processing. Upstream processing focuses on the early stages including organism selection and growth, while downstream processing involves purification and formulation of the final product. Both stages are crucial in creating bioproducts and must avoid contamination.