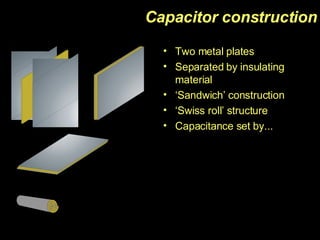
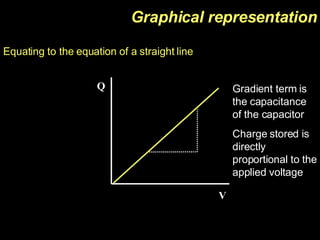
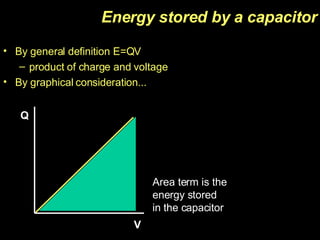
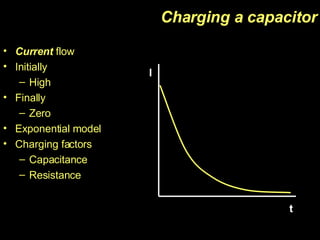
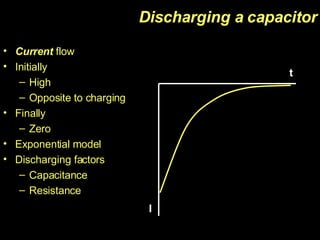
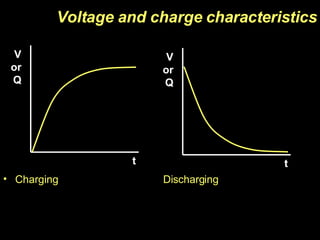
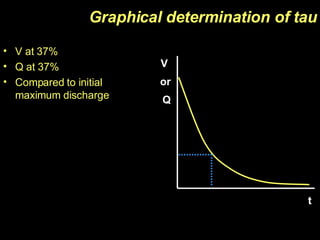
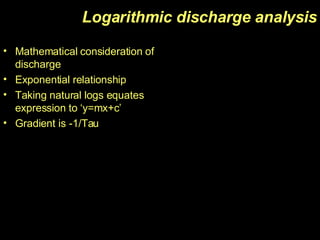
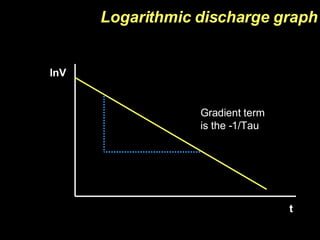
The document discusses capacitors, including their construction using two conductive plates separated by an insulating material, how they store electric charge, and definitions of capacitance and factors that determine it such as plate size and separation distance. It also covers graphical representations of capacitors, how energy is stored in capacitors, the exponential charging and discharging behavior over time defined by the time constant, and using logarithmic graphs to determine the time constant.