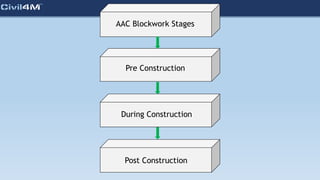
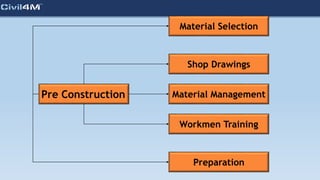
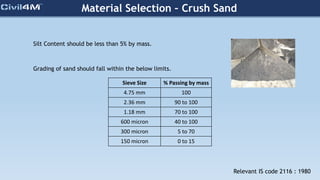
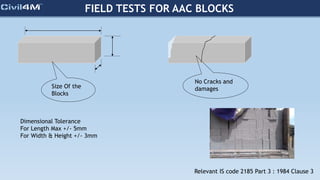
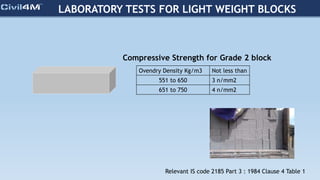
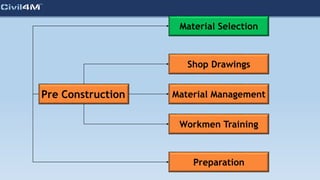
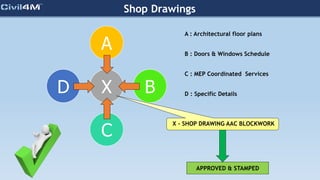
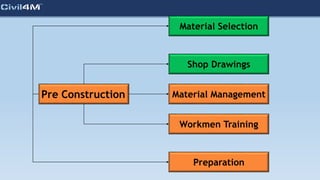
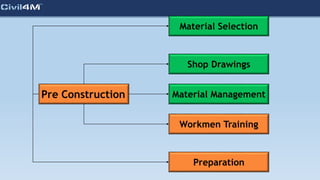
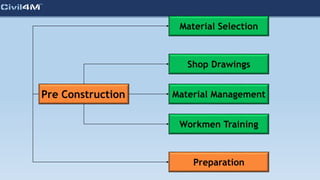
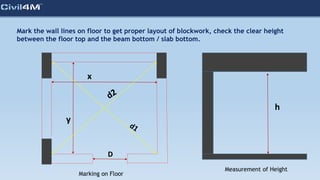
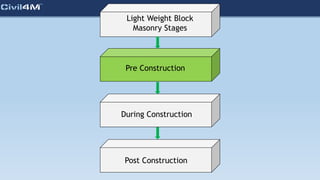
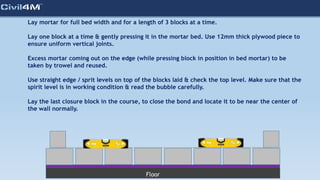
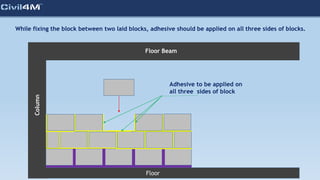
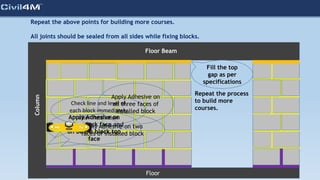
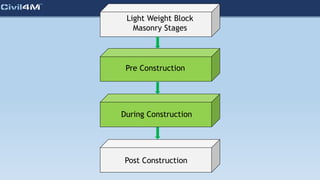
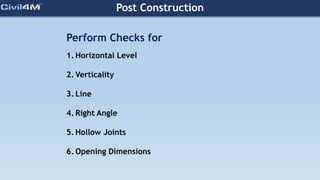
The document provides safety and construction guidelines for AAC blockwork, emphasizing proper stacking, workspace clearance, and the use of appropriate materials and tools. It outlines pre-construction procedures, material selection criteria, and stages during and post-construction, including checks for quality and adherence to safety regulations. Additionally, it highlights the importance of worker training and adherence to best practices to prevent accidents and ensure quality in masonry work.