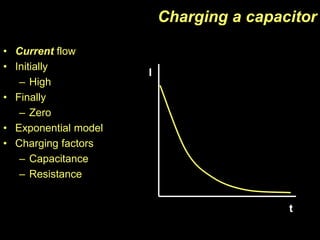
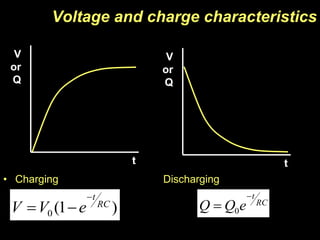
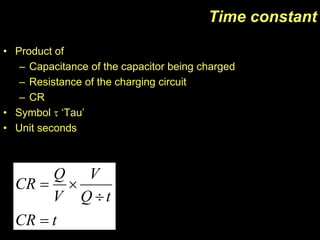
- A capacitor is an electronic component that stores charge and consists of two conducting surfaces separated by an insulating material. It is used for time delays, filtering, and tuned circuits.
- Capacitors come in sandwich or Swiss roll constructions with metal plates separated by an insulating material. The capacitance is determined by the dielectric material and plate separation distance.
- Capacitance is defined as the amount of charge stored per applied voltage. It is measured in Farads. The energy stored in a capacitor is equal to one-half the capacitance times the square of the applied voltage.