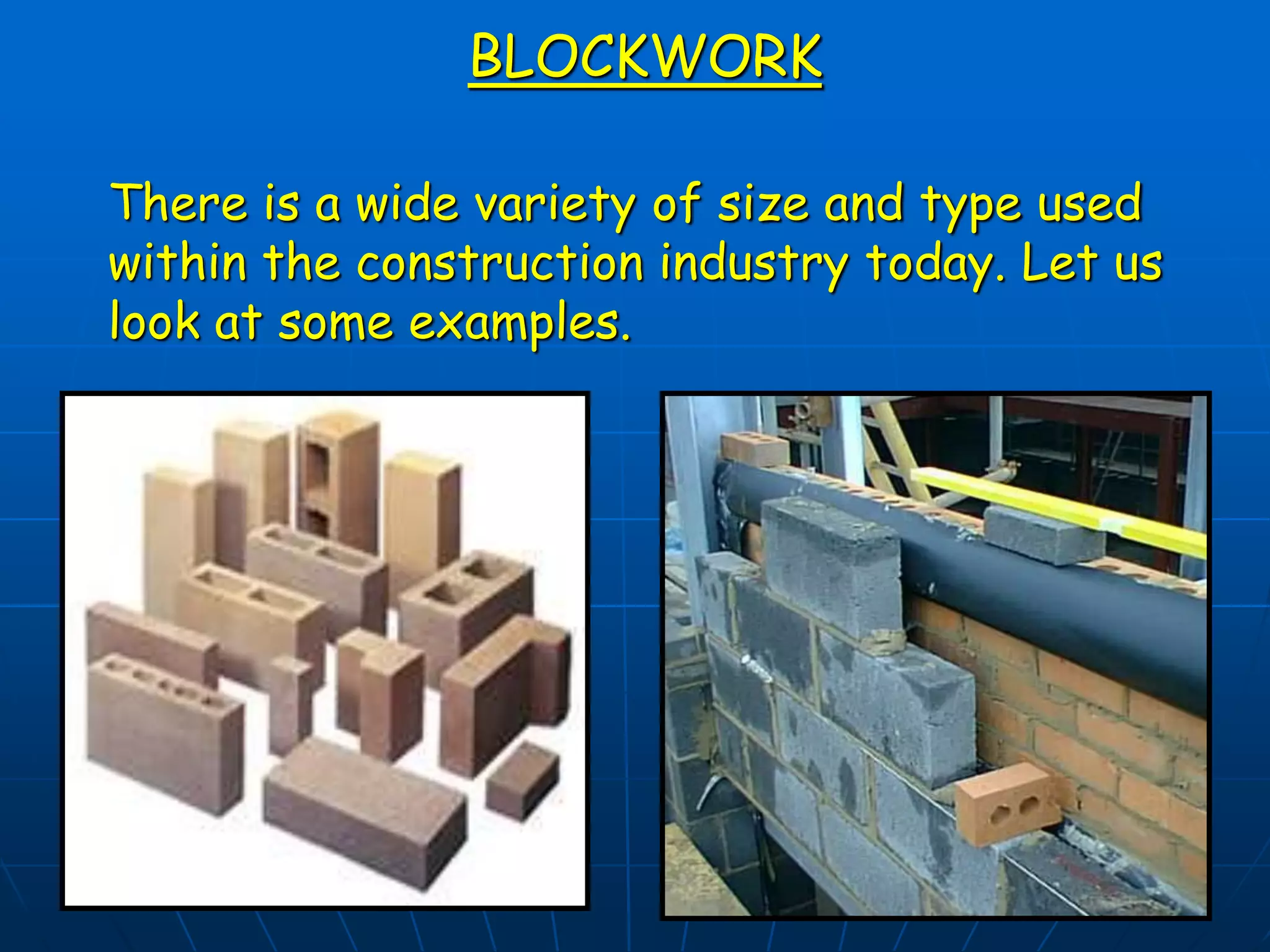
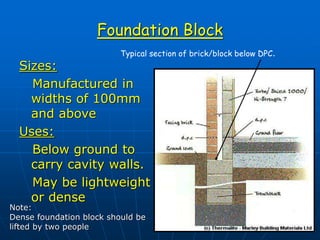
This document discusses different types of blocks used in construction, including their manufacture, sizes, uses, and advantages/disadvantages. It describes load-bearing blocks, non-load bearing blocks, lightweight blocks, foundation blocks, and more. Guidelines are provided for safely handling, storing, and preparing blocks for construction work, as well as considerations for cold weather.